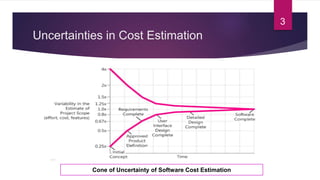
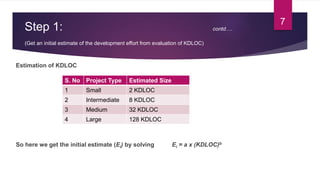
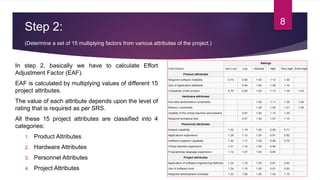
COCOMO (Constructive Cost Model) is a software cost estimation model developed by Barry Boehm in 1981. It estimates the effort required to develop a software project in terms of person-months. The model has three main steps: 1) Calculate an initial effort estimate based on thousands of delivered lines of source code. 2) Determine a set of 15 factors that adjust the initial estimate based on project attributes. 3) Calculate the final effort estimate by multiplying the initial estimate by the adjustment factors. The model accounts for factors like system size, organizational experience, and project attributes to provide a cost estimate for a software project.