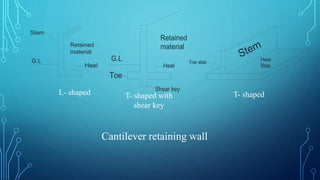
The document presents a comprehensive guide on the design of cantilever retaining walls, focusing on the specifications and calculations required for such structures, including stability checks and component design. It includes detailed calculations for earth pressure, dimensions, and stability factors based on given parameters, along with material specifications and reinforcement details. The design follows the requirements for a retaining wall with height specifications, ensuring safety against sliding and overturning forces.