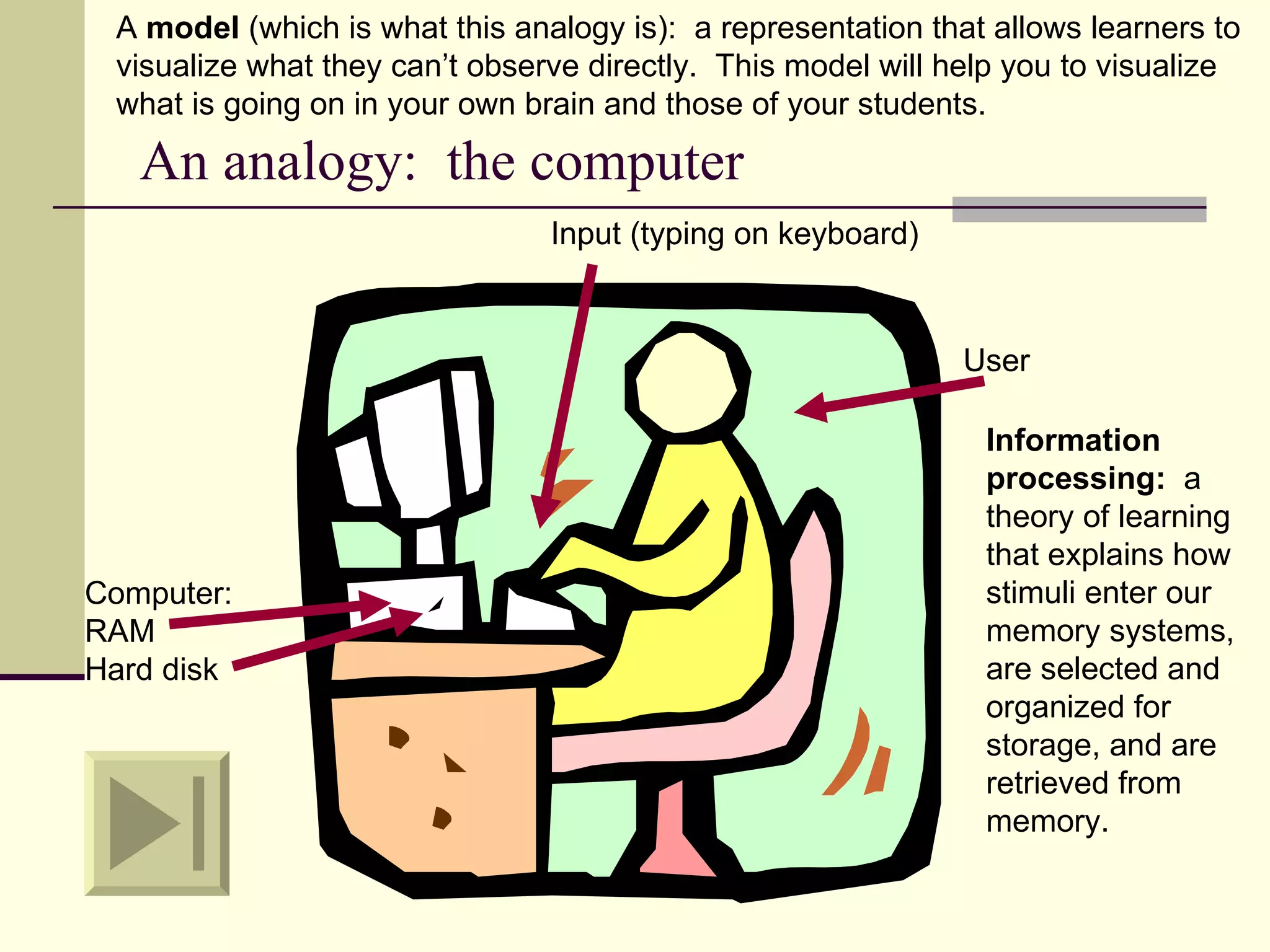
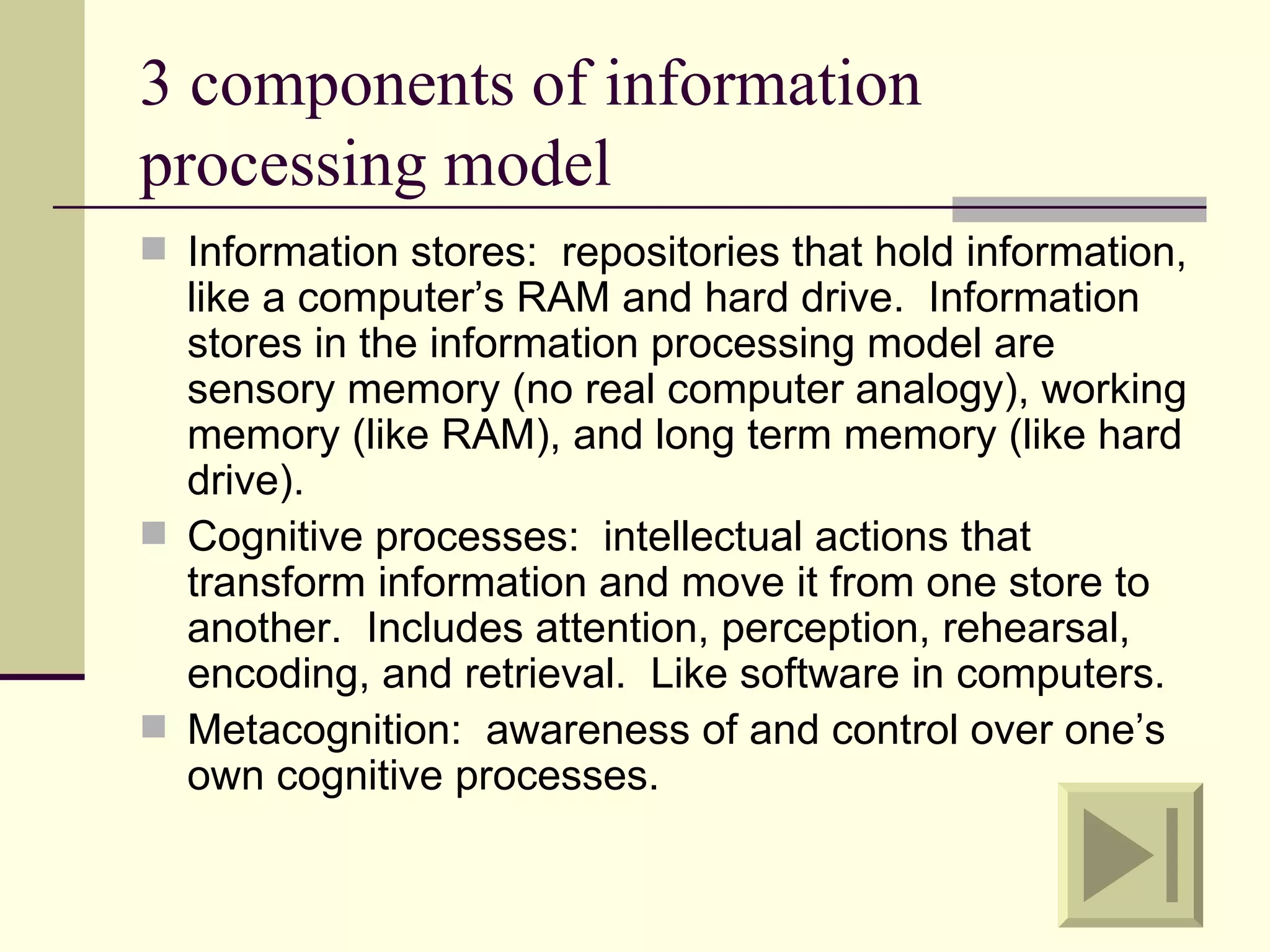
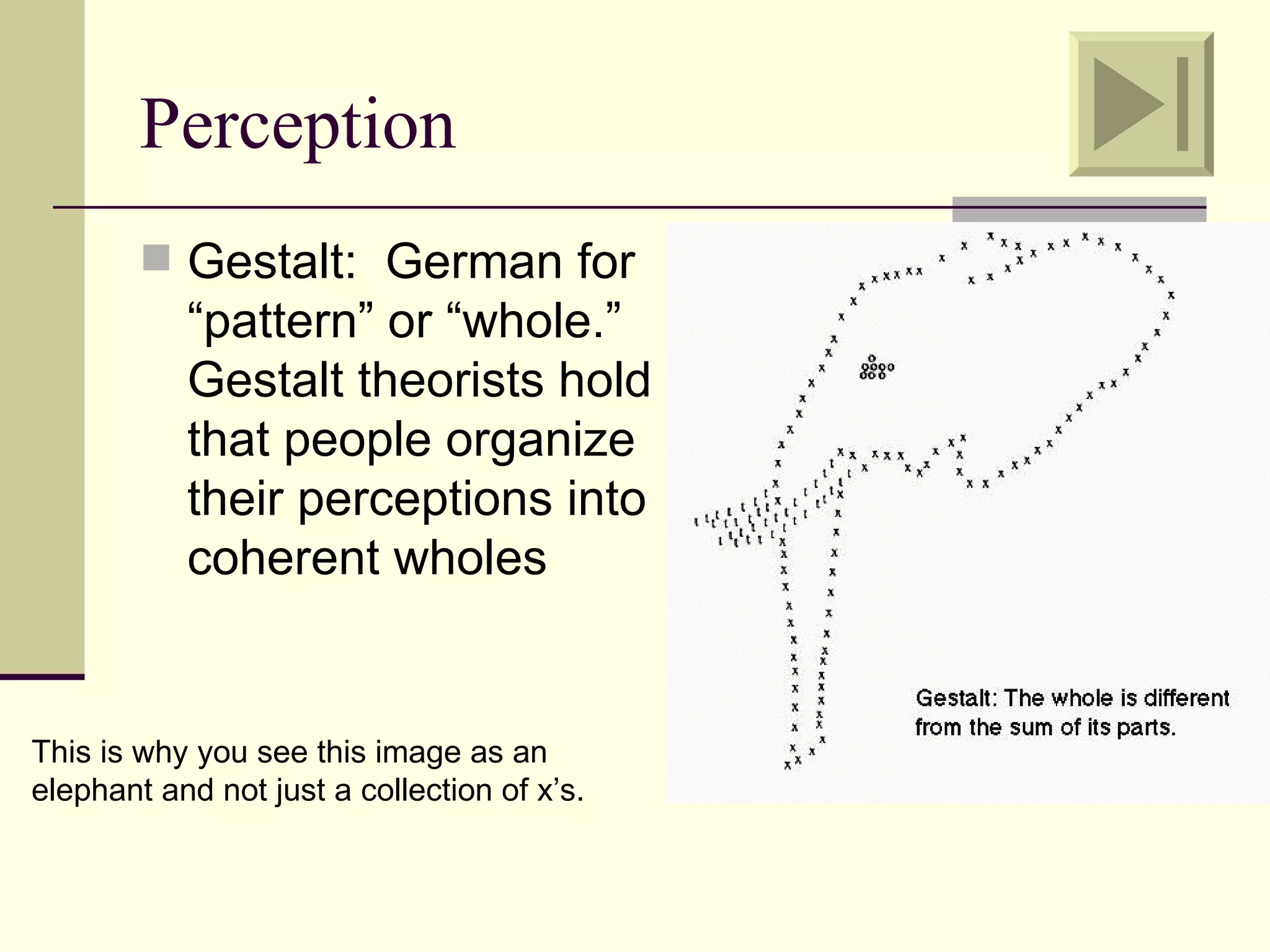
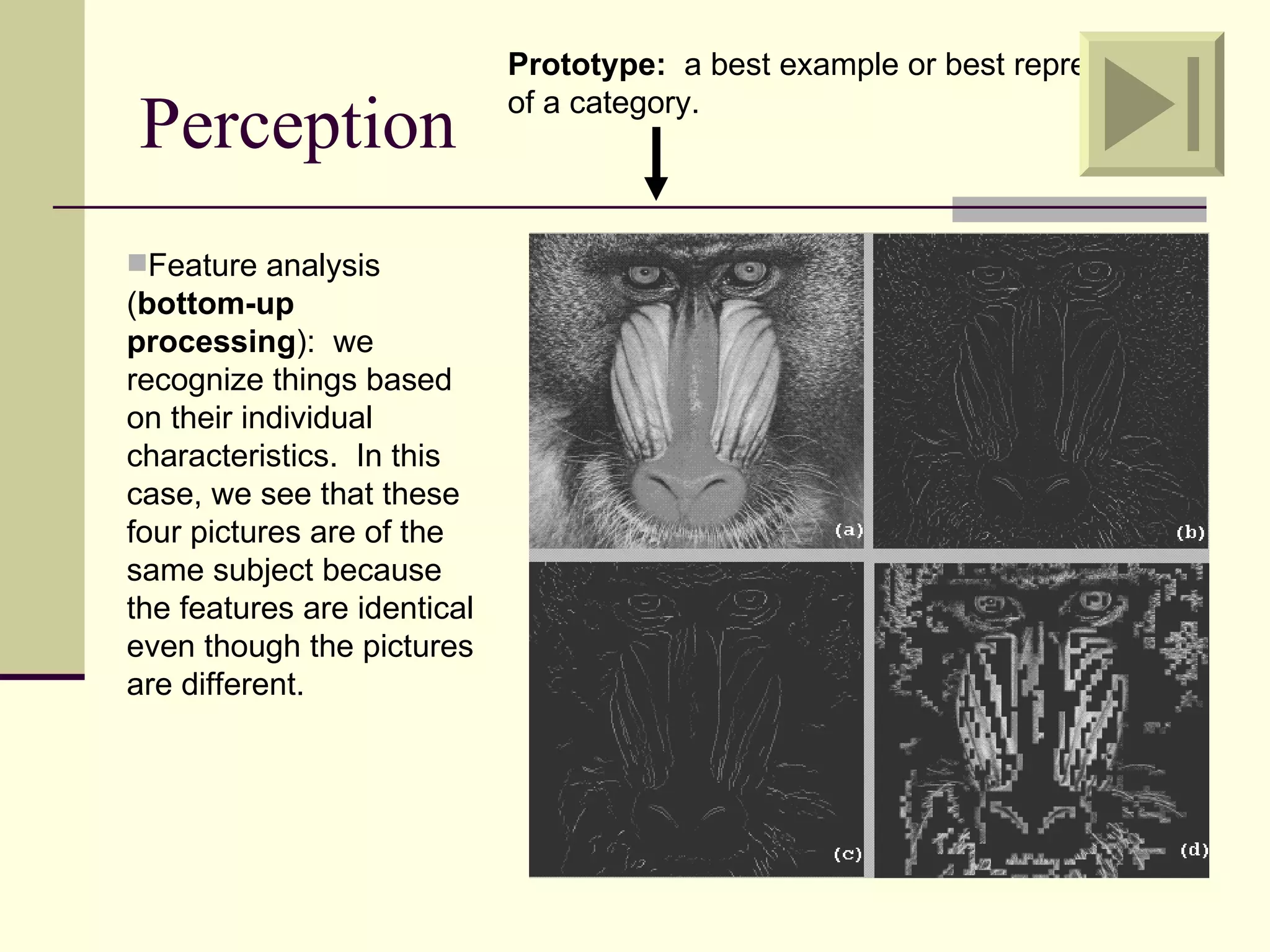
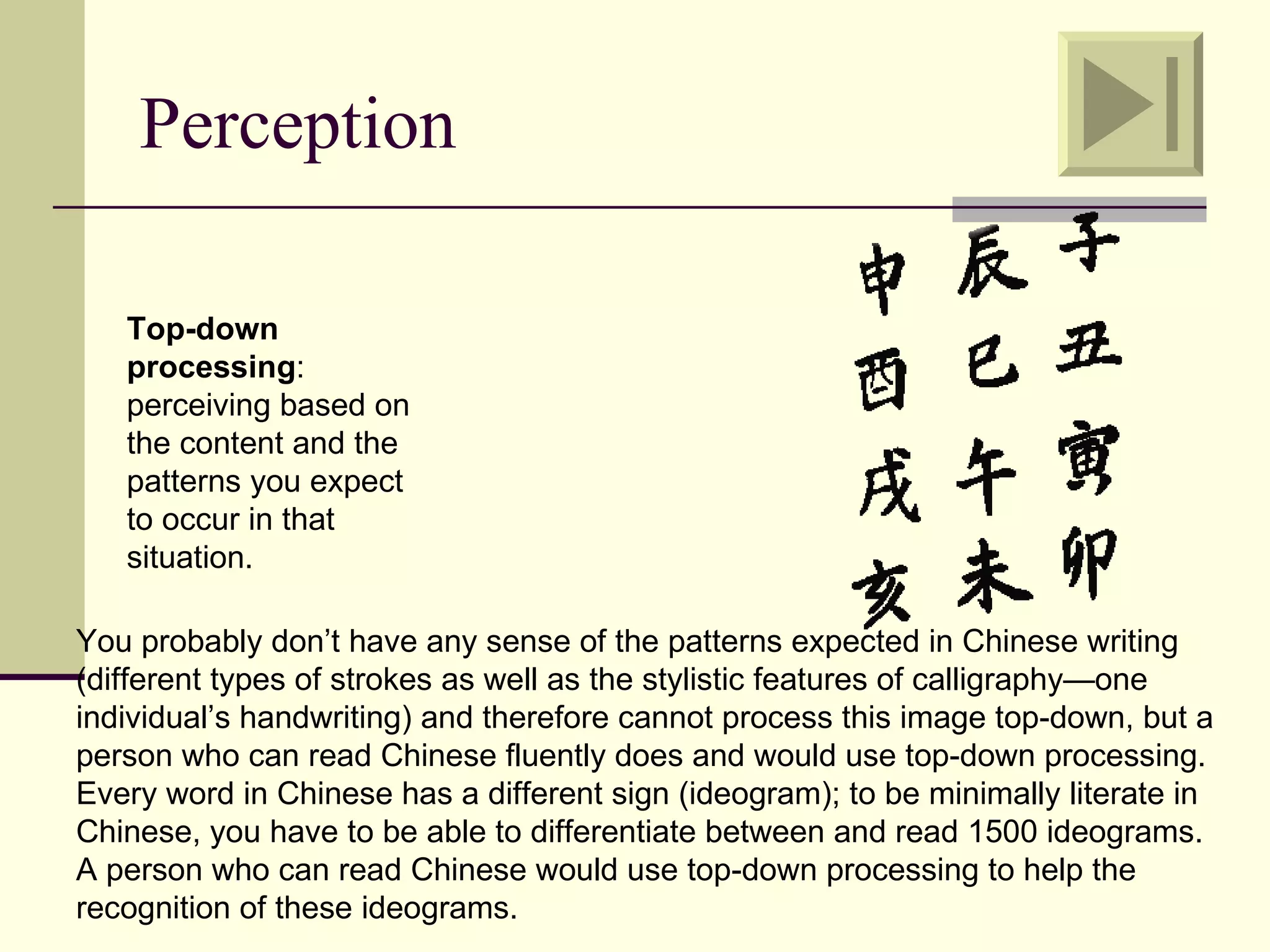
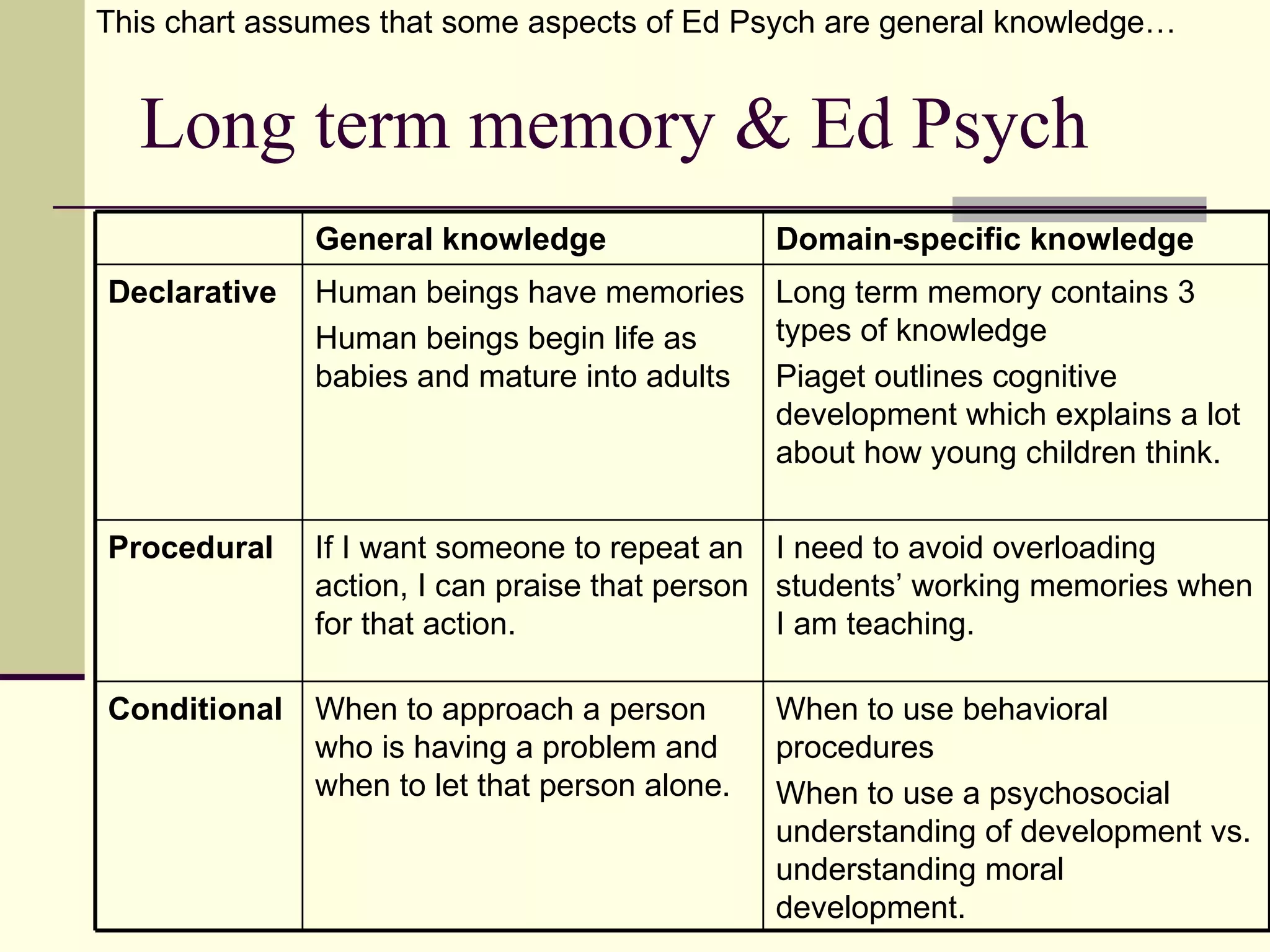
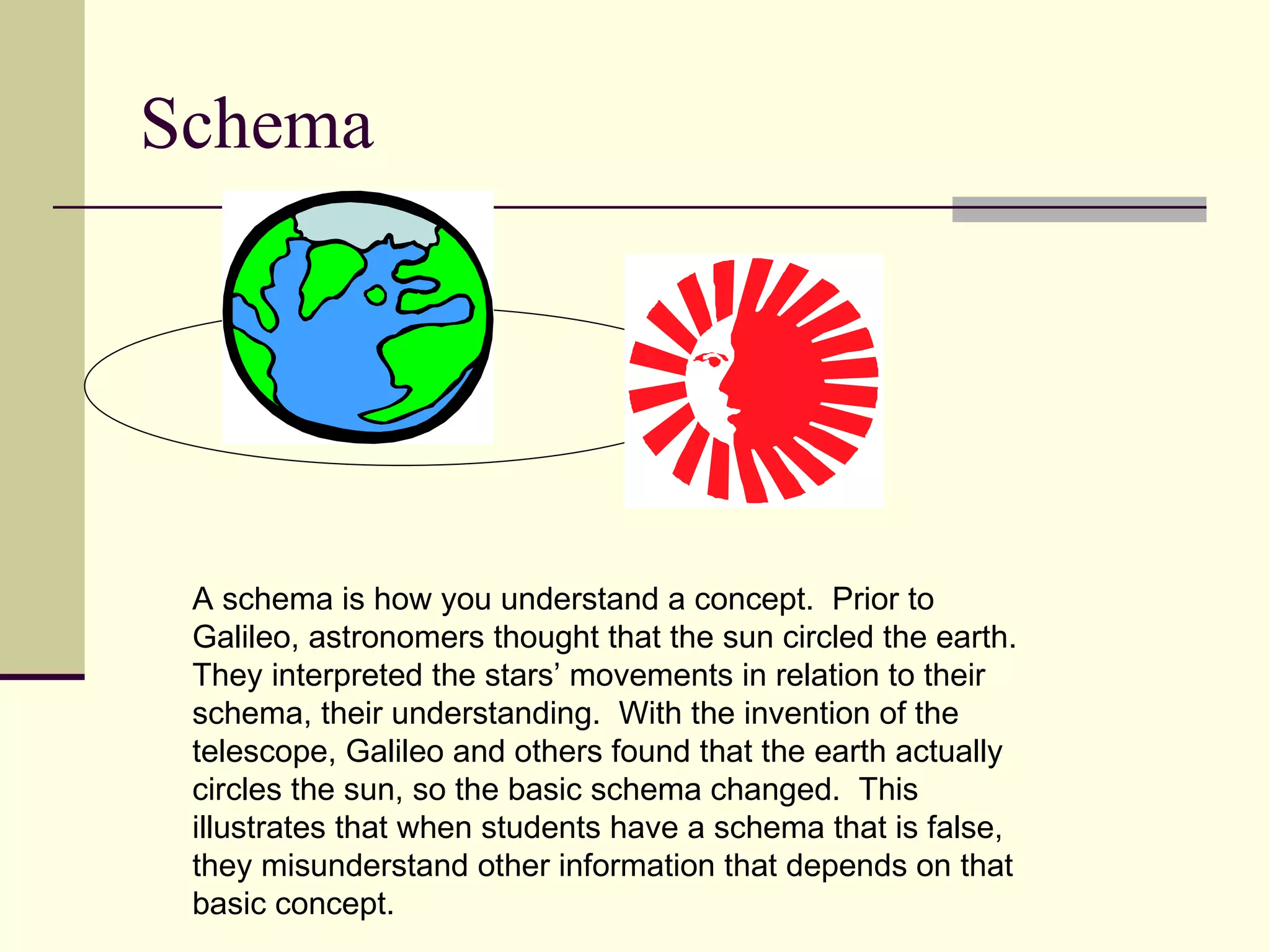
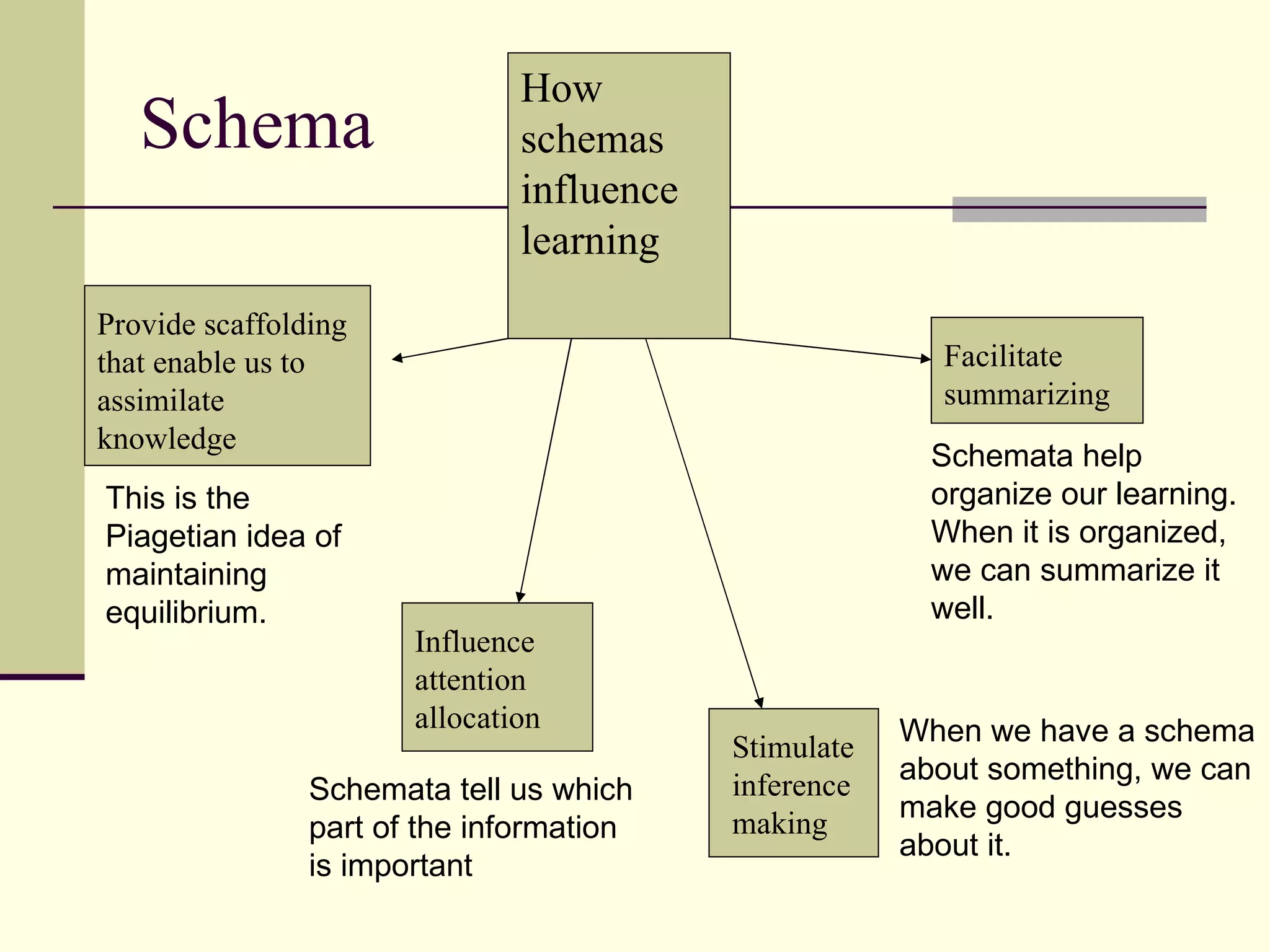
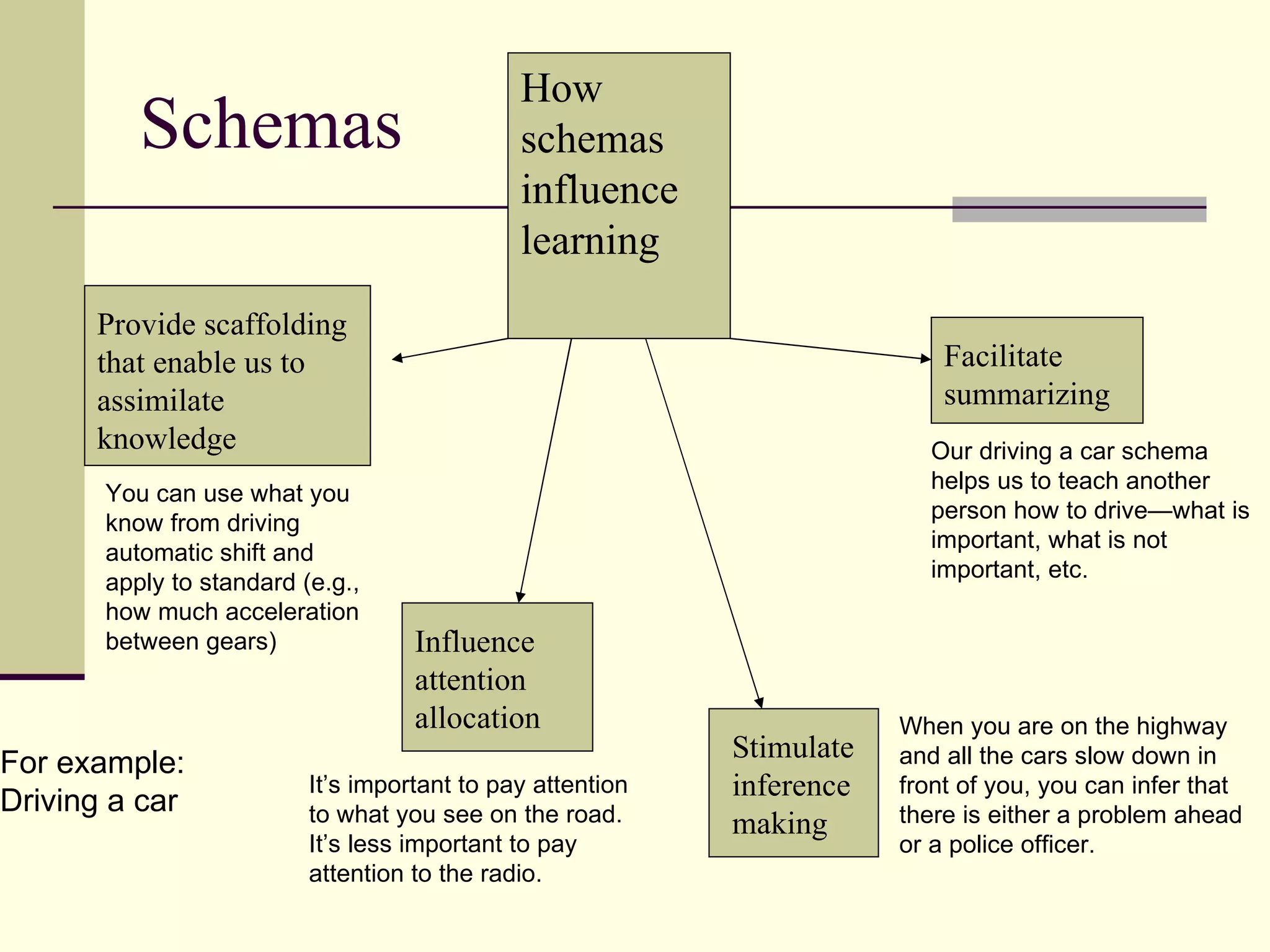
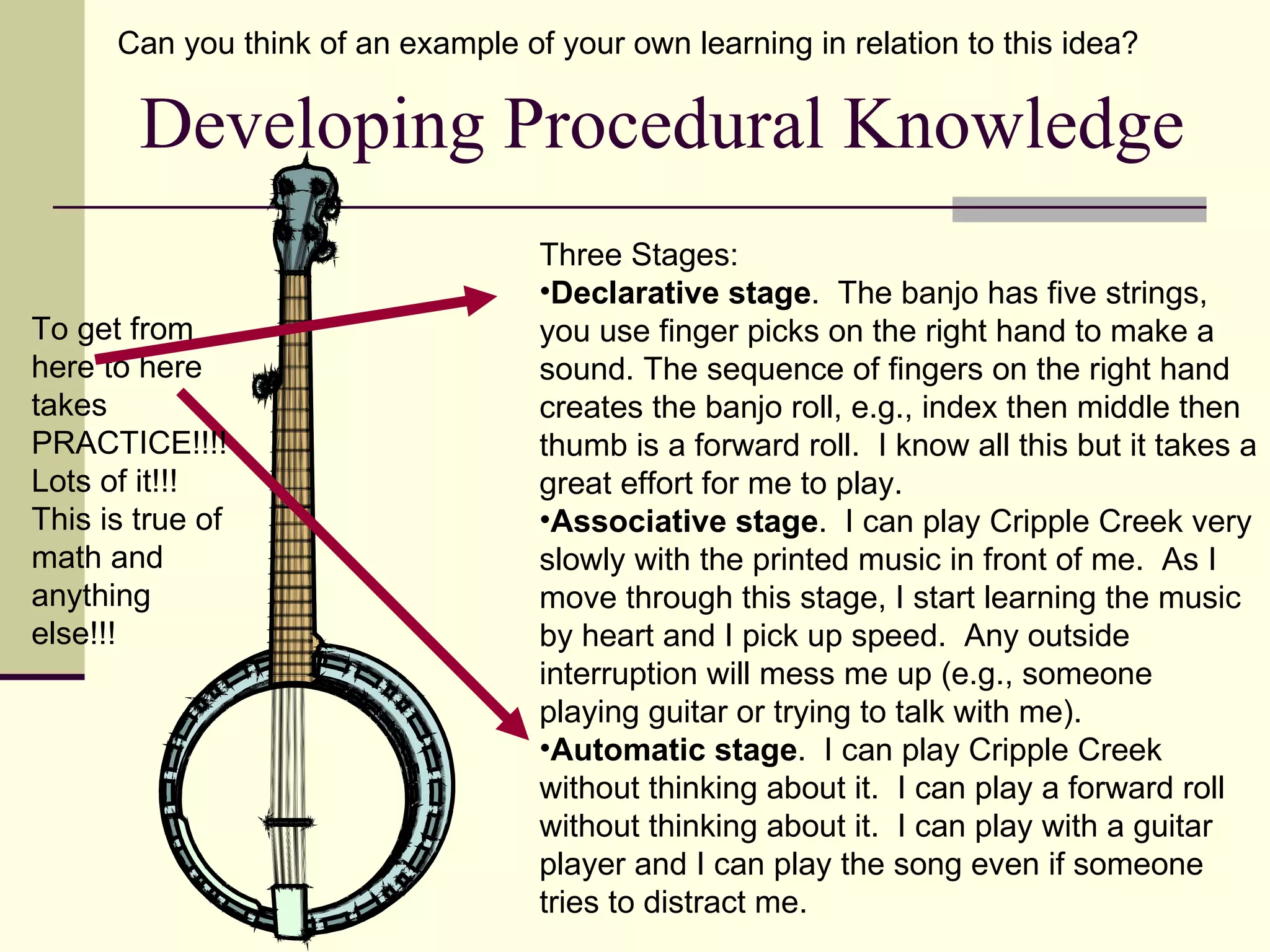
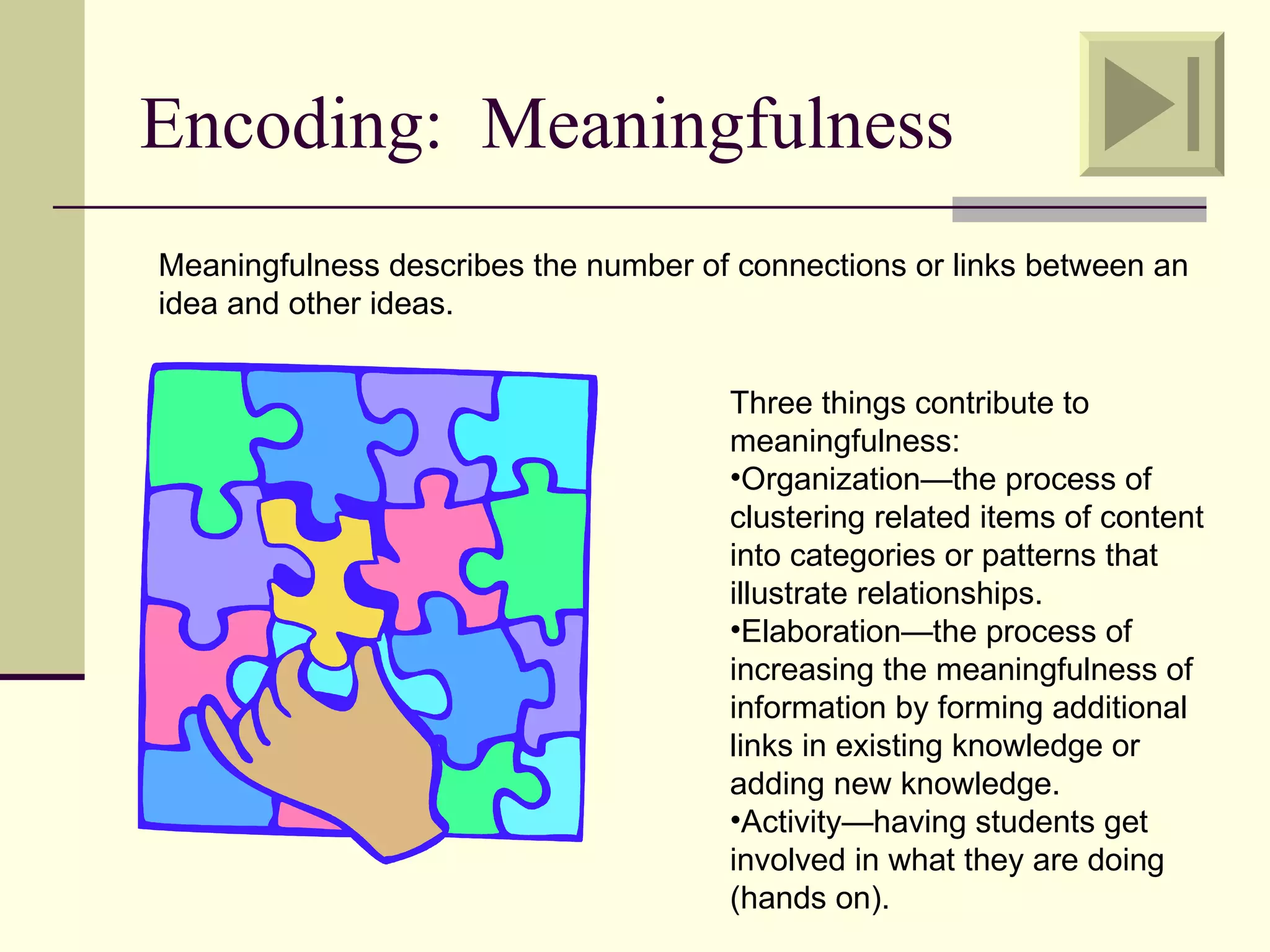
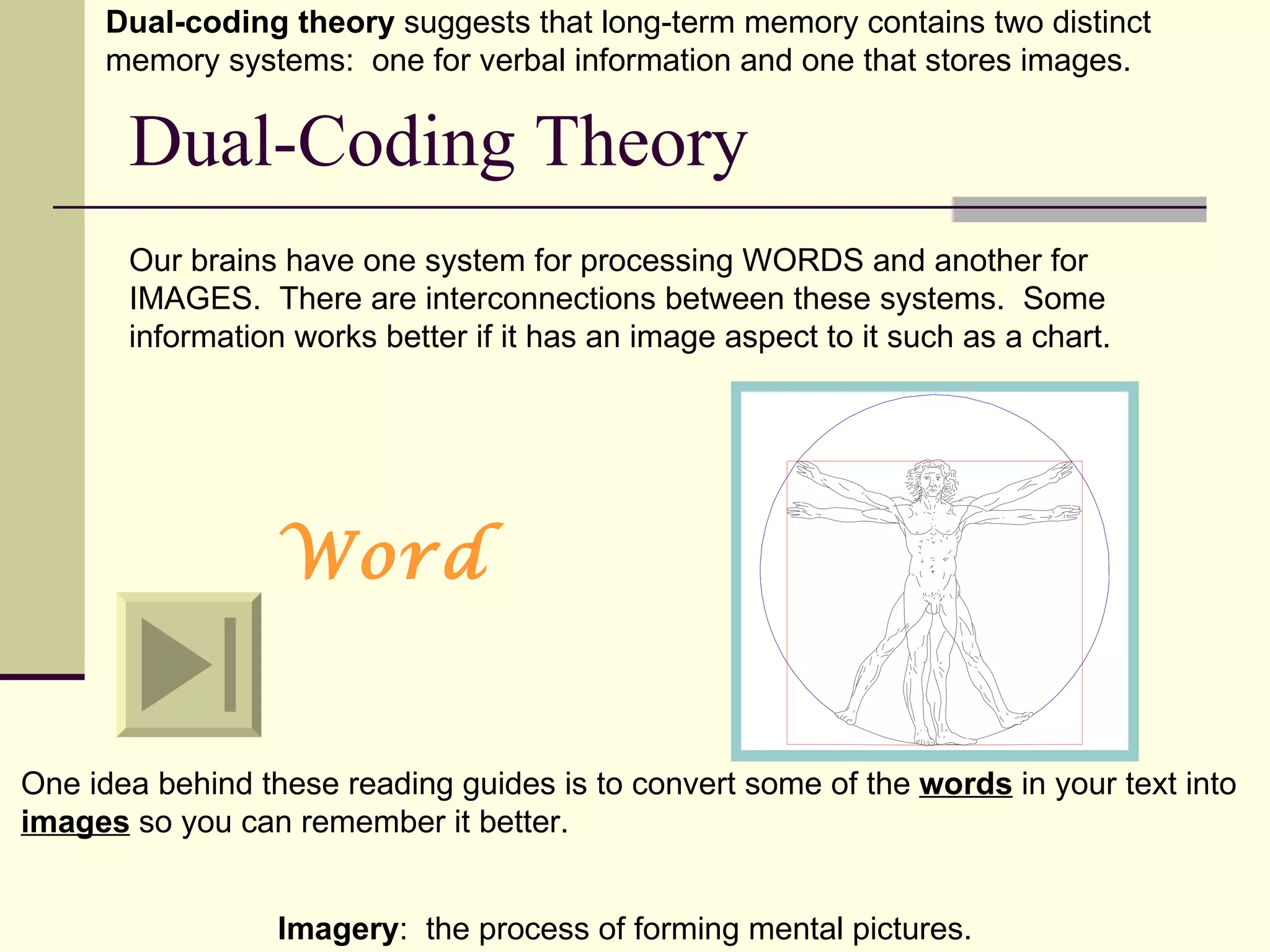
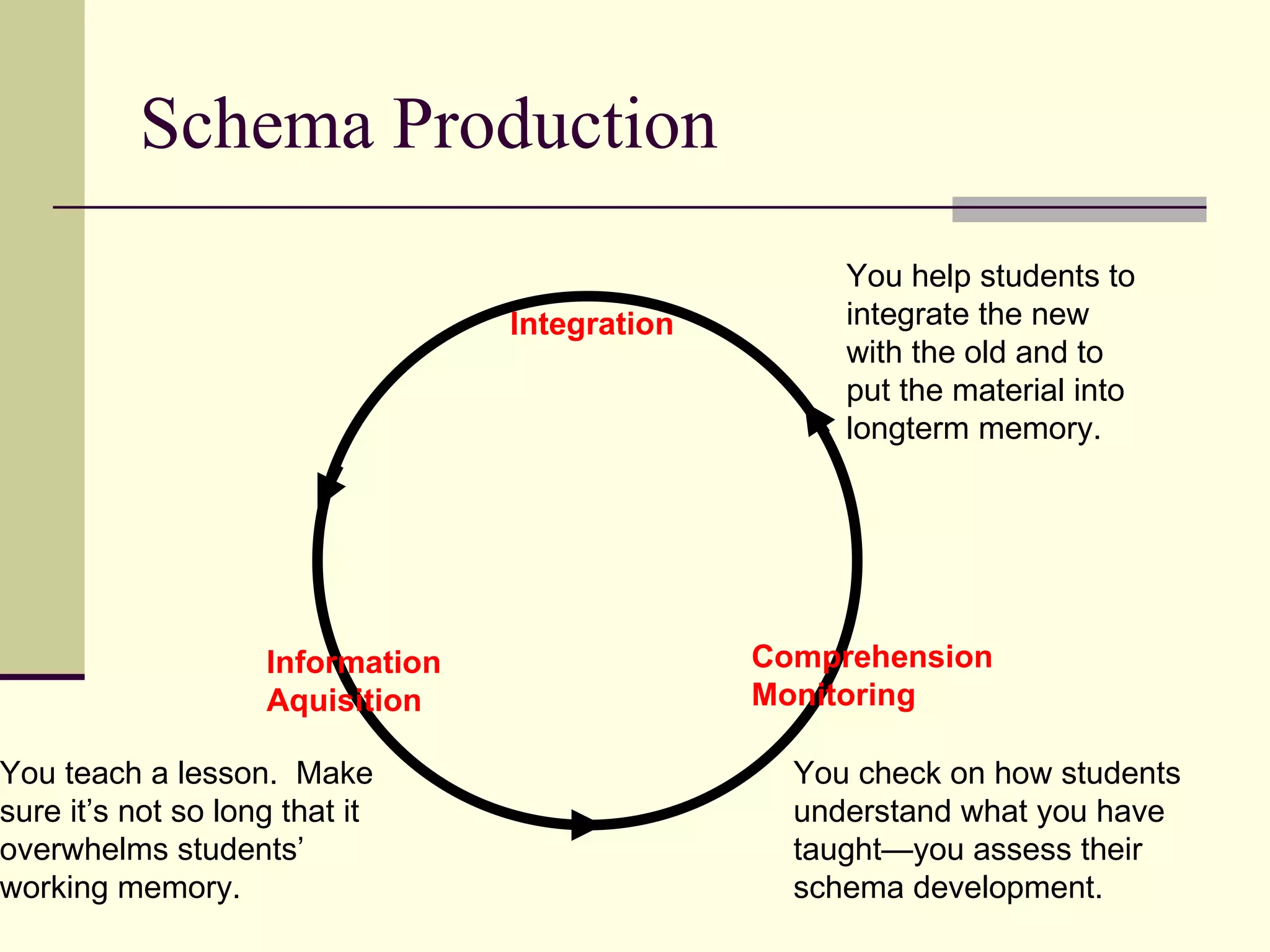
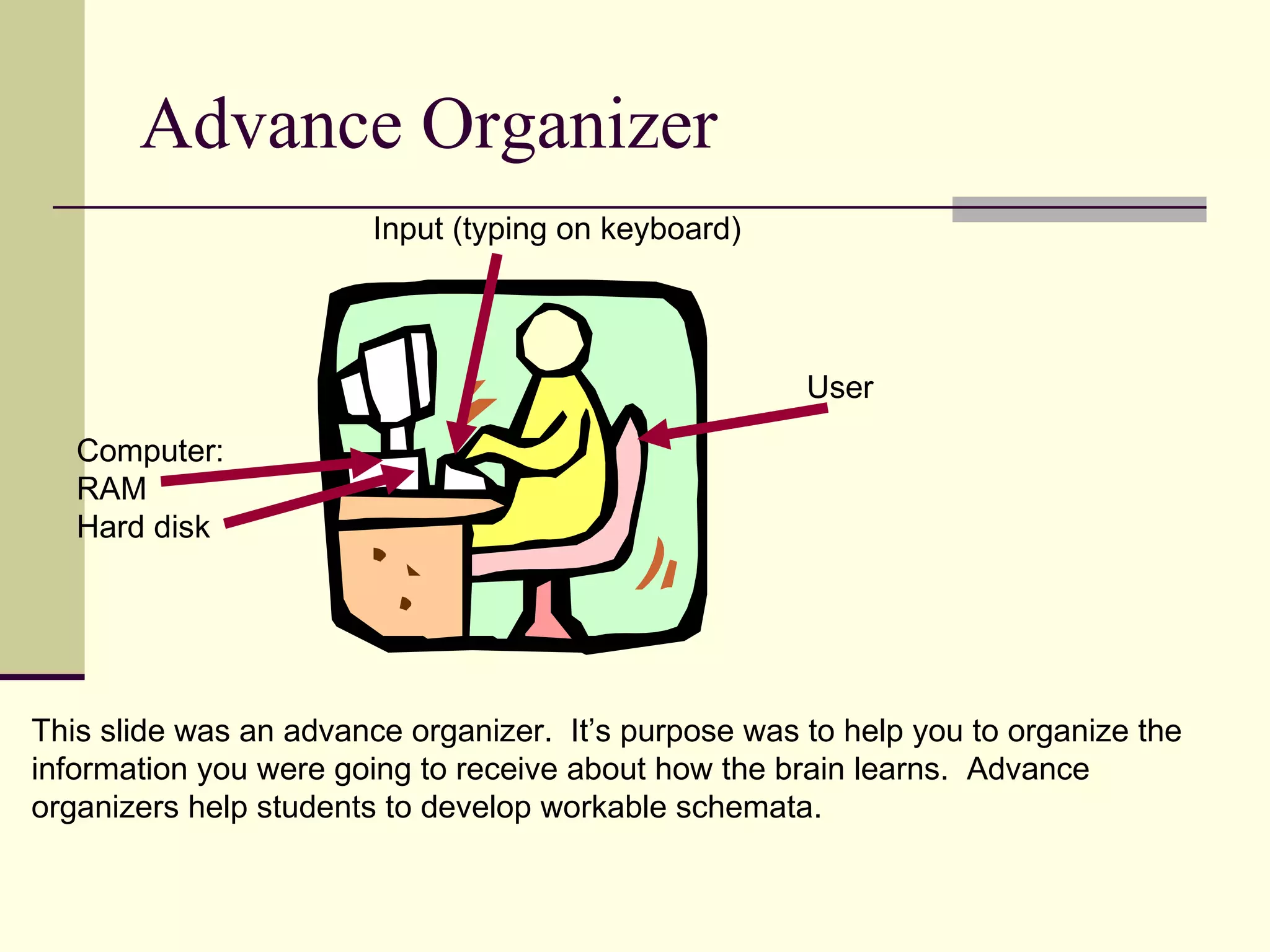
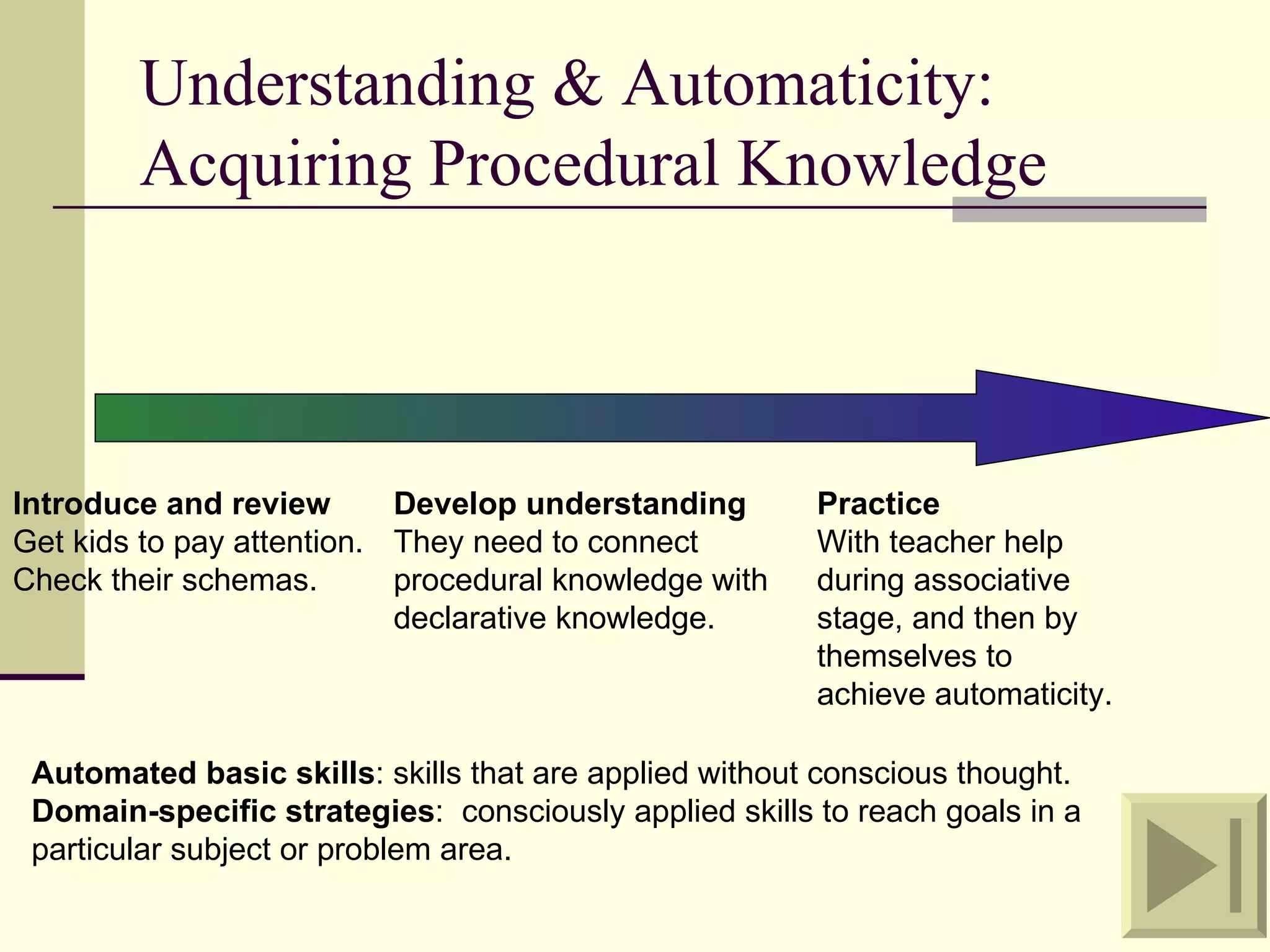
Cognitive learning theory focuses on mental processes and structures that occur as people make sense of the world. It explains learning as a change in mental structures that allows for different behaviors, rather than just a change in observable behavior. Learners are active constructors of knowledge who relate new information to what they already know in order to understand it. Learning involves changes in domain-specific and general knowledge stored in long-term memory through cognitive processes that operate on information held in working memory.