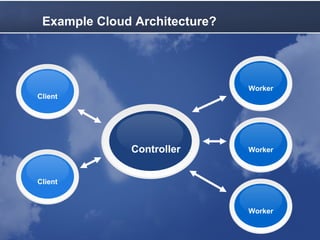
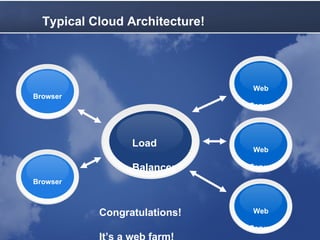
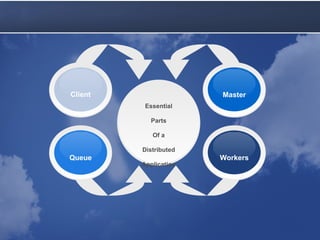
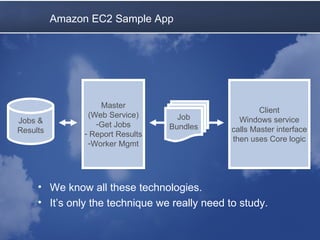
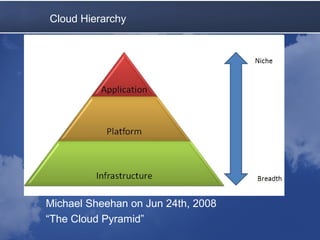
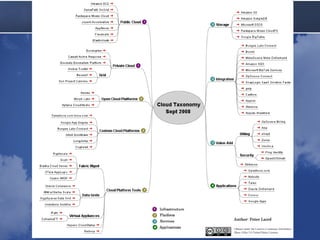
Cloud computing allows accessing computing resources on demand. It provides an architecture that offers flexibility and scalability. A typical cloud architecture has clients, controllers, and workers. An example application uses a master web service to distribute jobs to workers running on local and Amazon EC2 computers. The application demonstrates how existing technologies can be combined in the cloud. Benefits include varying resources, easy configuration, and pay-as-you-grow pricing. Latency must be considered, as queues and multiple servers can improve average response time.