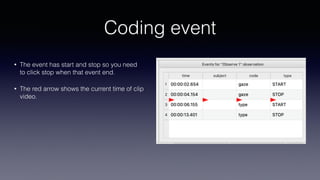
- Boris software allows researchers to code behavior by designing an ethogram (coding scheme) and recording point and state events during observations.
- Some benefits of Boris over manual observations include having a standardized coding scheme, ability to review data, and potential for integration of physiological signals.
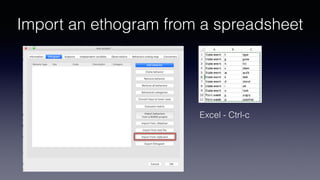
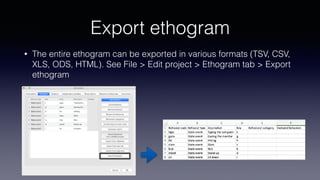
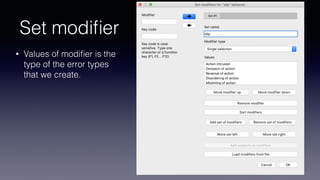
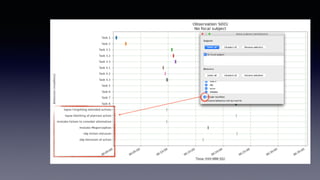
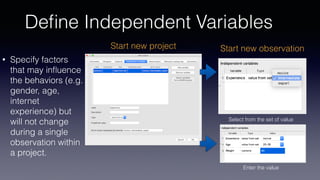
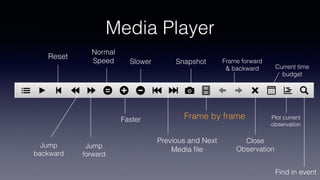
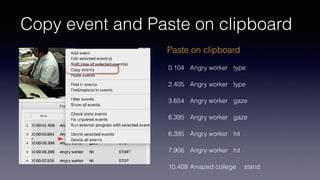
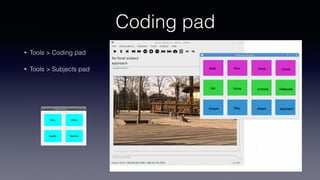
- Key features include importing/exporting ethograms, defining behaviors and modifiers, recording events during video observations with time stamps, and exporting coded data.






![Valid Keys for triggering behavior
• keys from a to z
• keys from A to Z
• keys from 0 to 9
• function keys from F1 to F12
• à é è ù ì ç
• ! " £ $ % & / ( ) = ? ^ [ ] { } @ | § ° #](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codingdataboris-201016020718/85/Coding-data-with-Boris-software-8-320.jpg)