The document discusses cloud computing trends across several African countries based on a study conducted by Research ICT Africa.
Key findings include:
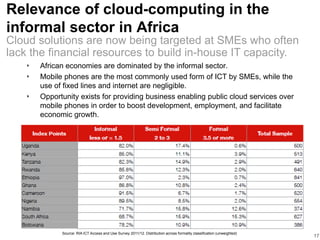
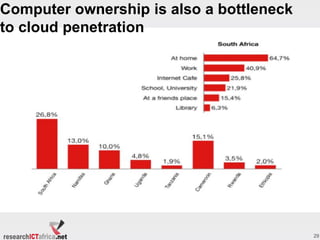
- Cloud computing is in early stages across Africa, with more developed markets in South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya. Infrastructure bottlenecks around broadband access remain a challenge.
- Global cloud providers have a presence but local African firms are also active as aggregators and integrators helping bring cloud services to domestic customers.
- Countries like Ethiopia, Ghana, and Nigeria have begun exploring cloud solutions to deliver e-government services more effectively.
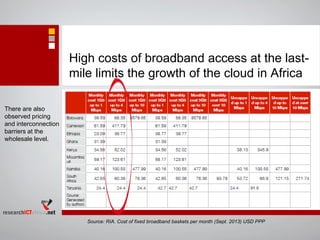
- Growing broadband access via undersea cables and mobile networks is helping drive cloud adoption, though high costs and limited rural connectivity still impede




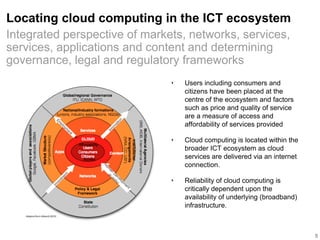
![Distinguishing cloud services & cloud-
based services
‣ ITU (2012) defines cloud services that are provided and utilised ‘on
demand at any time, through any access network, using any
connected devices [that use] cloud computing technologies’
• Cloud services utilise software and applications that are held in the cloud an not on the
users’ own devices (REF). These are used for internal administration by cloud user or for
the management of service delivery to end-users. An example is customer relations
management.
‣ On the other hand cloud based services include mass market
applications such as Facebook, YouTube, etc consisting of user
data that are then posted on the cloud.
‣ With the proliferation of mobile phones, the expansion of mobile
broadband networks and the increased access of the internet via
the mobile phone; the delivery of mobile based cloud services is
becoming important in the African context.
6
It is important to make a distinction between cloud
services and cloud-based services:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloud-20computing-20in-20africa-emerging-20trends-20-26-20perspectives-140505005429-phpapp02/85/Cloud-computing-in-africa-emerging-trends-perspectives-6-320.jpg)