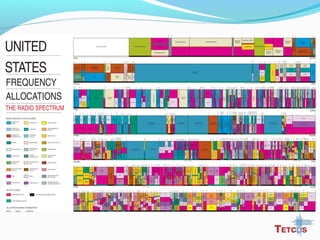
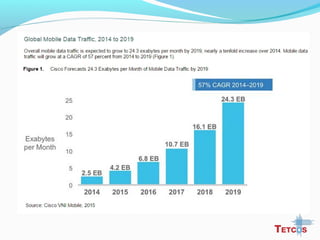
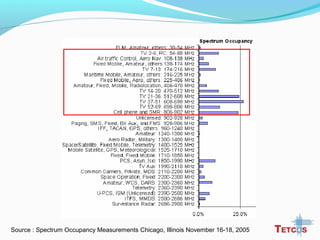
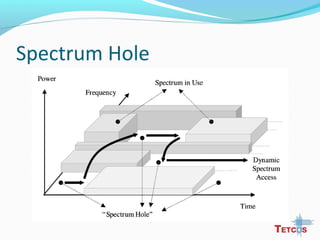
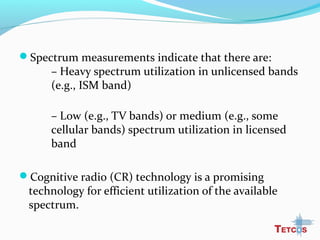
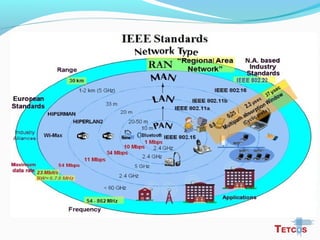
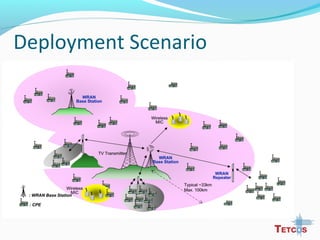
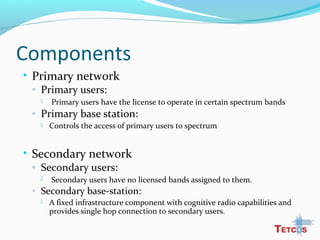
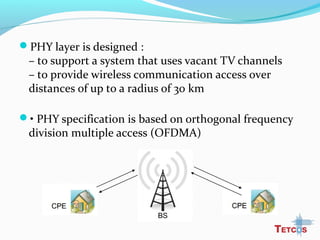
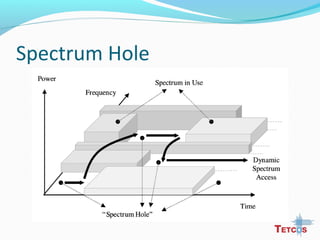
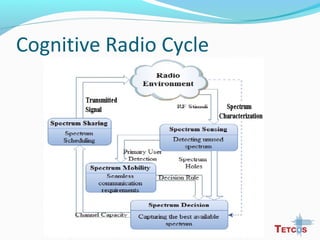
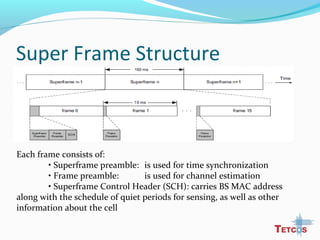
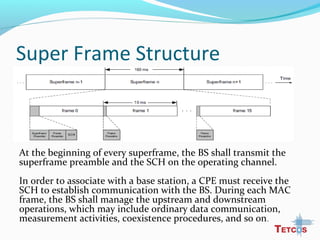
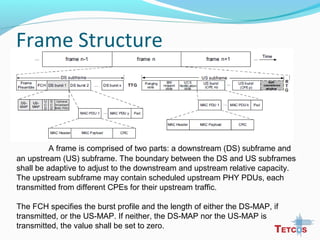
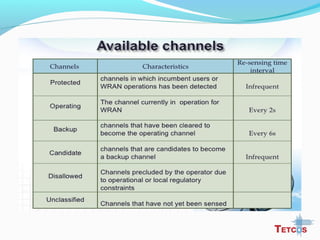
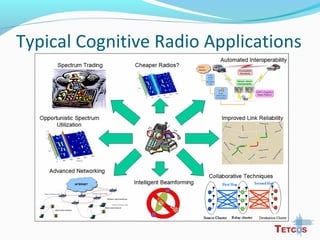
The document discusses the IEEE 802.22 standard for cognitive radio wireless regional area networks (WRANs). It describes how cognitive radio technology can help address the spectrum crunch by efficiently utilizing vacant TV bands and other licensed spectrum. The standard defines the MAC and PHY layer specifications for a cognitive radio system, including spectrum sensing, mobility, sharing, and a superframe structure to manage communication in available TV channels while avoiding interference with primary users. The goal is to provide wireless connectivity over distances of up to 30 km using the cognitive radio capabilities defined in the 802.22 standard.