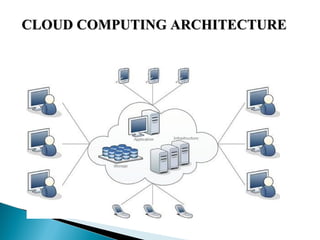
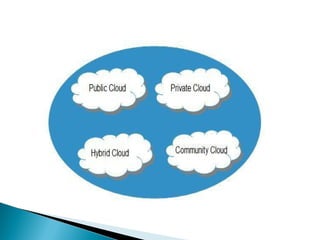
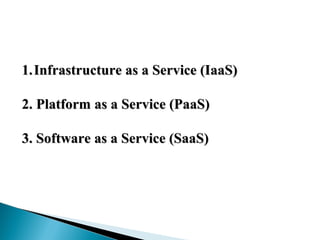
This document provides an introduction to cloud computing, including definitions of cloud, cloud computing, and cloud computing architecture. It describes the basic concepts of deployment models (public, private, hybrid, and community clouds) and service models (IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS). Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides access to computing infrastructure resources, Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides development and deployment platforms, and Software as a Service (SaaS) provides access to software applications. The document notes advantages of cloud computing like lower costs and improved performance, as well as disadvantages like requiring internet access and potential security and performance issues.