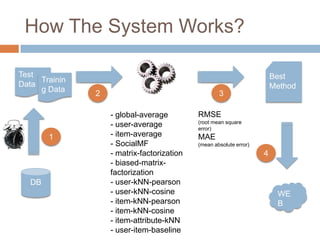
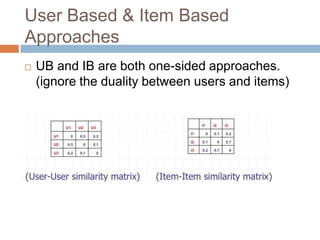
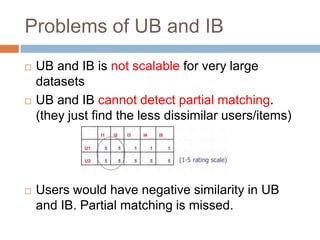
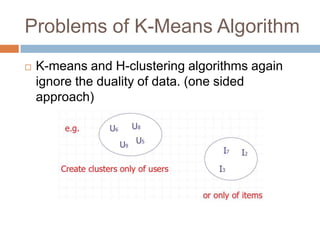
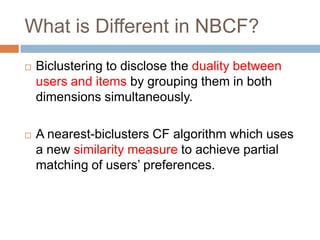
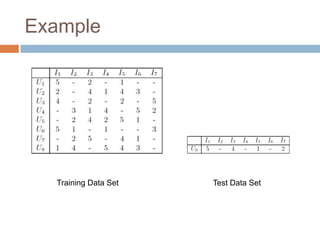
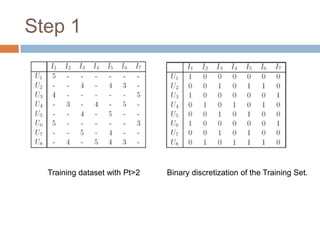
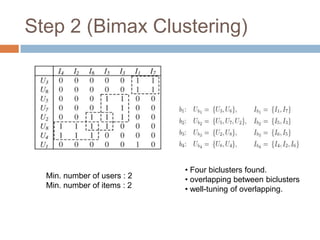
This document presents nearest bi-clusters collaborative filtering (NBCF), which improves upon traditional collaborative filtering approaches. NBCF uses biclustering to group users and items simultaneously, addressing the duality between them. It introduces a new similarity measure to achieve partial matches between users' preferences. The algorithm first performs biclustering on the training data. It then calculates similarity between a test user and biclusters to find the k-nearest biclusters. Finally, it generates recommendations by weighting items based on bicluster size and similarity. An example demonstrates how NBCF provides more accurate recommendations than one-sided approaches.



![Step 3 – Part 1To find the k-nearest biclusters of a test user:We divide items they have in common to the sum of items they have in common and the number of items they differ. Similarity values range between [0,1].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfsurvey-110605201121-phpapp01/85/Collaborative-Filtering-Survey-15-320.jpg)