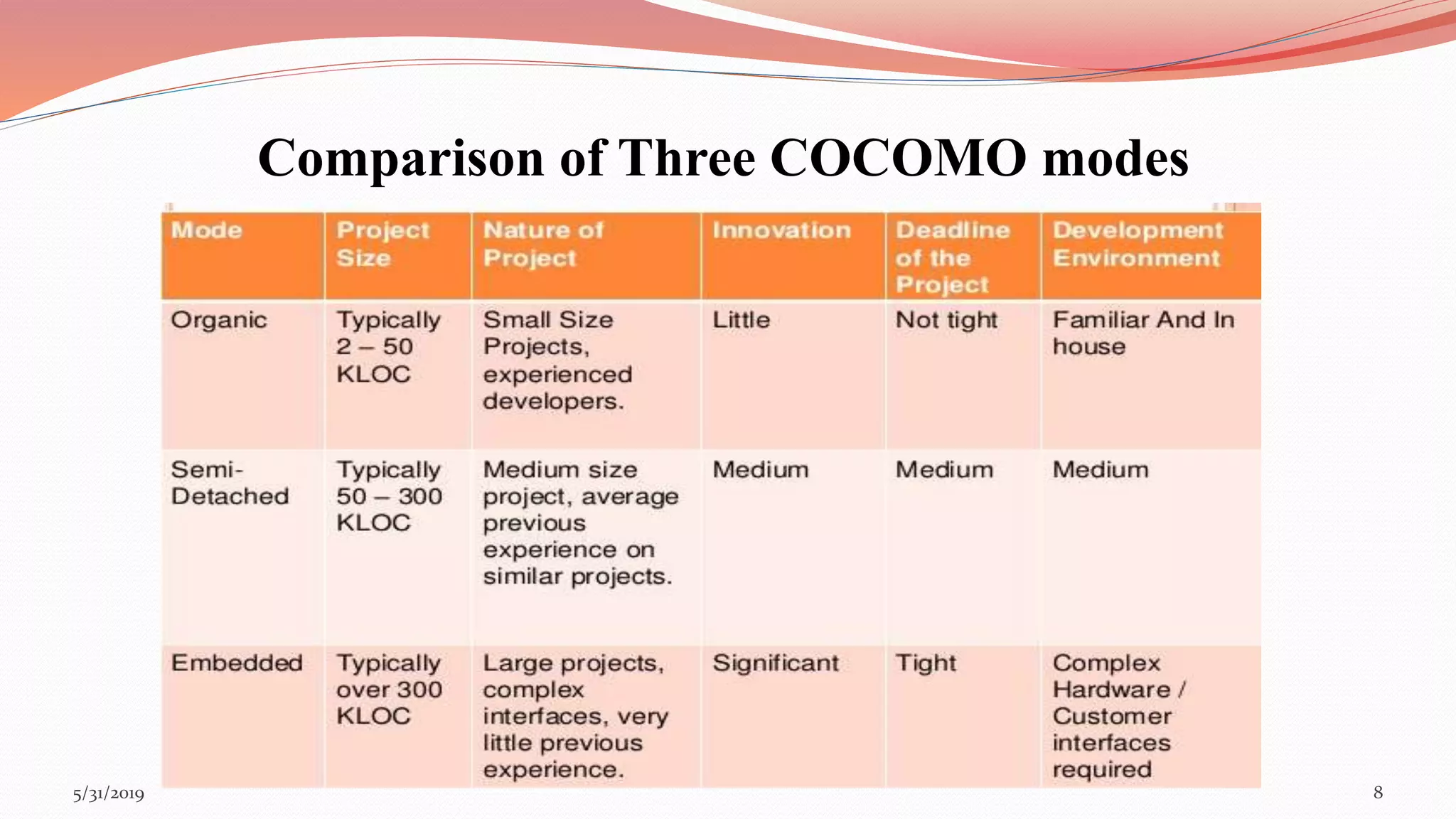
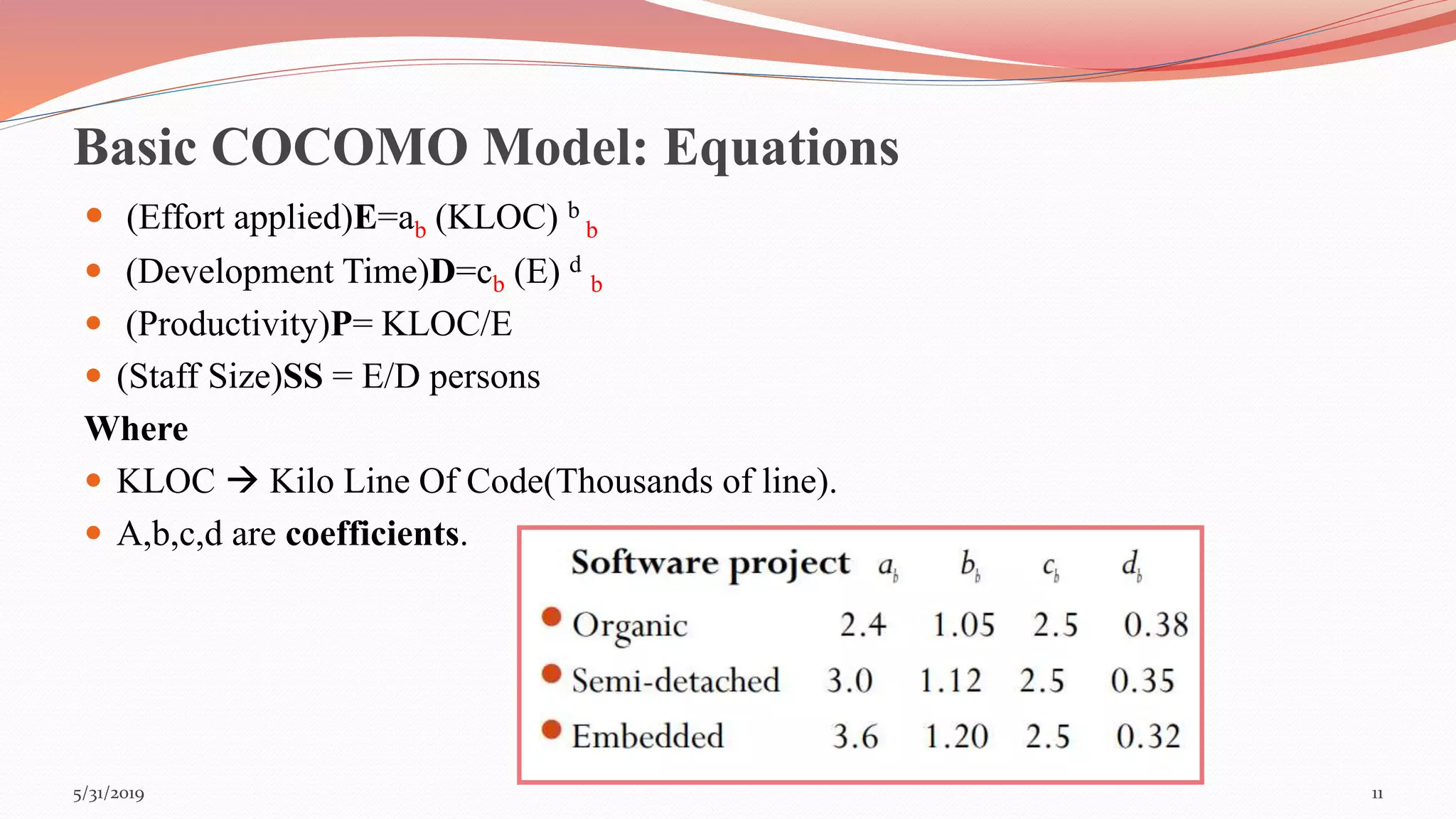
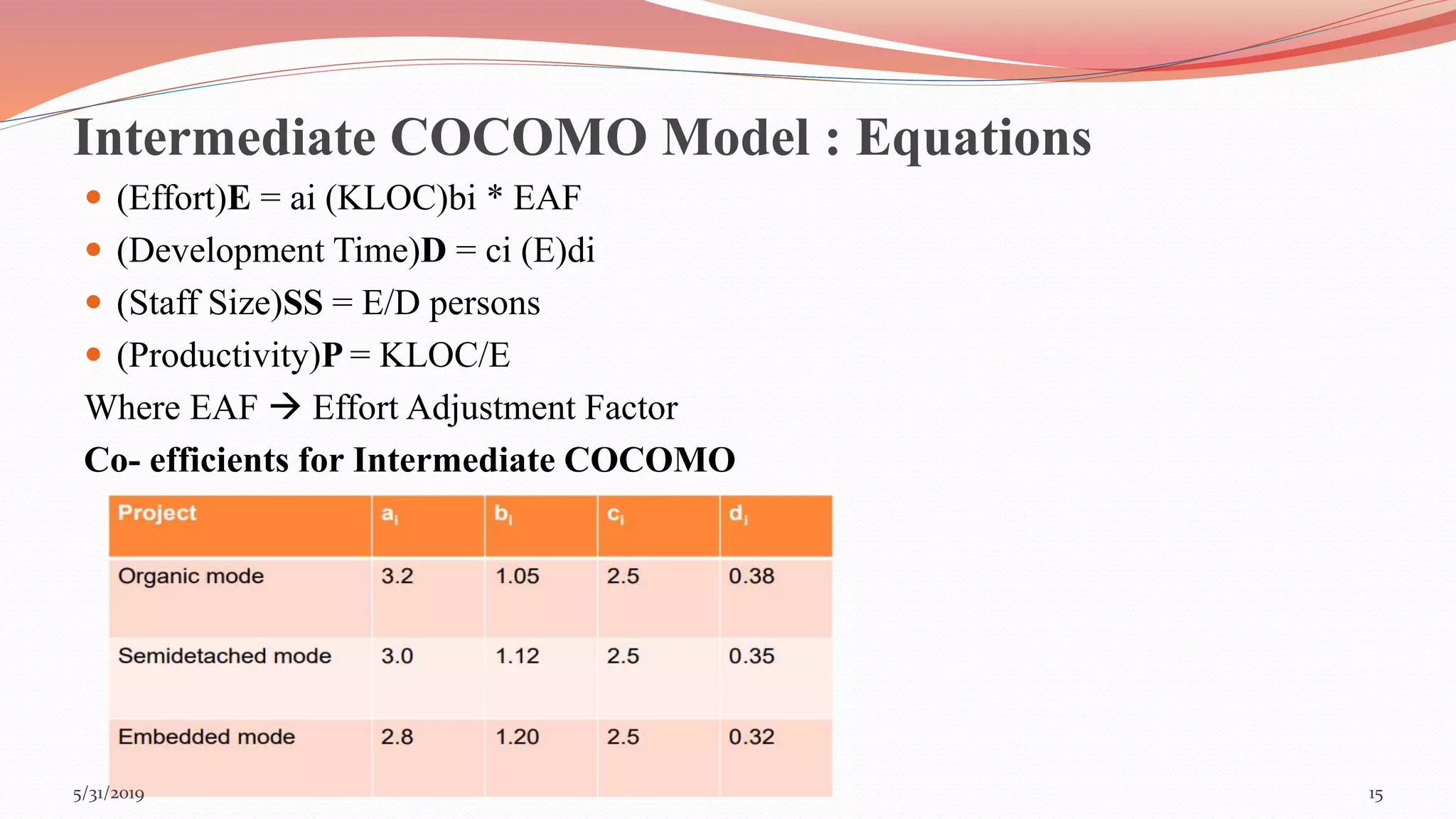
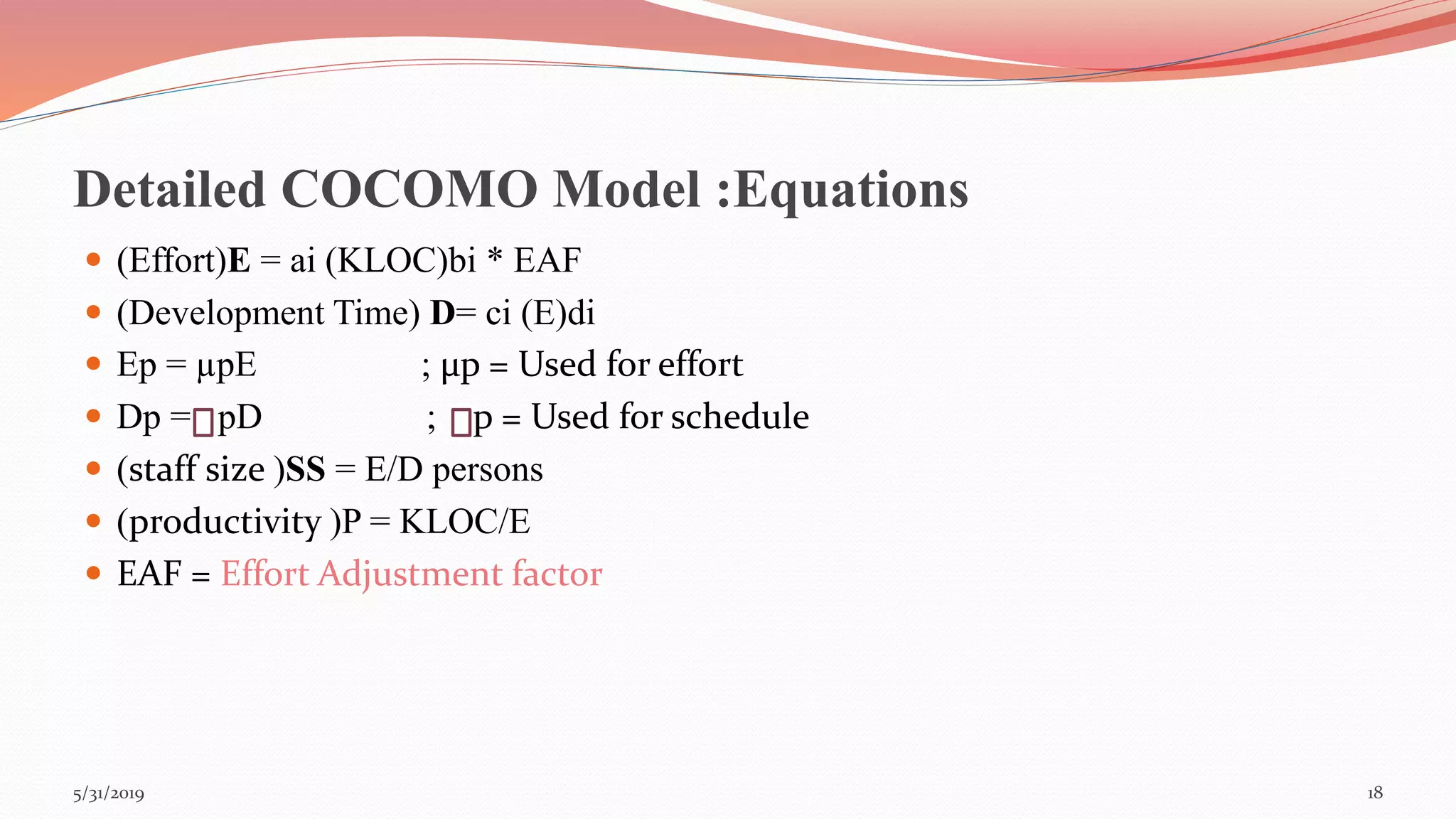
The document discusses the COCOMO (Constructive Cost Model) used for cost estimation in software engineering based on lines of code. It outlines three development modes—organic, semi-detached, and embedded—along with their characteristics, and describes basic, intermediate, and detailed COCOMO models, including their equations for estimating effort, schedule, and productivity. Additionally, it highlights the advantages of COCOMO, such as its realism and predictability, while noting disadvantages like the neglect of certain project parameters.