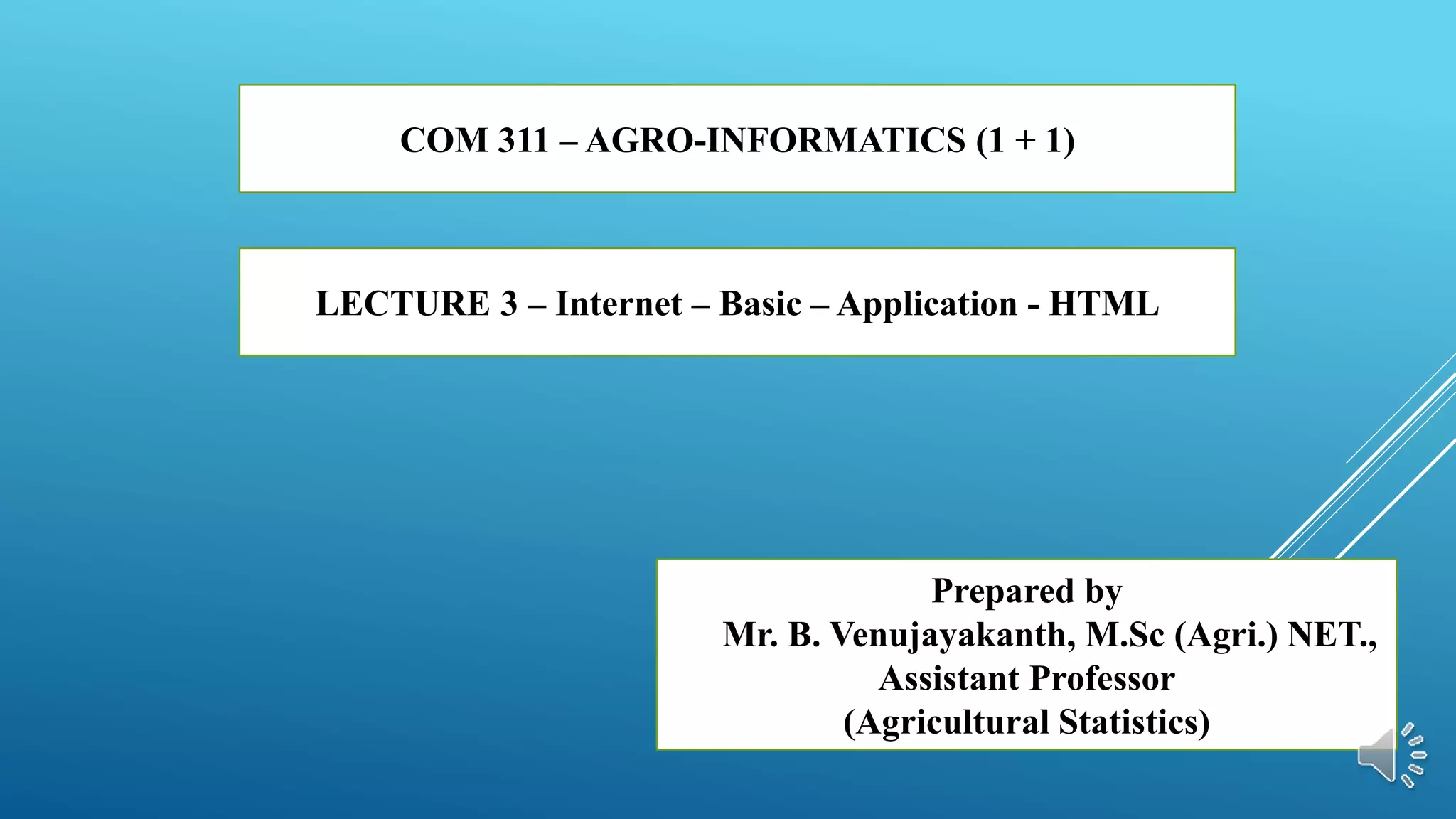
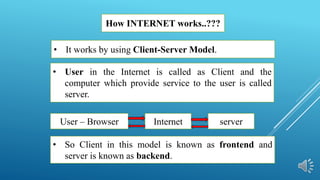
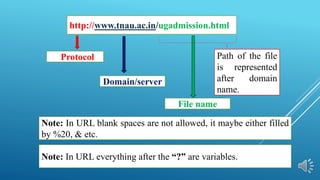
This document provides an overview of basic internet concepts and HTML. It defines the internet as a network of networks that connects computers globally using a client-server model. It describes common internet protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, FTP. It also explains basics of HTML like tags, structure, editors and how HTML pages are executed in web browsers to display content. The document serves as an introduction to fundamental internet and web technologies.