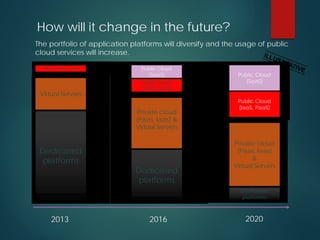
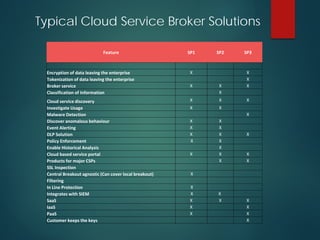
The presentation discusses the security of data in cloud computing, highlighting the importance of assessing cloud service providers and understanding compliance and governance issues. It emphasizes the need for businesses to navigate both sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud services, addressing challenges such as shadow IT and data processing regulations, especially in the context of EU and US policies. Furthermore, it suggests utilizing cloud security alliance strategies and broker services to enhance security and manage risks associated with cloud adoption.