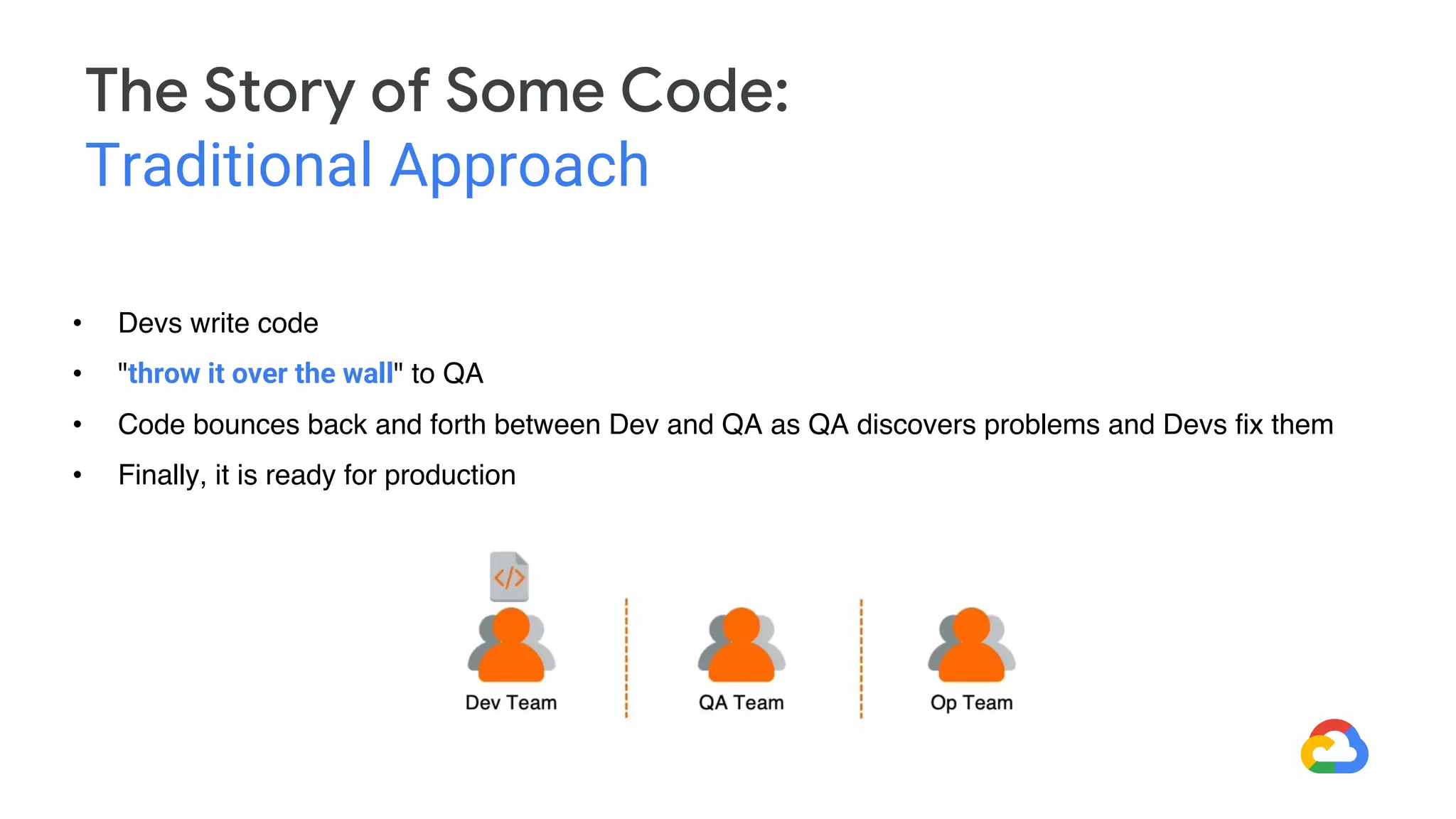
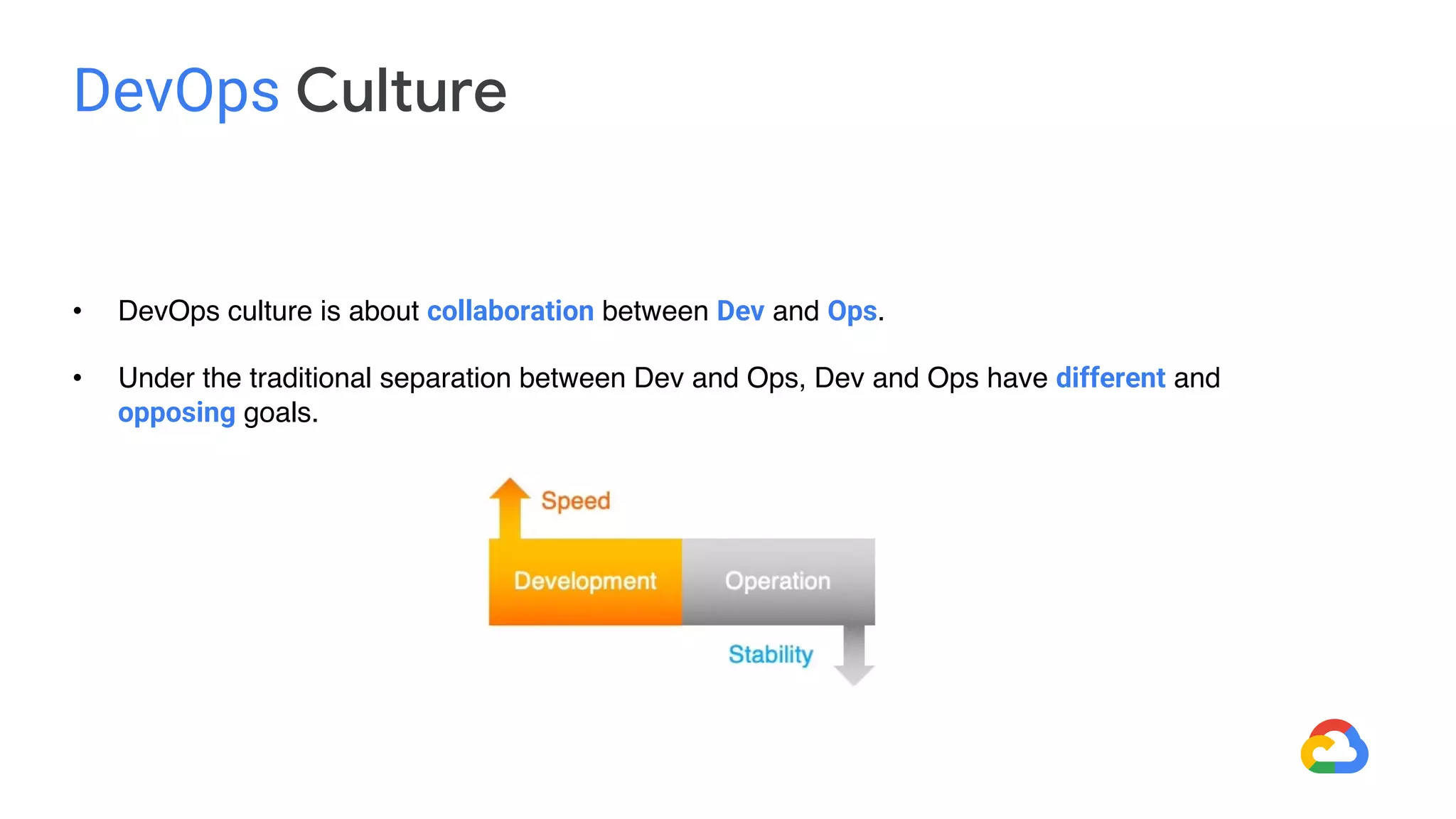
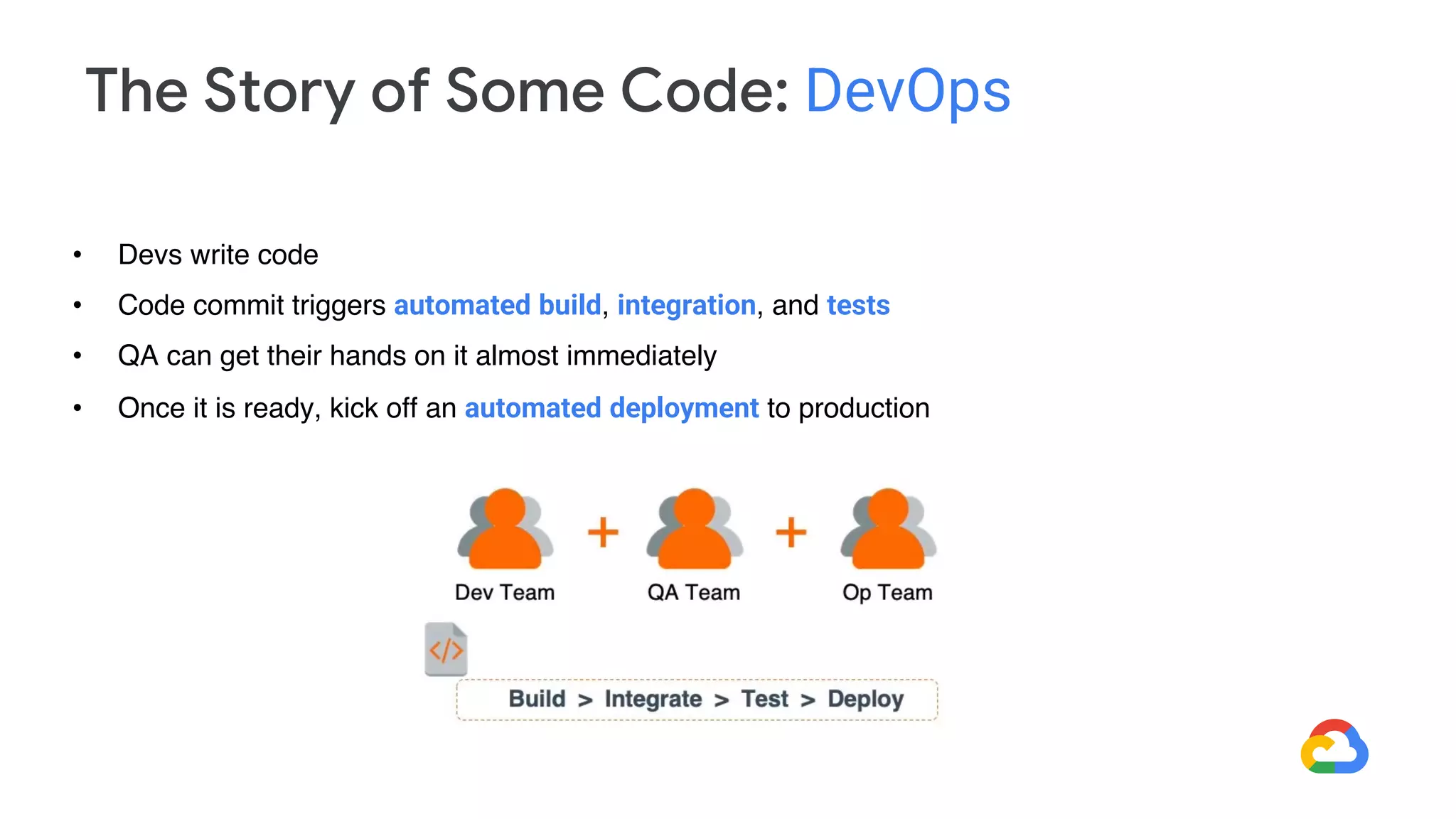
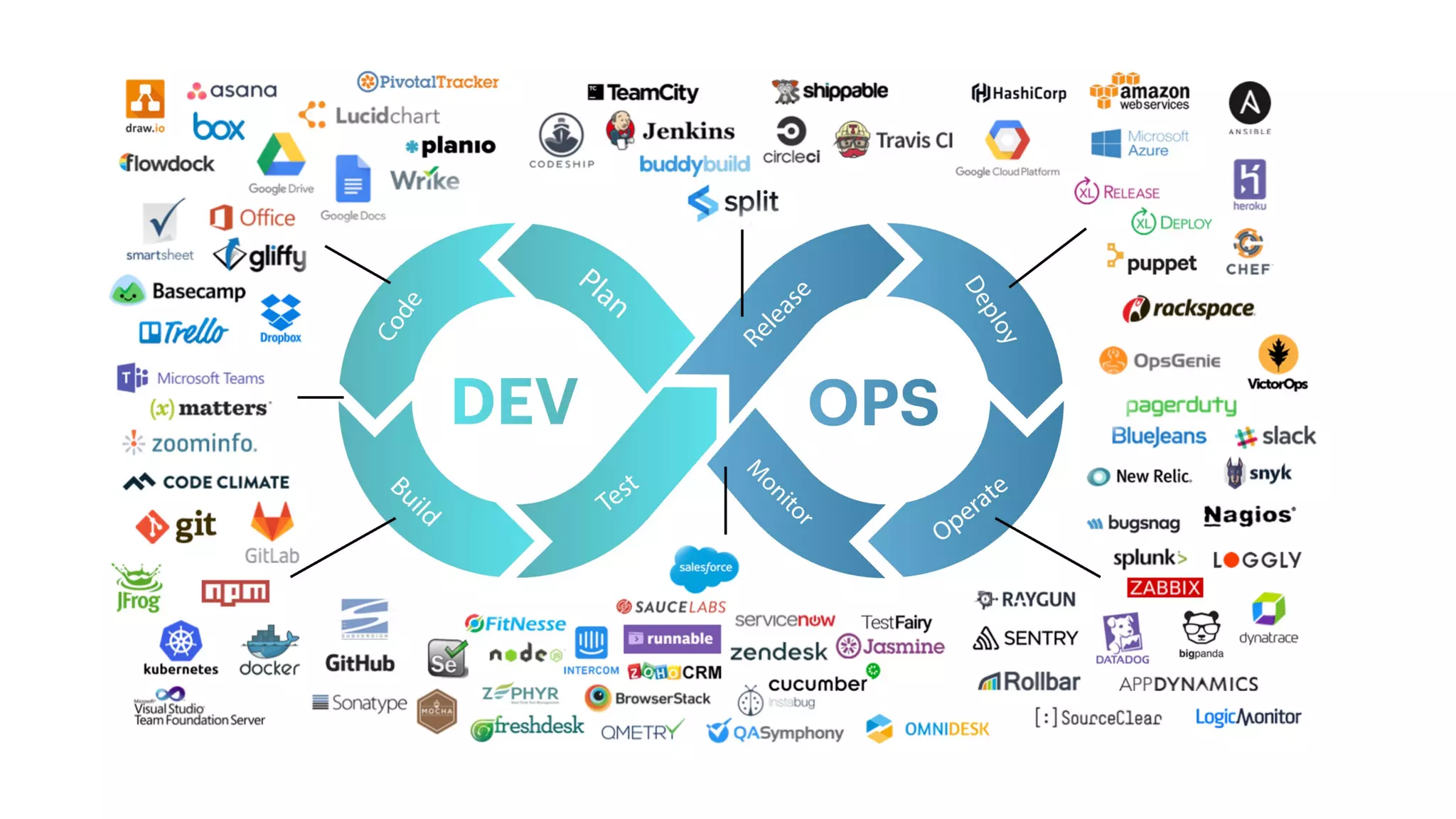
DevOps aims to break down silos between development and operations teams through collaboration and automation. It combines cultural philosophies and tools to help organizations rapidly deliver high quality software. Under the traditional approach, dev and ops teams worked separately with different priorities, leading to slow delivery and finger pointing when problems arose. DevOps establishes a shared culture and goals between the teams through practices like continuous integration, automated testing, and deployment pipelines. While DevOps has no single tool, many tools have emerged to support its goals, such as configuration management, containers, orchestration, and monitoring tools.