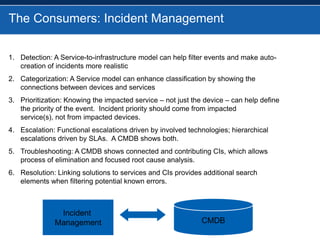
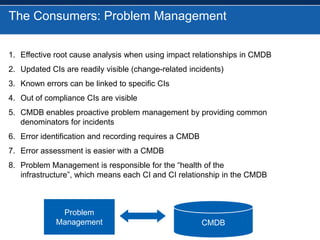
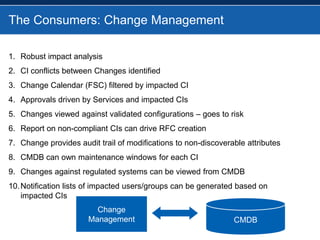
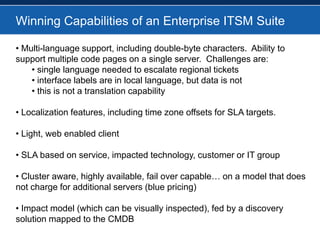
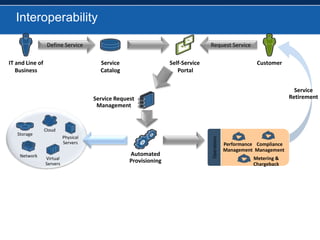
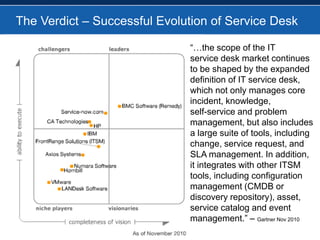
BMC overhauled its BMC Remedy ITSM offering with version 7.0, focusing heavily on ITIL. While users initially found the interface cumbersome, BMC enhanced and simplified it. An effective configuration management database (CMDB) provides benefits across various ITSM processes like incident management, problem management, and change management by showing connections between IT components and services. For service providers, Remedy 7.0 added multi-tenancy capabilities. Gartner analysis found the IT service desk market now includes additional tools like change management and broader integration capabilities.