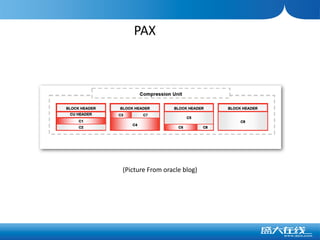
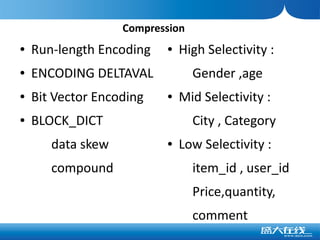
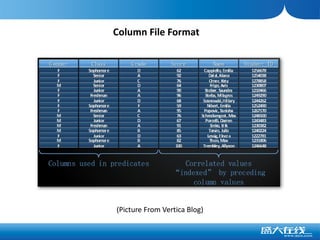
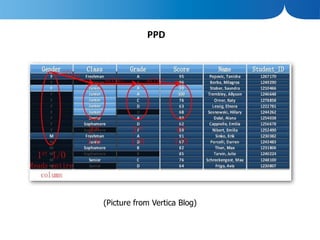
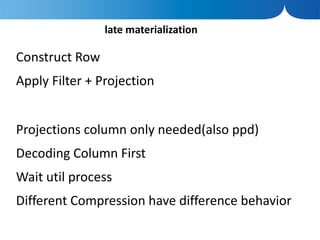
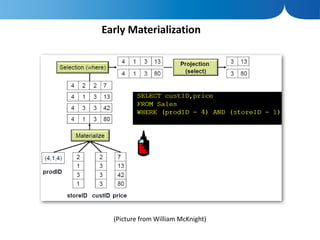
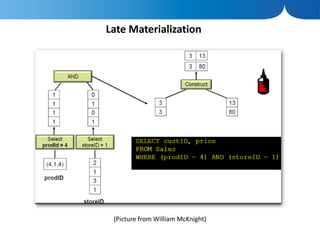
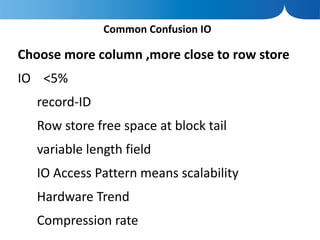
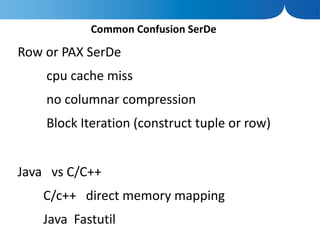
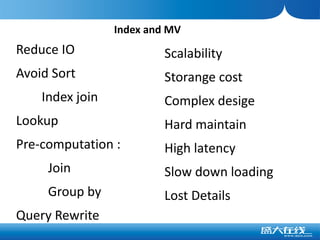
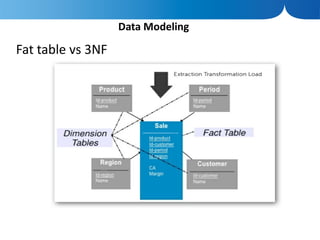
The document discusses the advantages of columnar databases and their integration with Hadoop, focusing on storage processes, compression techniques, and performance improvements. It highlights key topics such as late materialization, the benefits of columnar storage over traditional row stores, and data ingestion strategies using HBase and Flume. Additionally, it addresses challenges in Hadoop related to file formats, data modeling, and performance tuning.