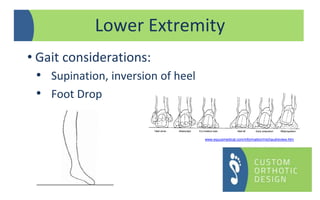
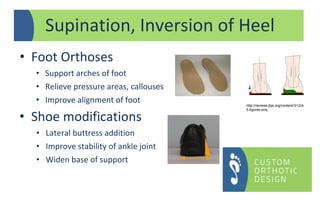
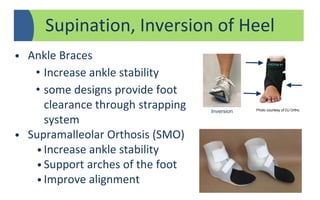
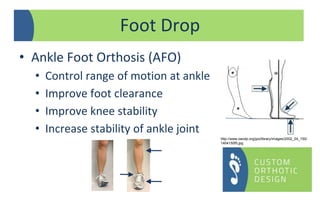
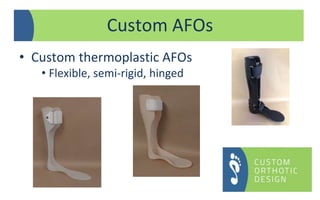
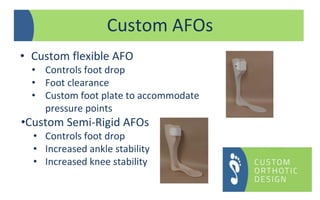
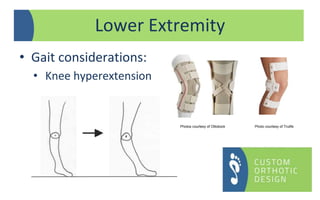
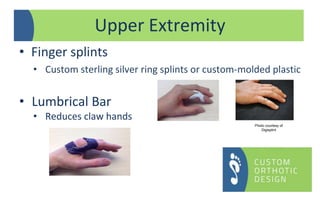
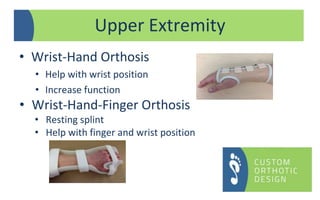
The document provides a comprehensive overview of orthotic treatments for patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease, highlighting the impact of the condition on both lower and upper limbs. It discusses various goals of orthotic intervention, including stability and balance improvement, as well as different types of orthotic devices for foot drop and upper extremity support. Additionally, it addresses the need for personalized treatment based on individual patient assessments.