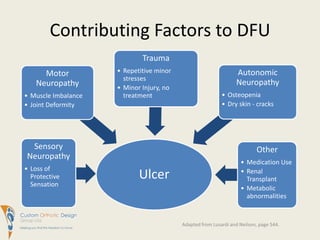
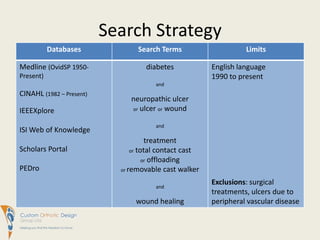
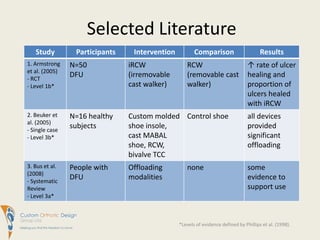
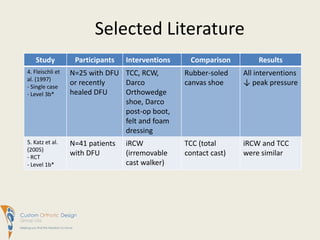
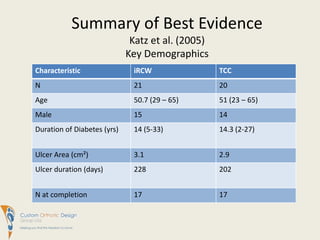
This document summarizes evidence comparing the effectiveness of removable cast walkers (RCW) to total contact casts (TCC) for treating diabetic foot ulcers. It finds that RCWs can achieve similar healing outcomes to TCCs when made non-removable, reducing healing times and complication rates. While TCC application requires more expertise, RCWs are easier for patients to don and doff and have lower costs. The document recommends RCWs as an effective alternative to TCCs when used on a full-time basis.