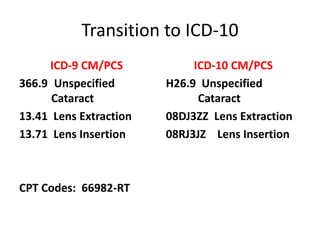
This document describes a cataract surgery procedure and evaluates the coding of the procedure using ICD-9 CM/PCS and ICD-10 CM/PCS. It notes that while the procedure was coded correctly using ICD-9, the ICD-10 coding had some discrepancies. Specifically, the procedure should have been coded with one ICD-10 PCS code for replacement rather than separate extraction and insertion codes. It also highlights the importance of complete documentation for accurate coding and the need for ongoing coder education on clinical guidelines and coding rules.