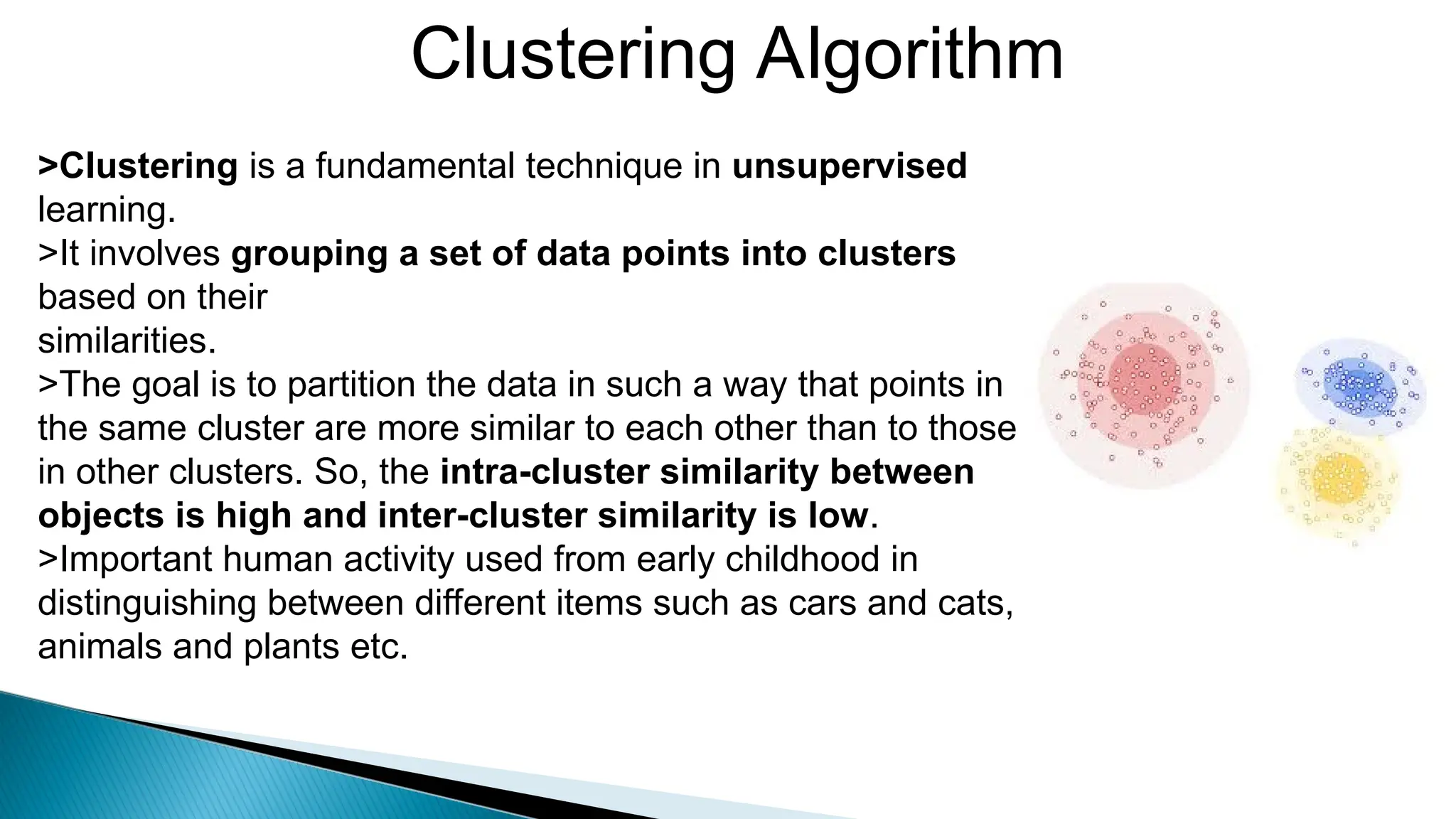
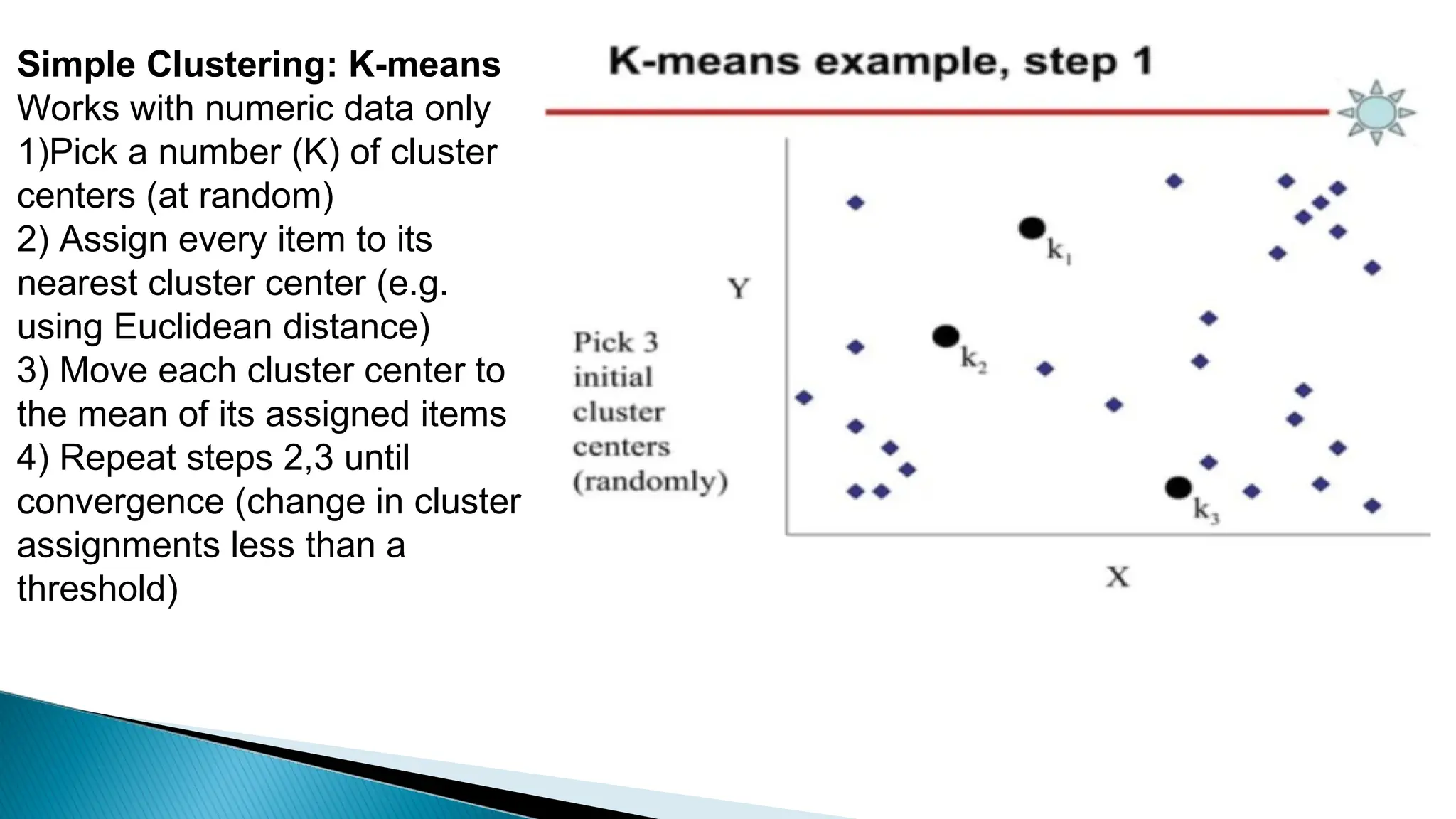
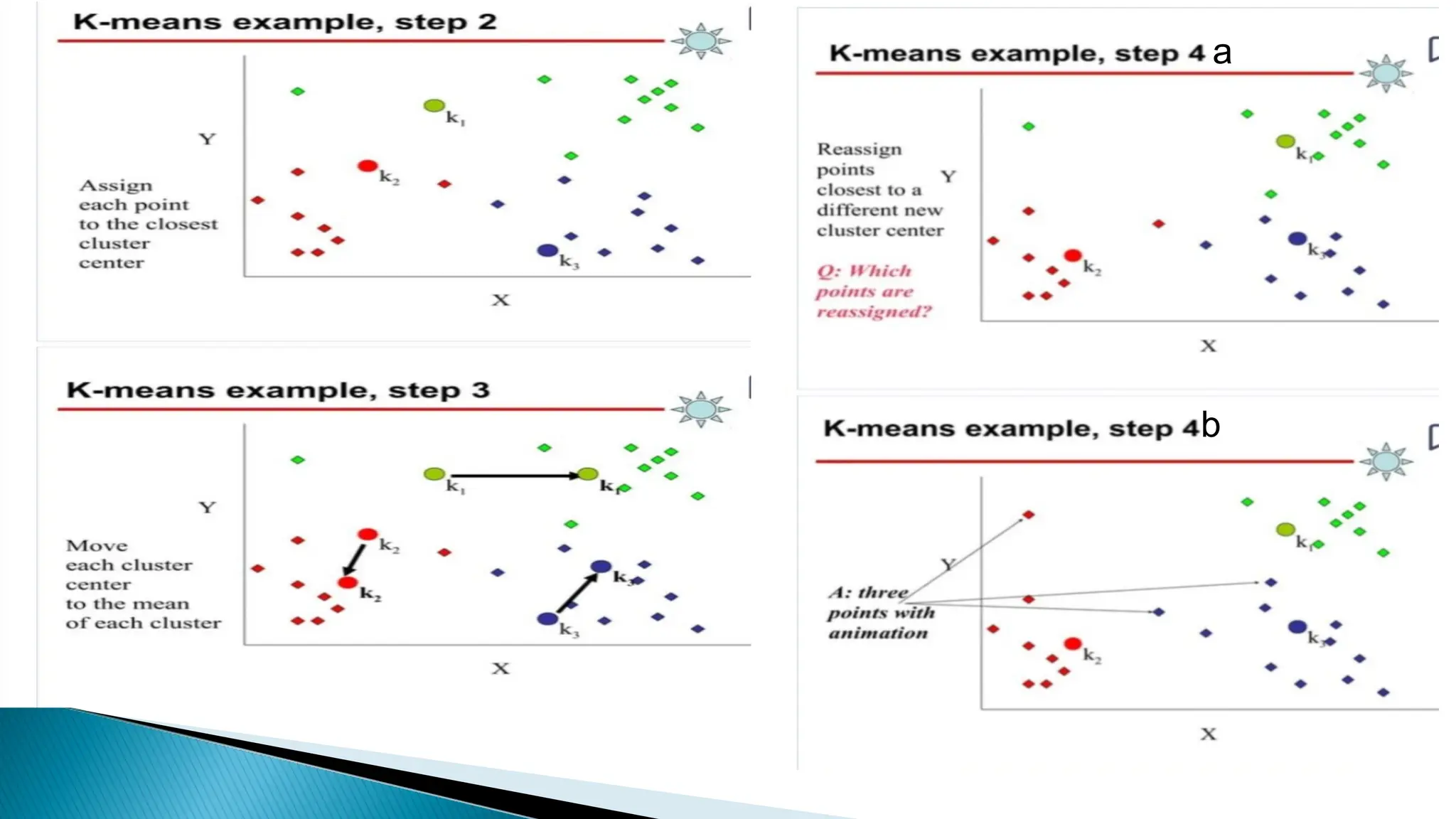
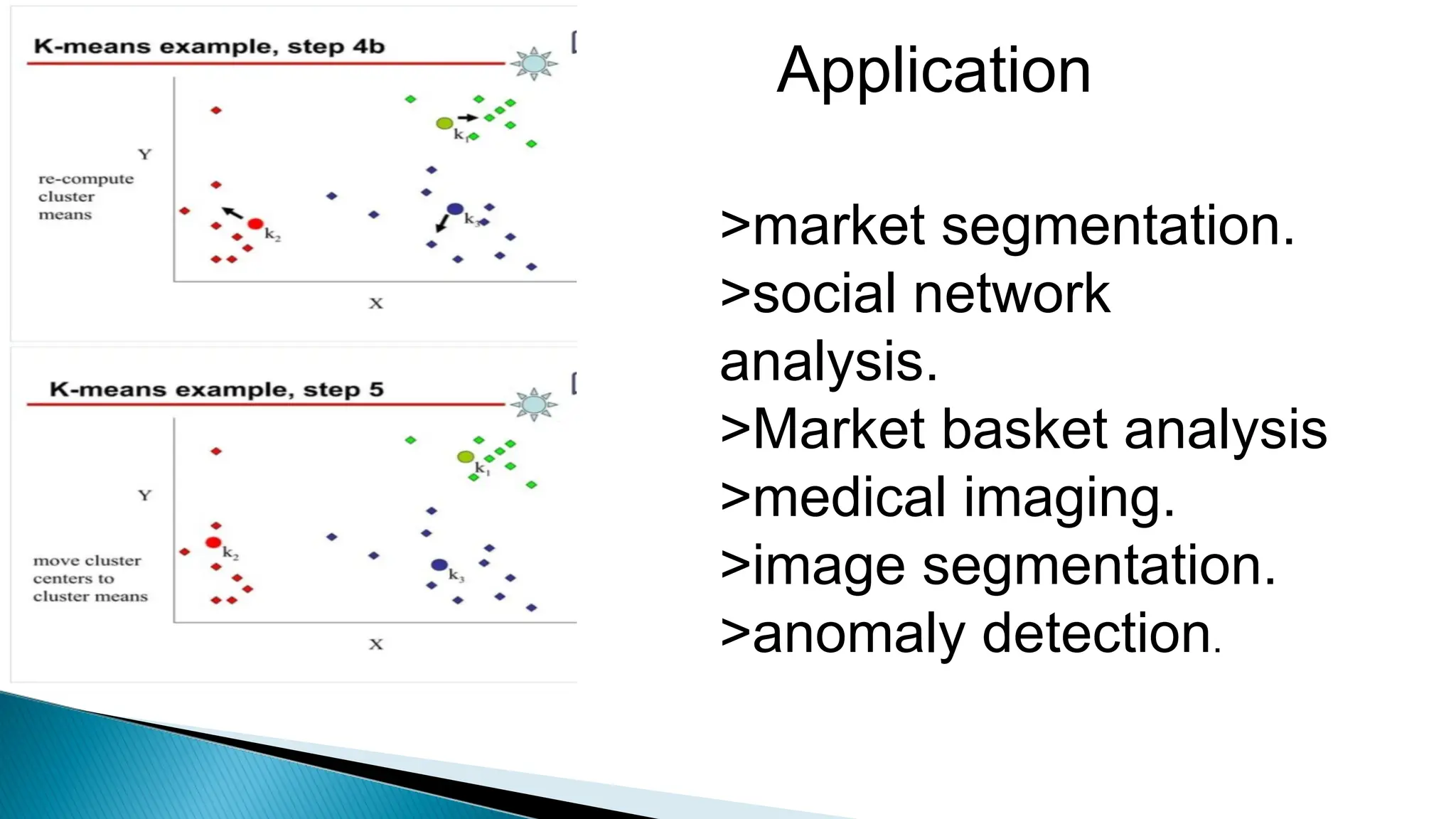
Clustering algorithms group data points into clusters based on similarities, aiming for high intra-cluster and low inter-cluster similarity. Key steps include distance measurement, cluster assignment, and evaluation, with methods like k-means facilitating this process. While clustering is valuable for applications such as market segmentation and anomaly detection, challenges like sensitivity to outliers and the need for specifying the number of clusters can affect results.