The document provides an overview of cloud computing concepts including:
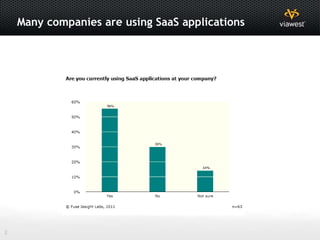
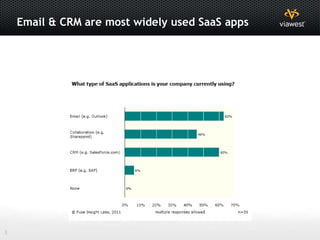
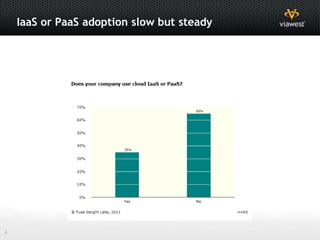
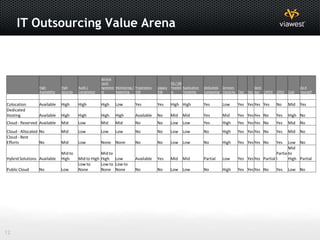
- Software as a Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) are commonly used cloud models.
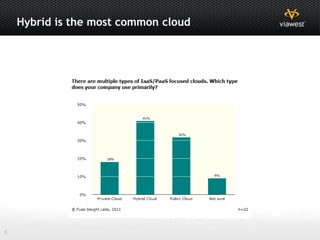
- Hybrid cloud, using both public and private clouds together, is a popular approach.
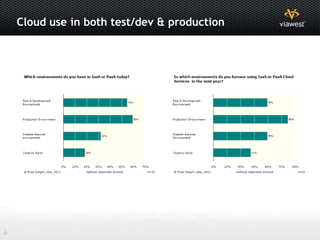
- Cloud services can be used for both testing/development and production workloads.