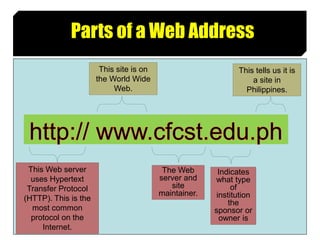
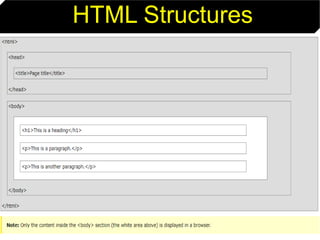
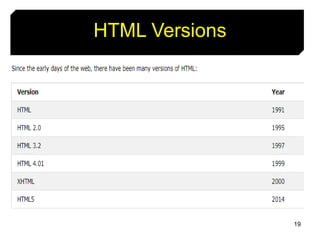
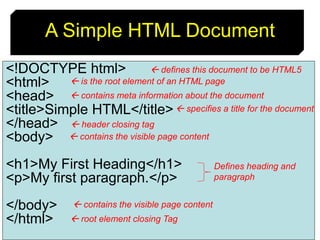
This document provides an introduction to HTML by outlining its objectives and defining key terms like the Internet, World Wide Web, web pages, and browsers. It describes the basic structure of an HTML document and different versions of HTML. Common HTML tags are explained, and a simple HTML document example is provided and displayed in a web browser to demonstrate how tags determine page structure and formatting.