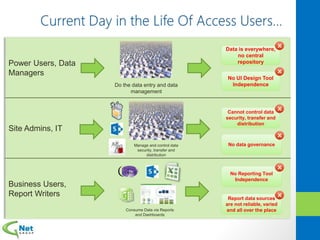
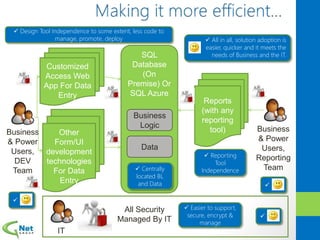
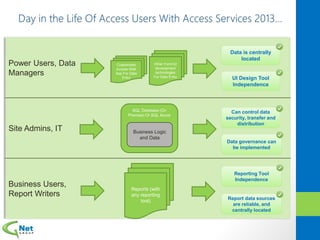
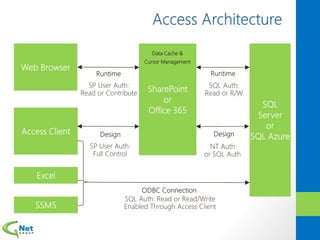
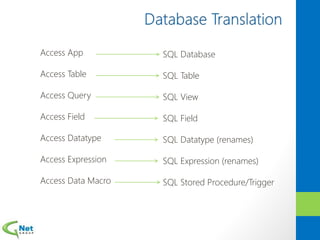
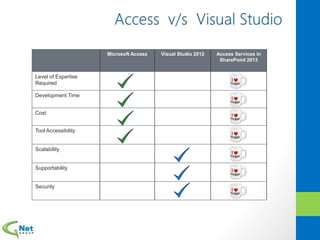
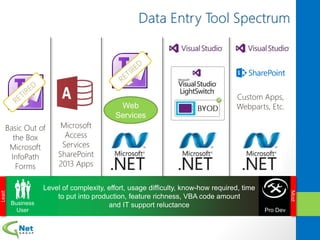
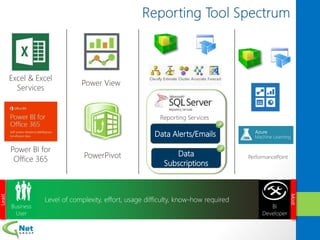
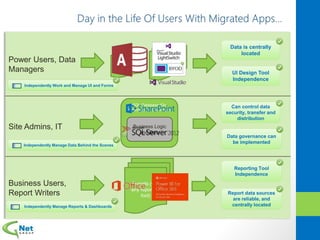
This document discusses Microsoft Access Services 2013 and the benefits it provides for migrating existing Access databases. It allows centralizing data in a SQL database while giving business users independence in designing user interfaces and reports. This improves data security, governance and reliability while making solutions easier to develop and maintain. It also provides tools for deploying Access apps in SharePoint, managing permissions and distribution.