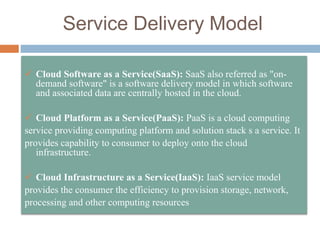
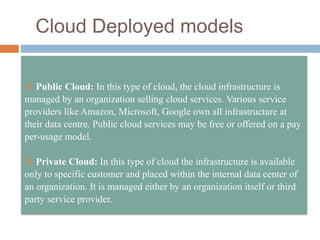
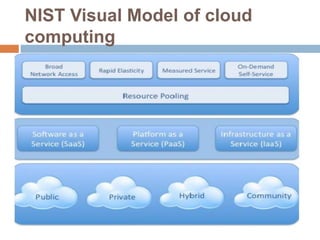
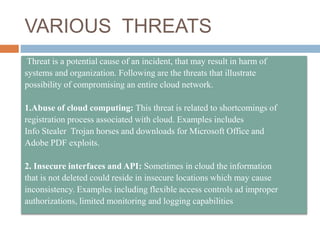
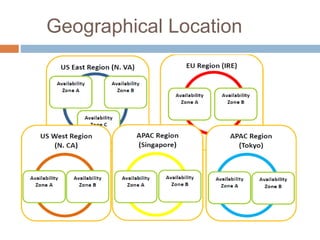
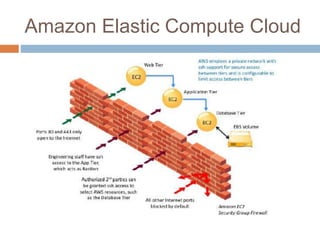
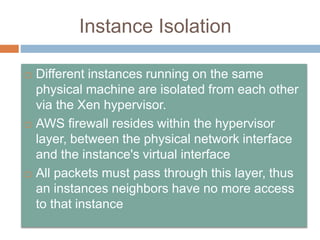
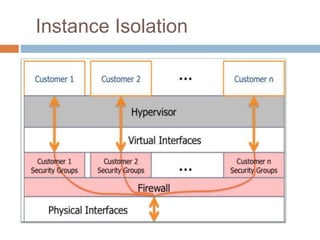
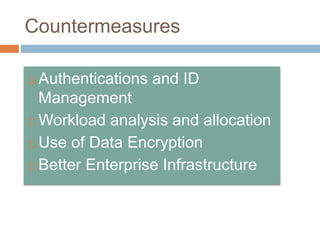
This document discusses cloud services and security. It begins by defining cloud computing and its key characteristics such as broad network access, rapid elasticity, and resource pooling. It then covers the different cloud service models including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. The document also discusses the various cloud deployment models like public, private, community, and hybrid clouds. It identifies security as the top challenge for cloud adoption and outlines threats like abuse of cloud computing, insecure interfaces, data loss or leakage, and malevolence. Finally, it summarizes the security offerings and controls of Google Apps, Google Engine, Amazon Web Services, and the services they provide.