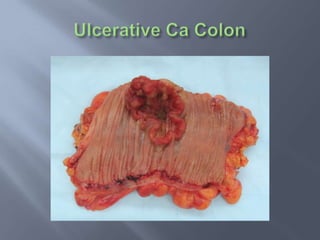
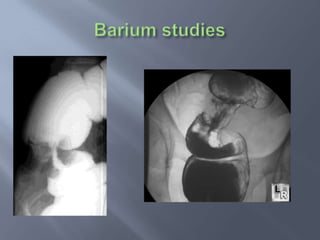
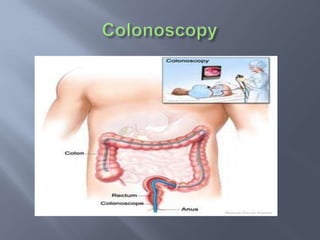
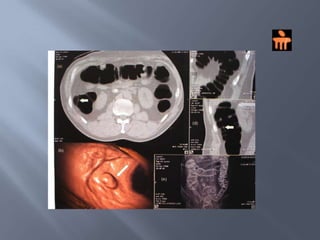
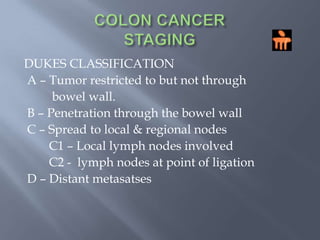
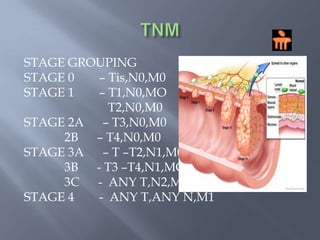
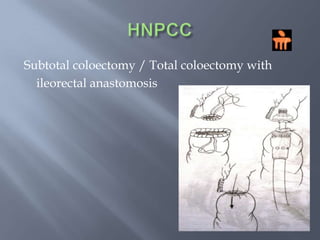
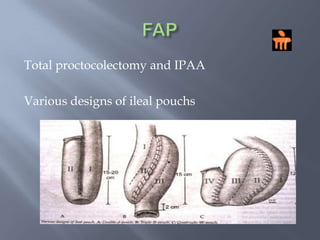
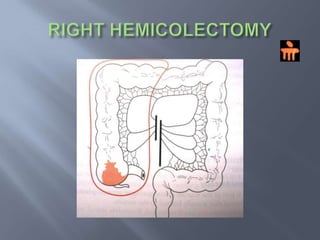
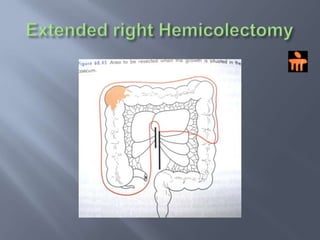
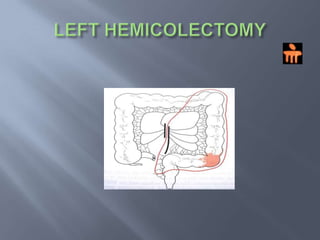
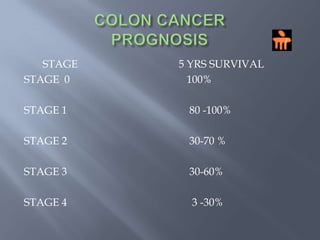
Colon cancer is the fourth most commonly diagnosed cancer. About 70% of cases are sporadic, while 23% are genetic. It most commonly presents in the descending and sigmoid colon as a change in bowel habits with blood or mucus in the stool. Staging involves clinical exams, imaging like CT scans, and blood tests like CEA. Treatment depends on the stage, with surgery being the main treatment and chemotherapy sometimes used adjuvantly or palliatively. The 5-year survival ranges from 100% for stage 0 to 3-30% for stage 4 disease.