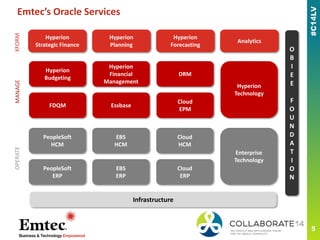
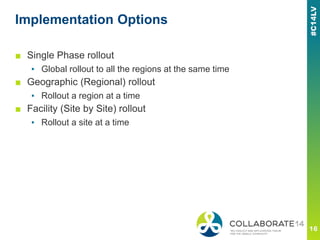
The document discusses Emtec's approach to implementing PeopleSoft globally, emphasizing functional considerations, various implementation strategies, and best practices for success. Key points include managing corporate versus local requirements, ensuring multi-language support, and adopting flexible rollouts while maintaining clarity and consistency across regions. A case study exemplifies successful deployment outcomes and highlights the importance of leadership involvement and thorough requirement gathering throughout the process.