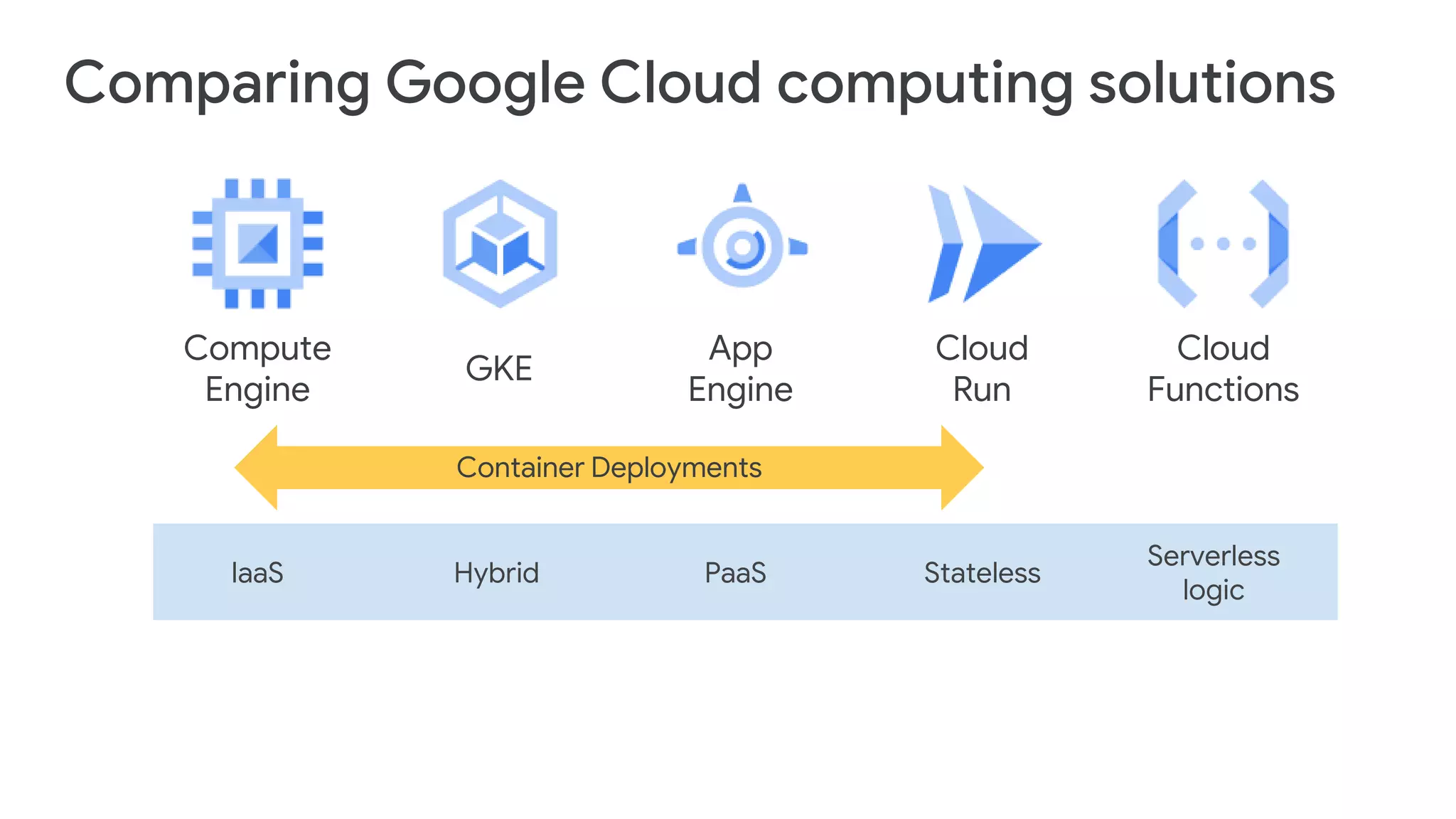
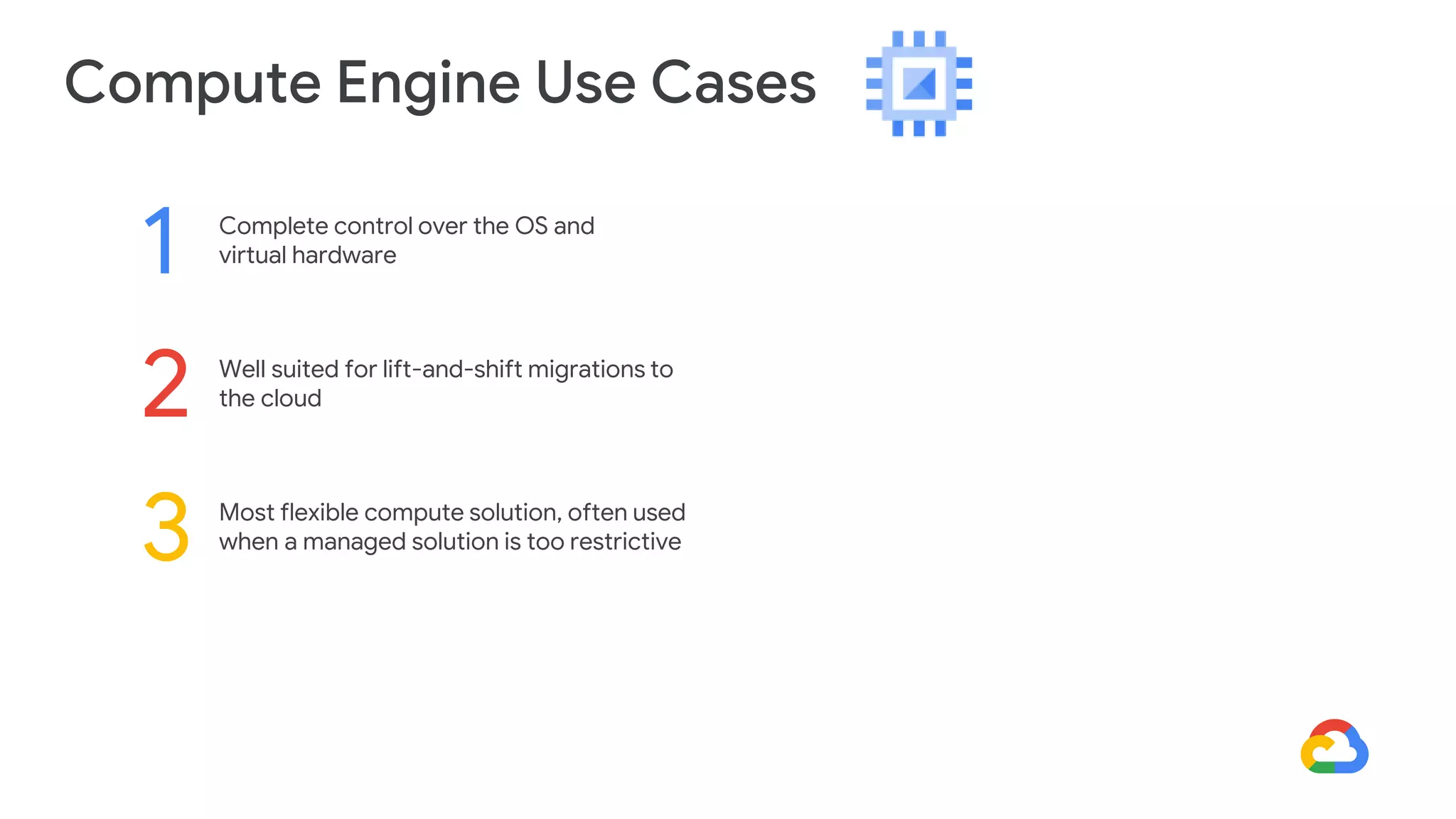
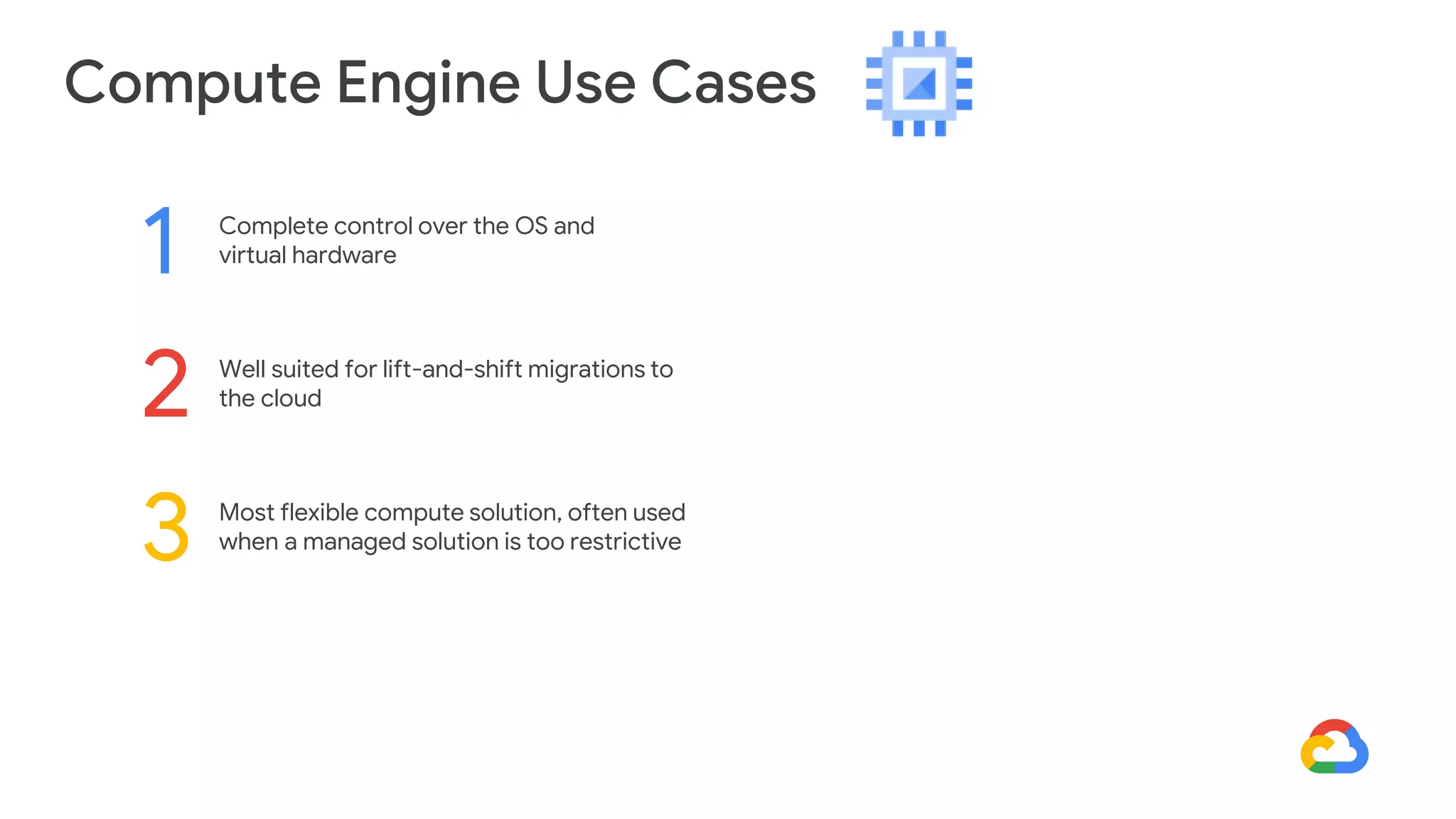
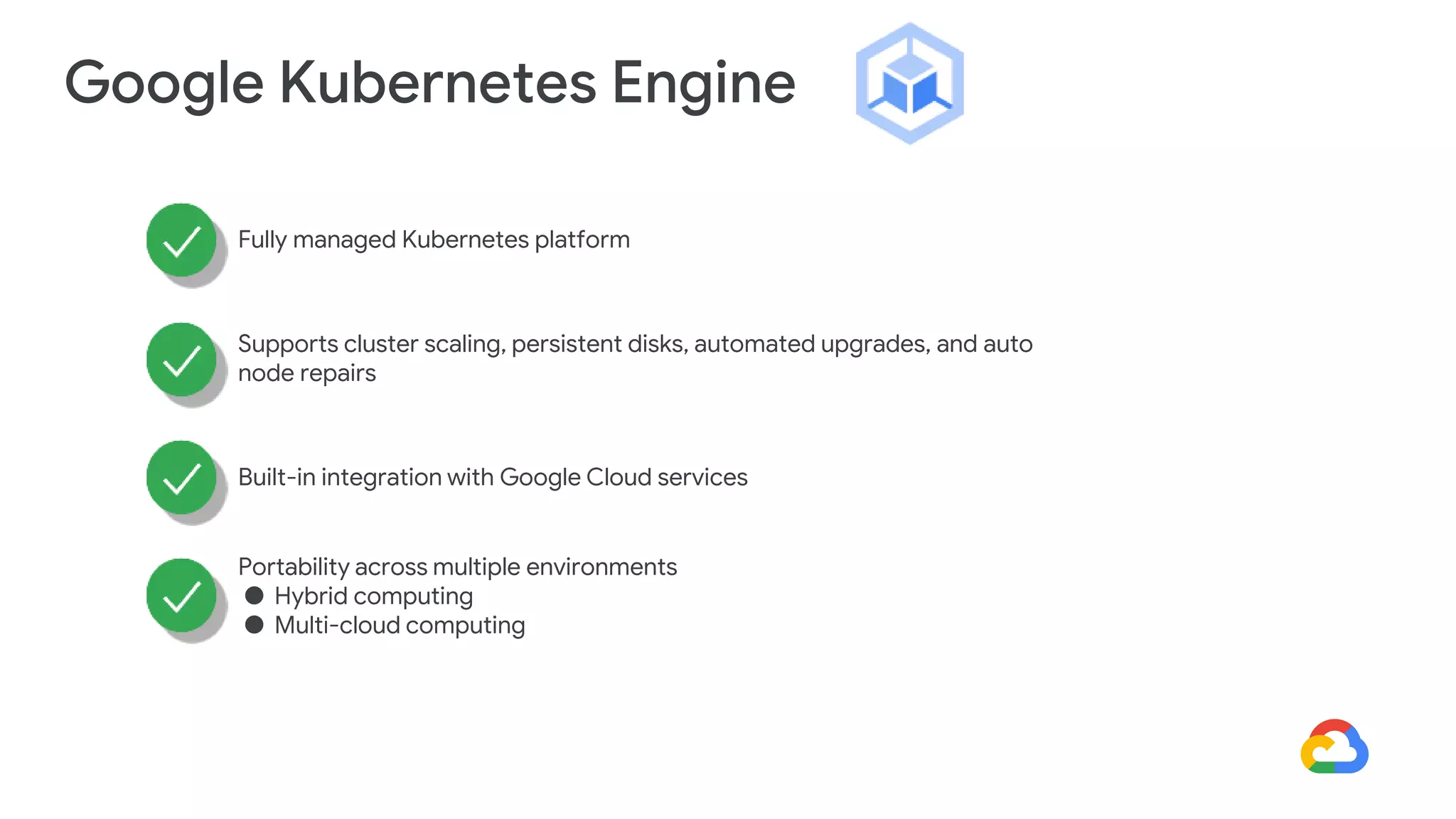
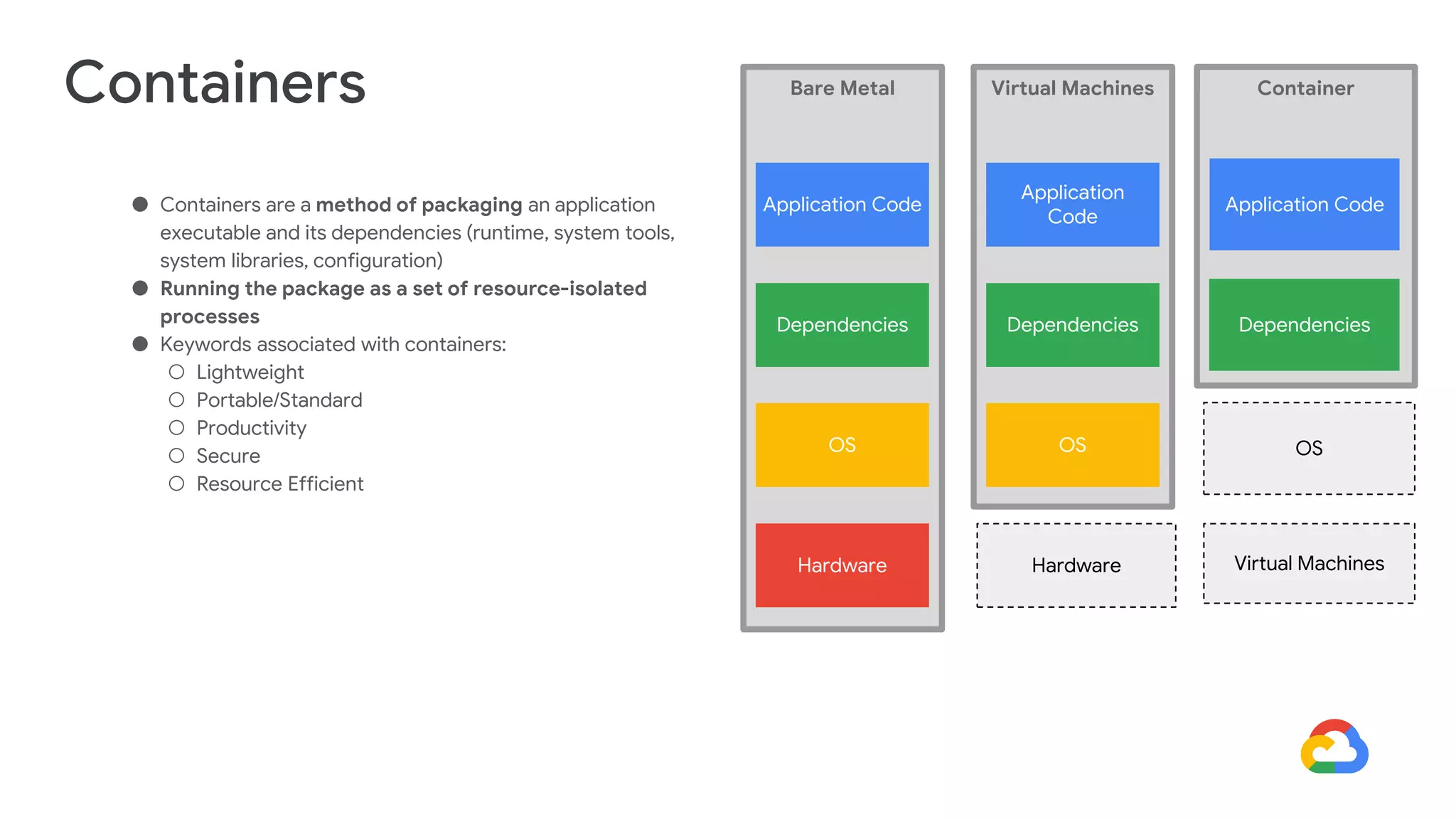
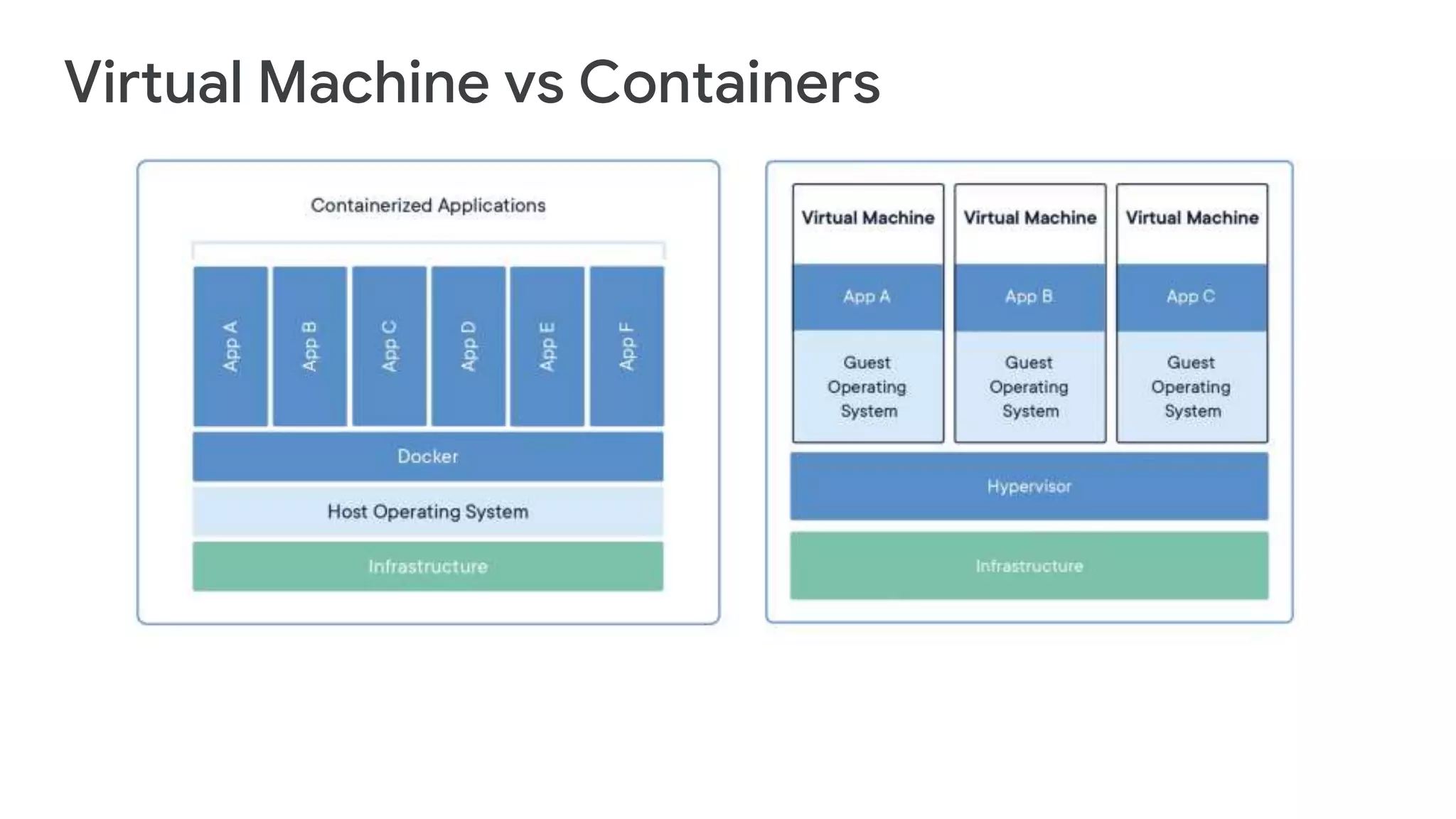
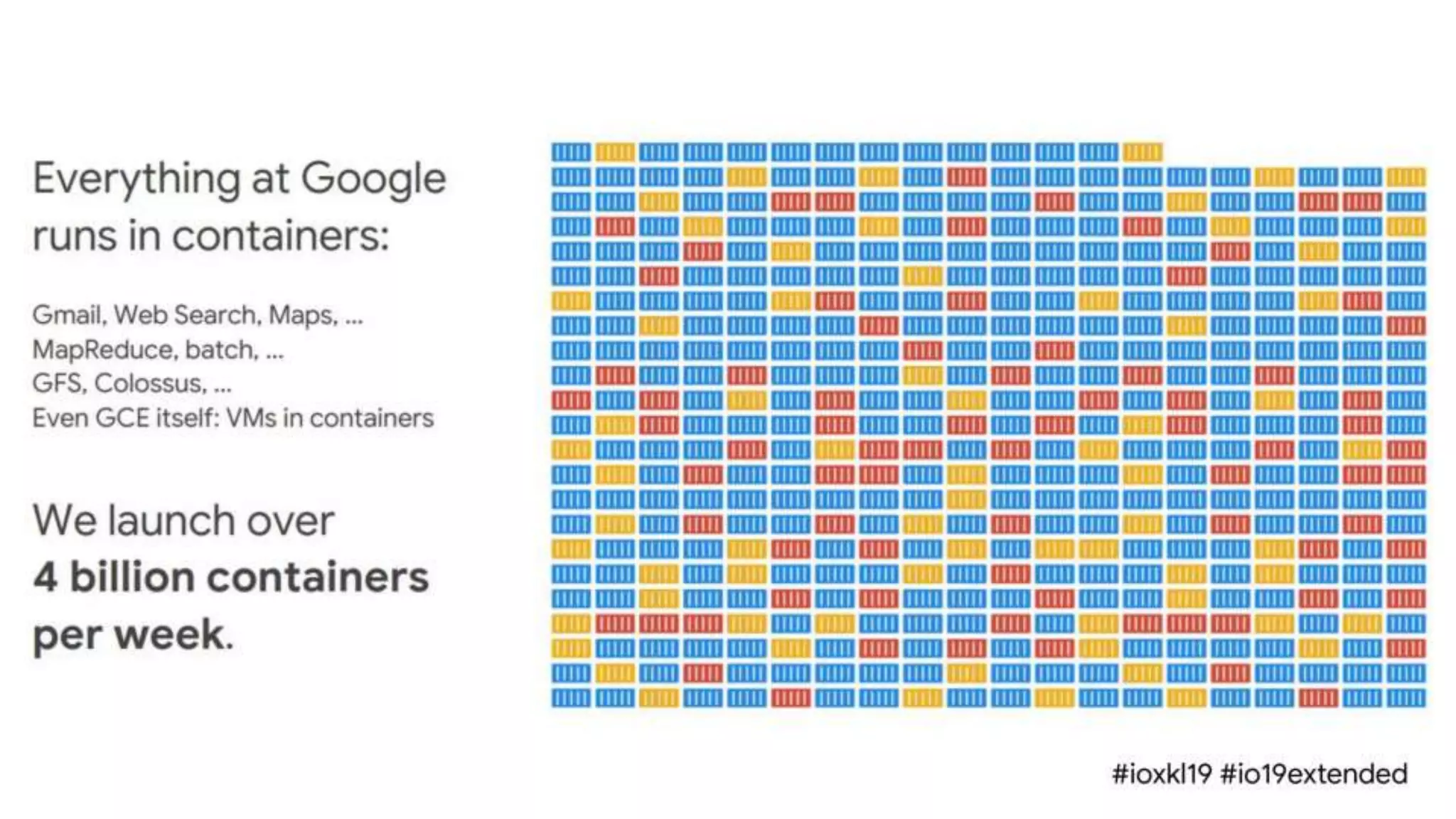
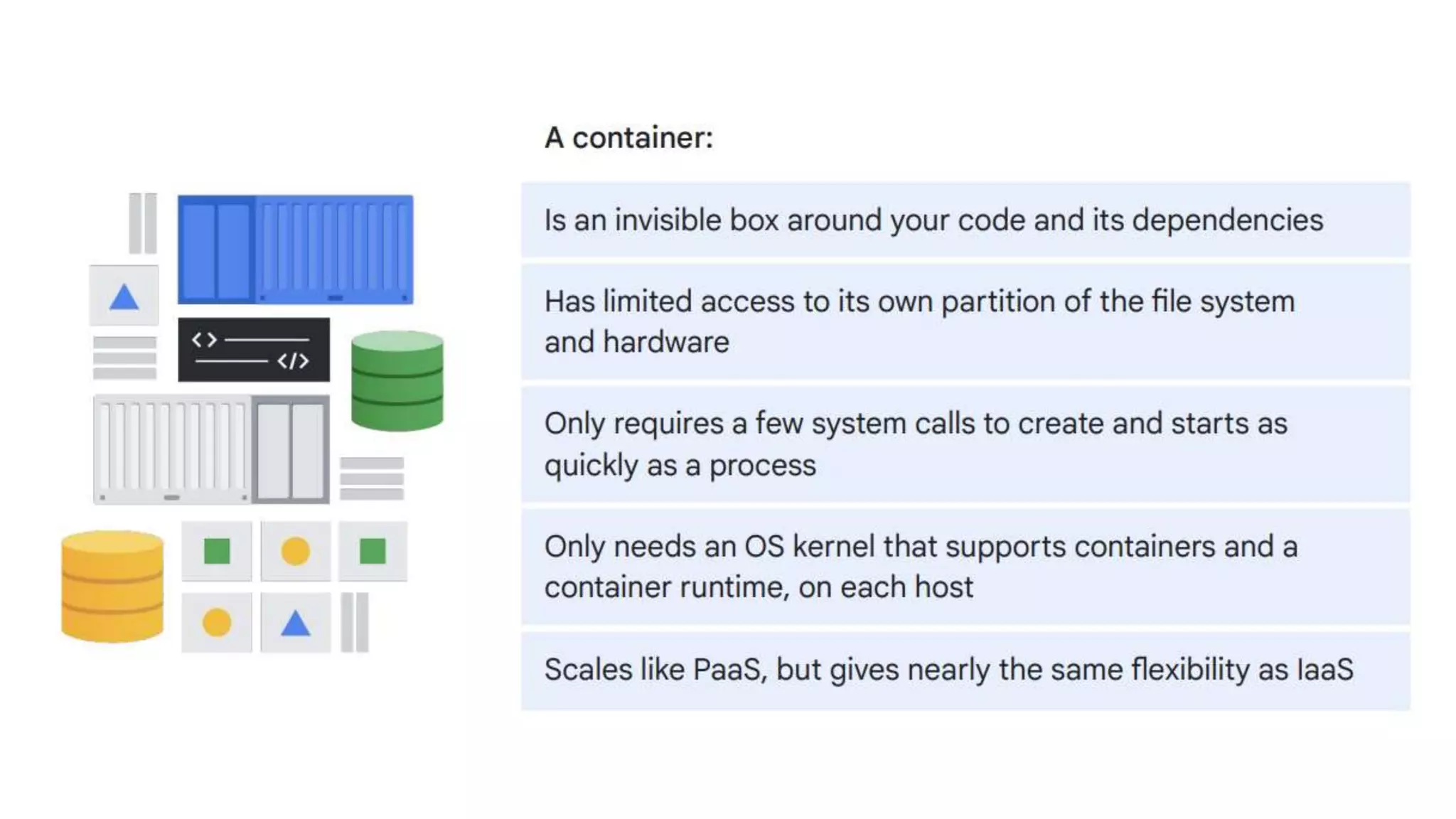
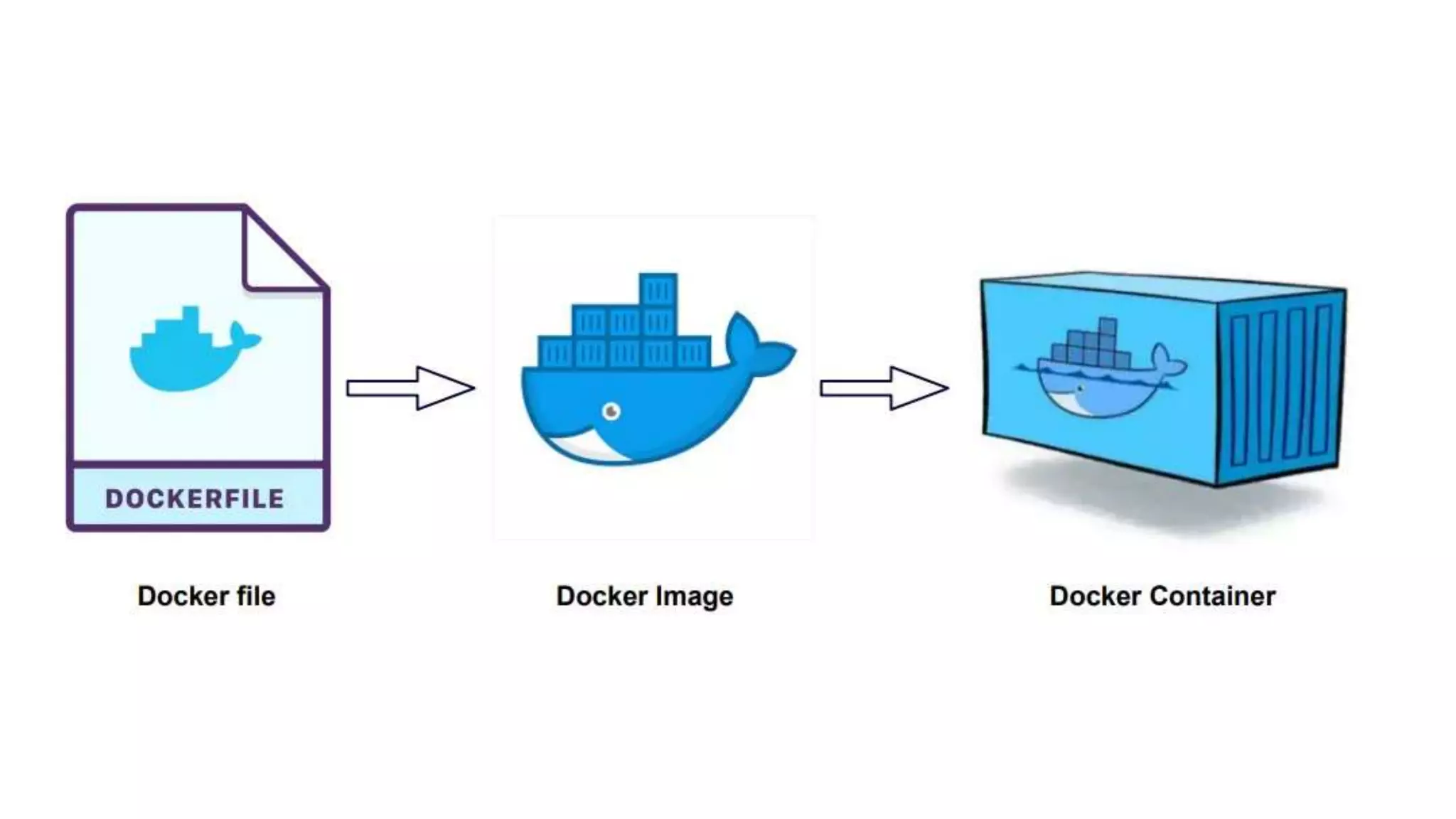
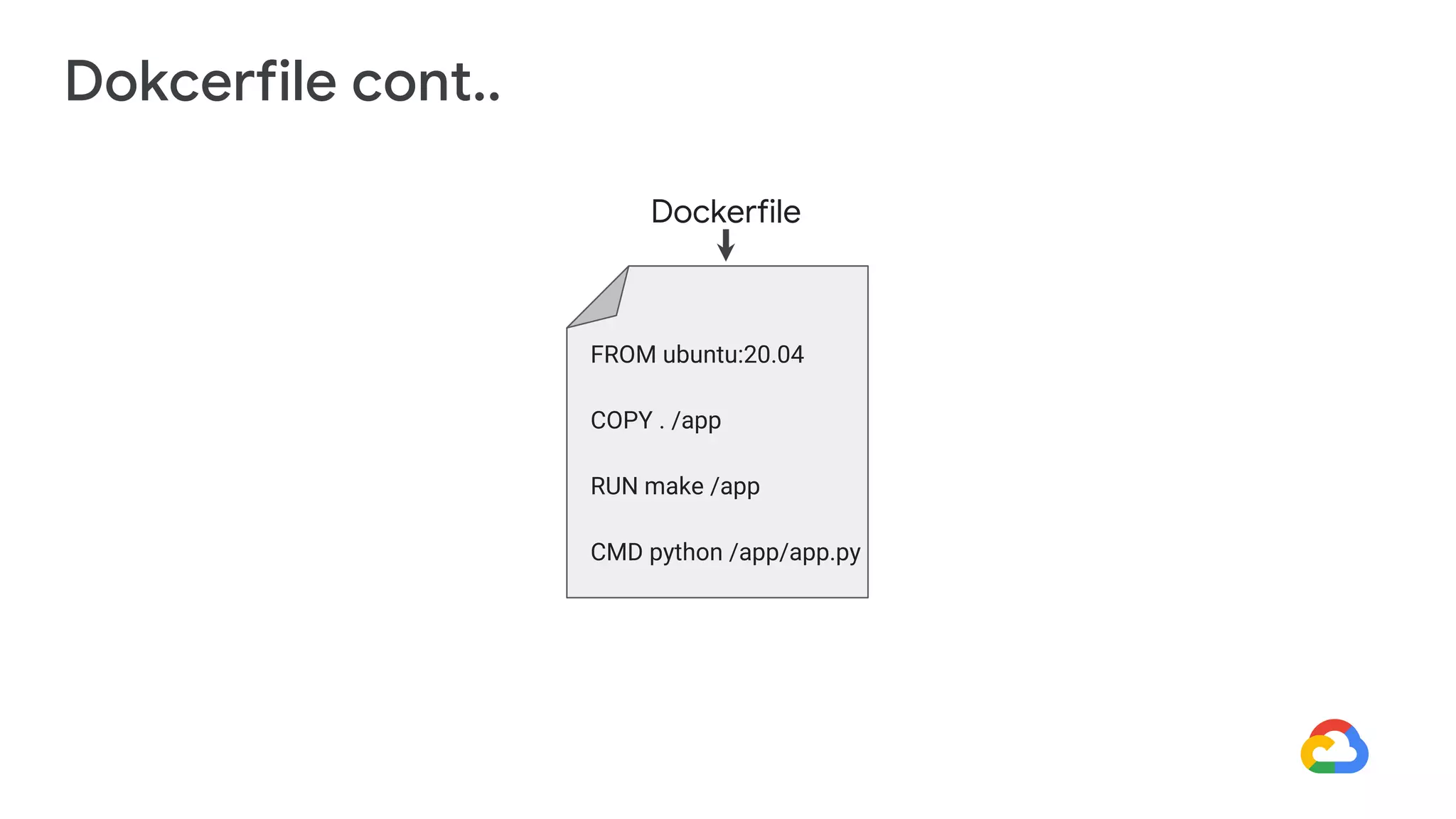
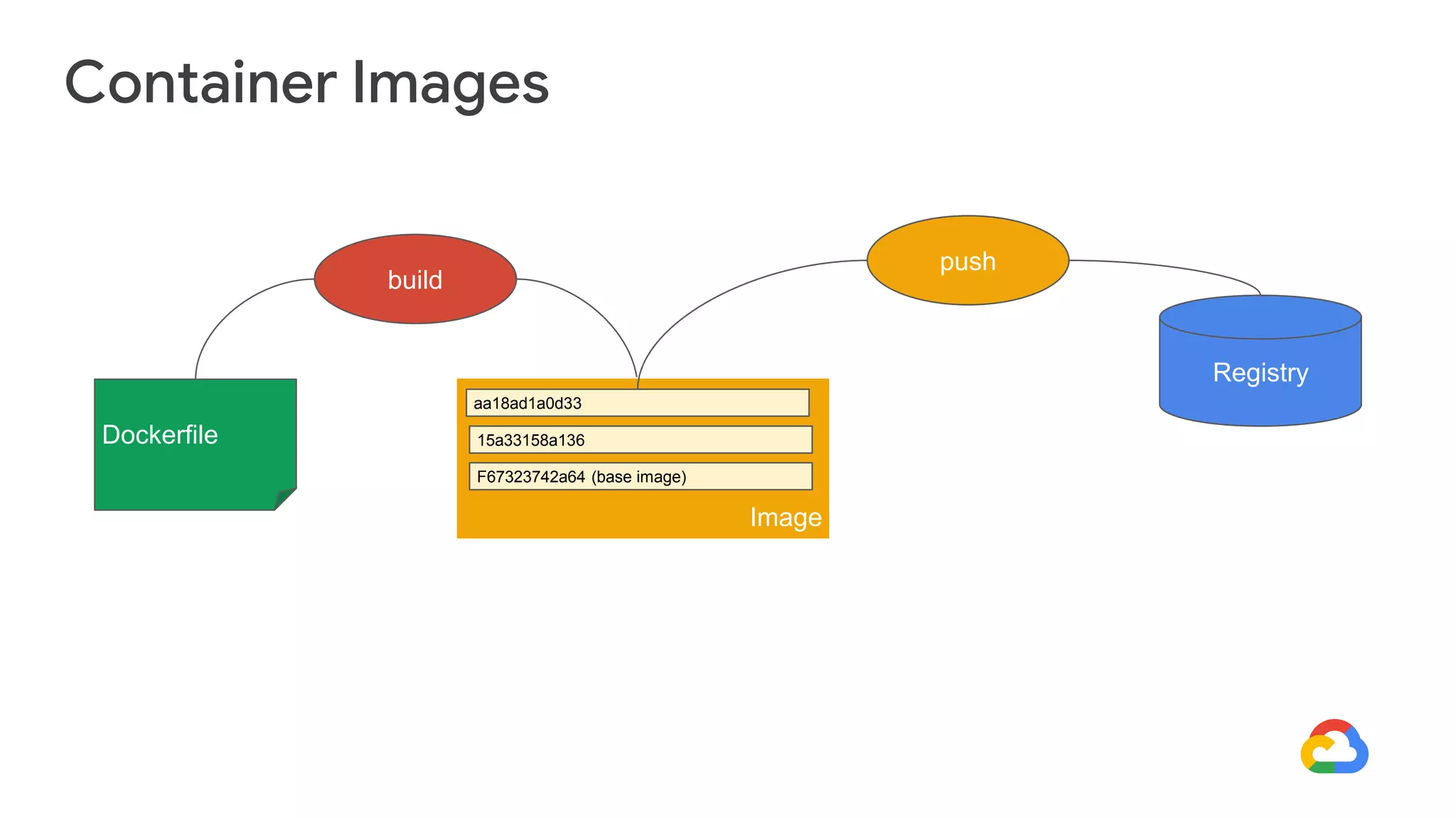
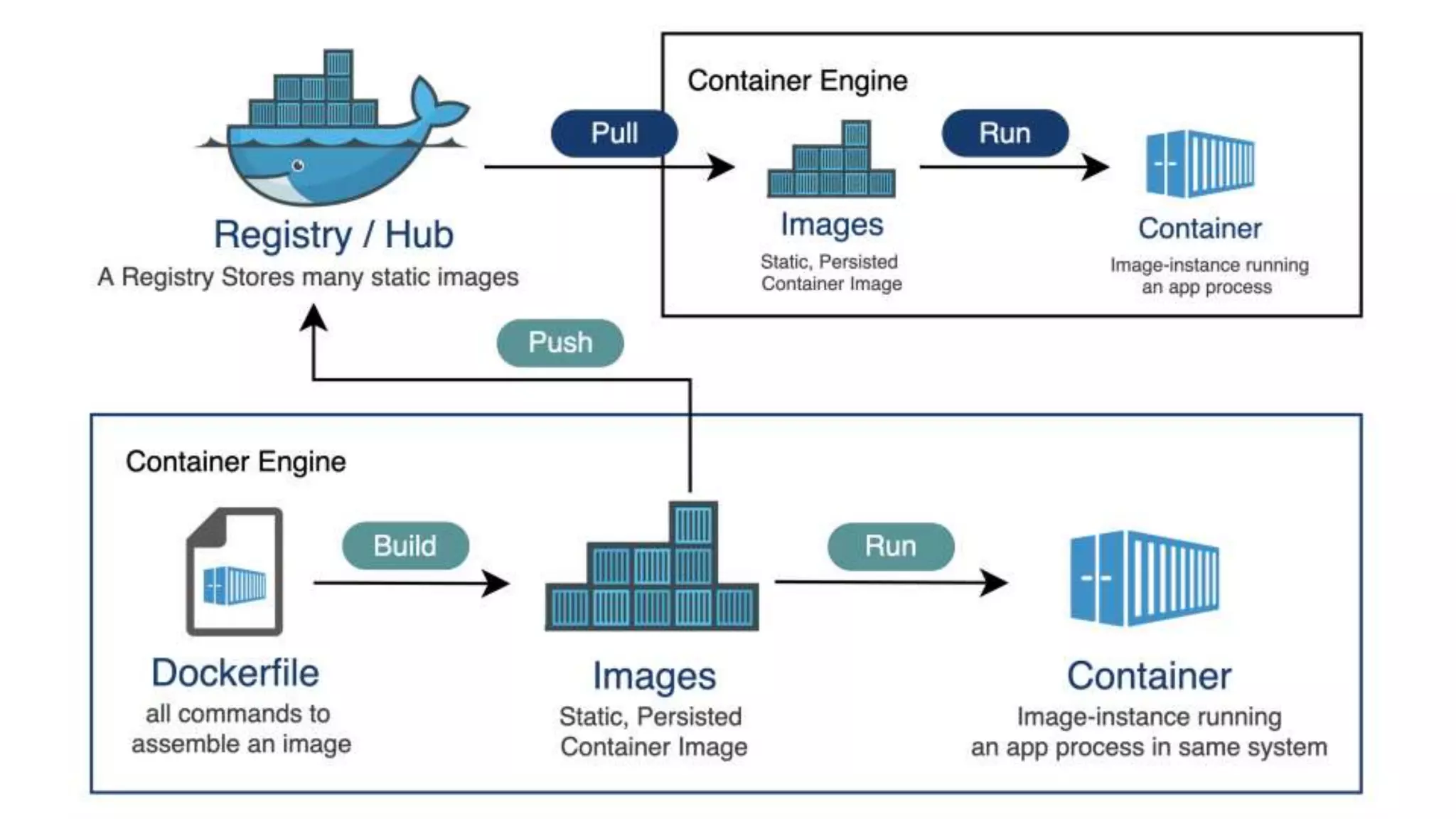
Cloud Run allows running stateless containers on Google Cloud Platform. It provides a serverless platform that automatically scales containers up and down based on traffic. Some key uses of Cloud Run include building applications using any programming languages or frameworks and deploying containers that listen for HTTP requests or events. The document then discusses comparing other Google Cloud computing solutions like Compute Engine, App Engine, Kubernetes Engine. It also covers the differences between virtual machines and containers, the components of Docker including Dockerfile, images, registries and containers.