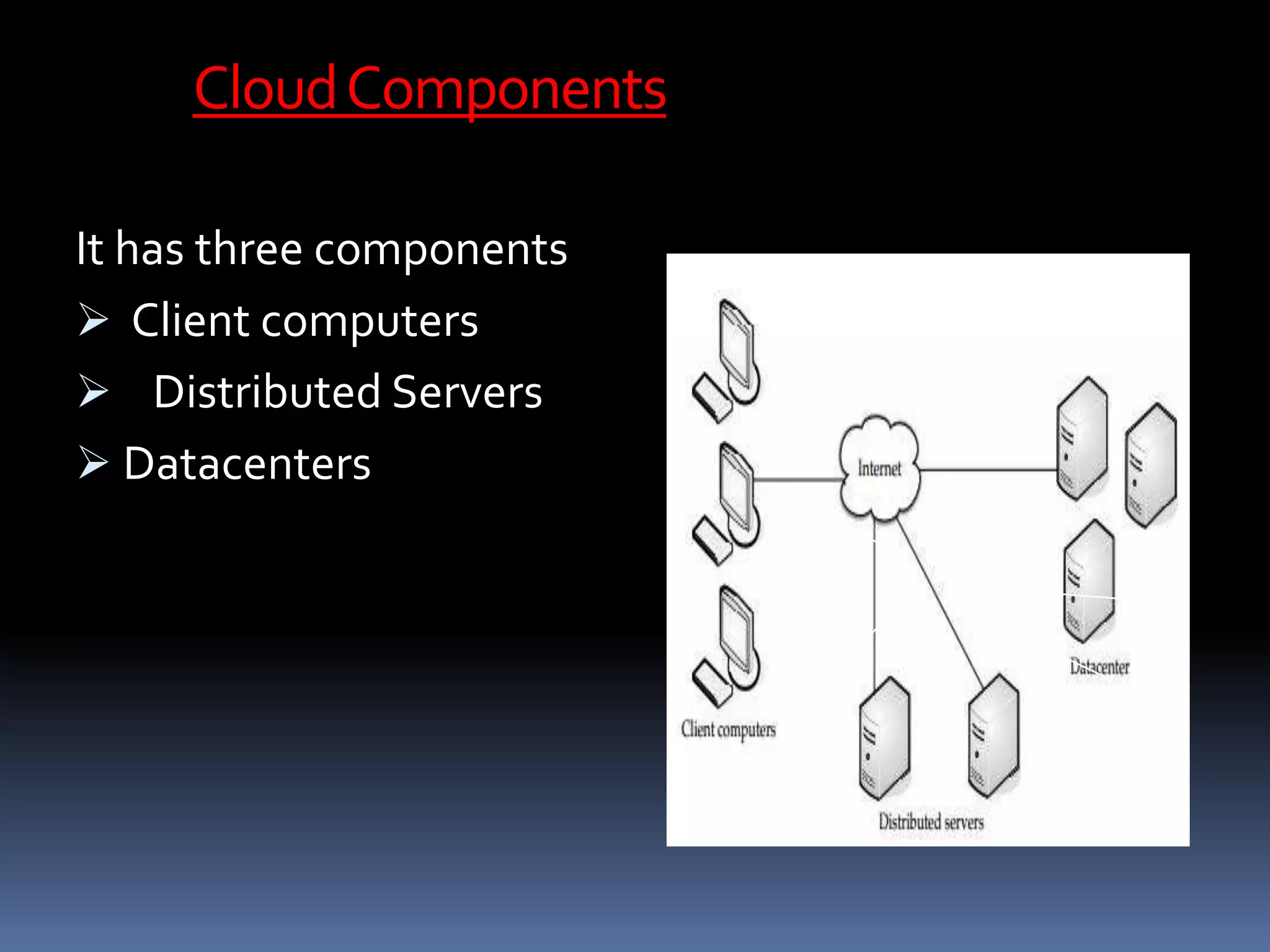
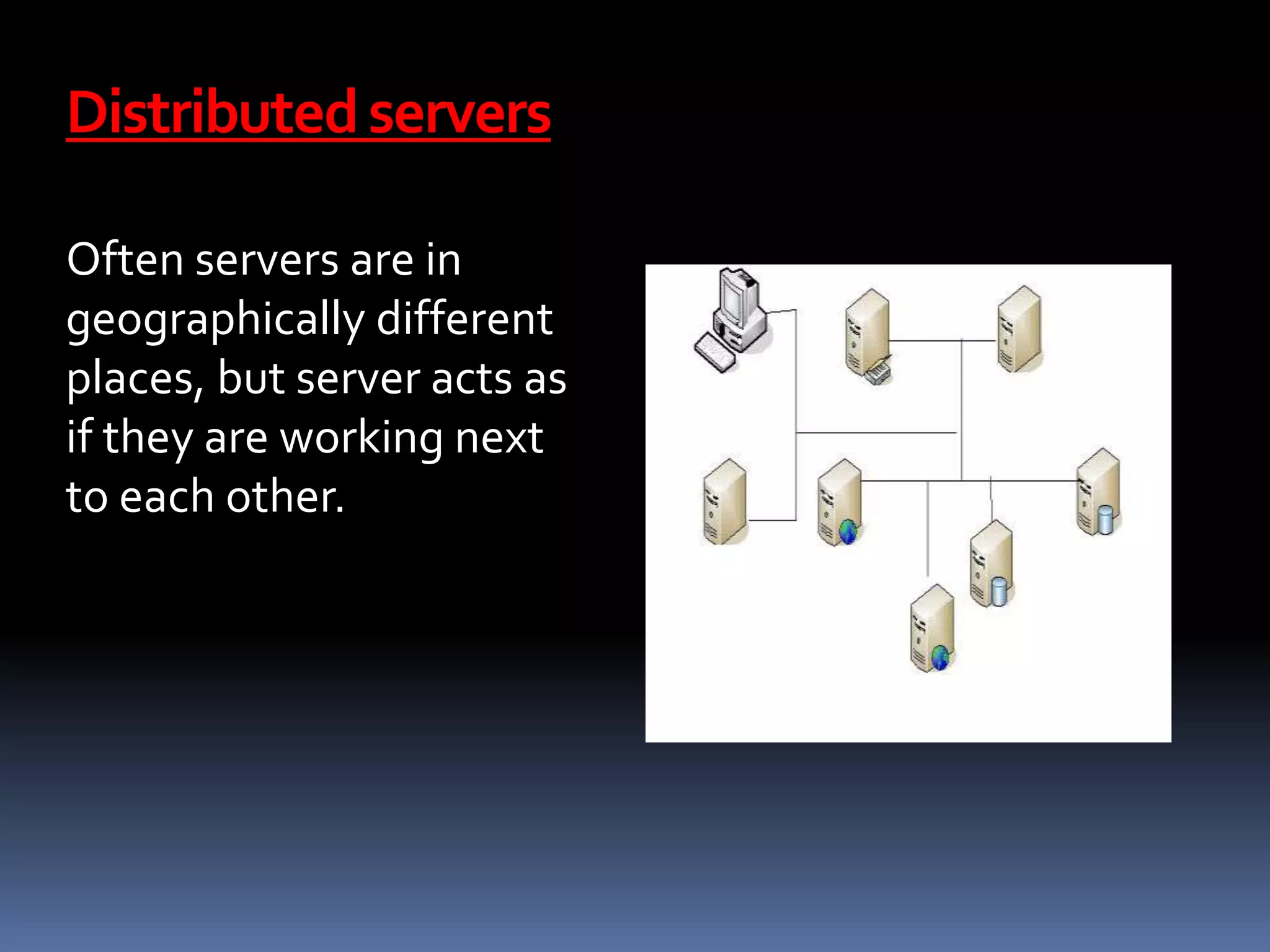
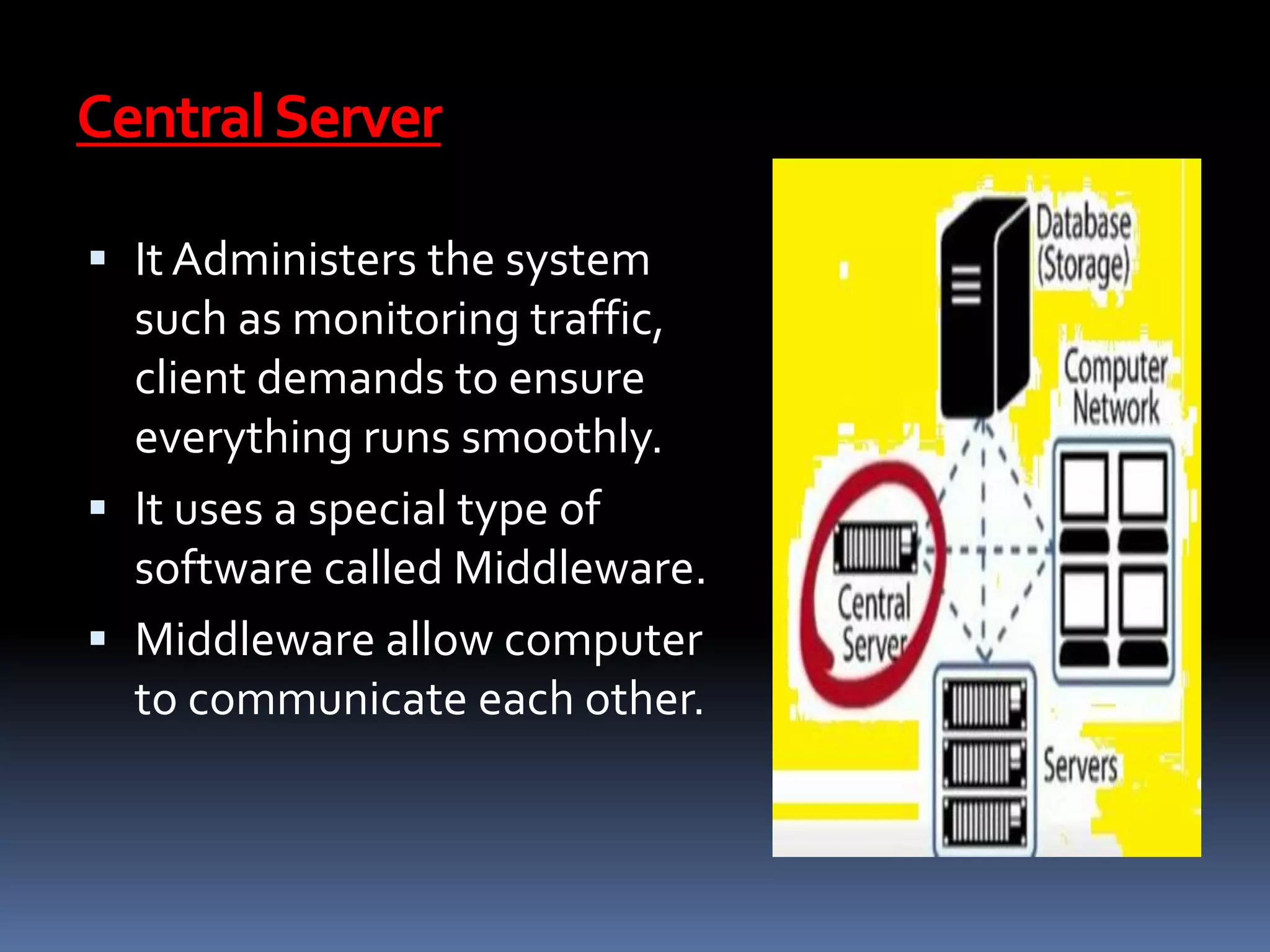
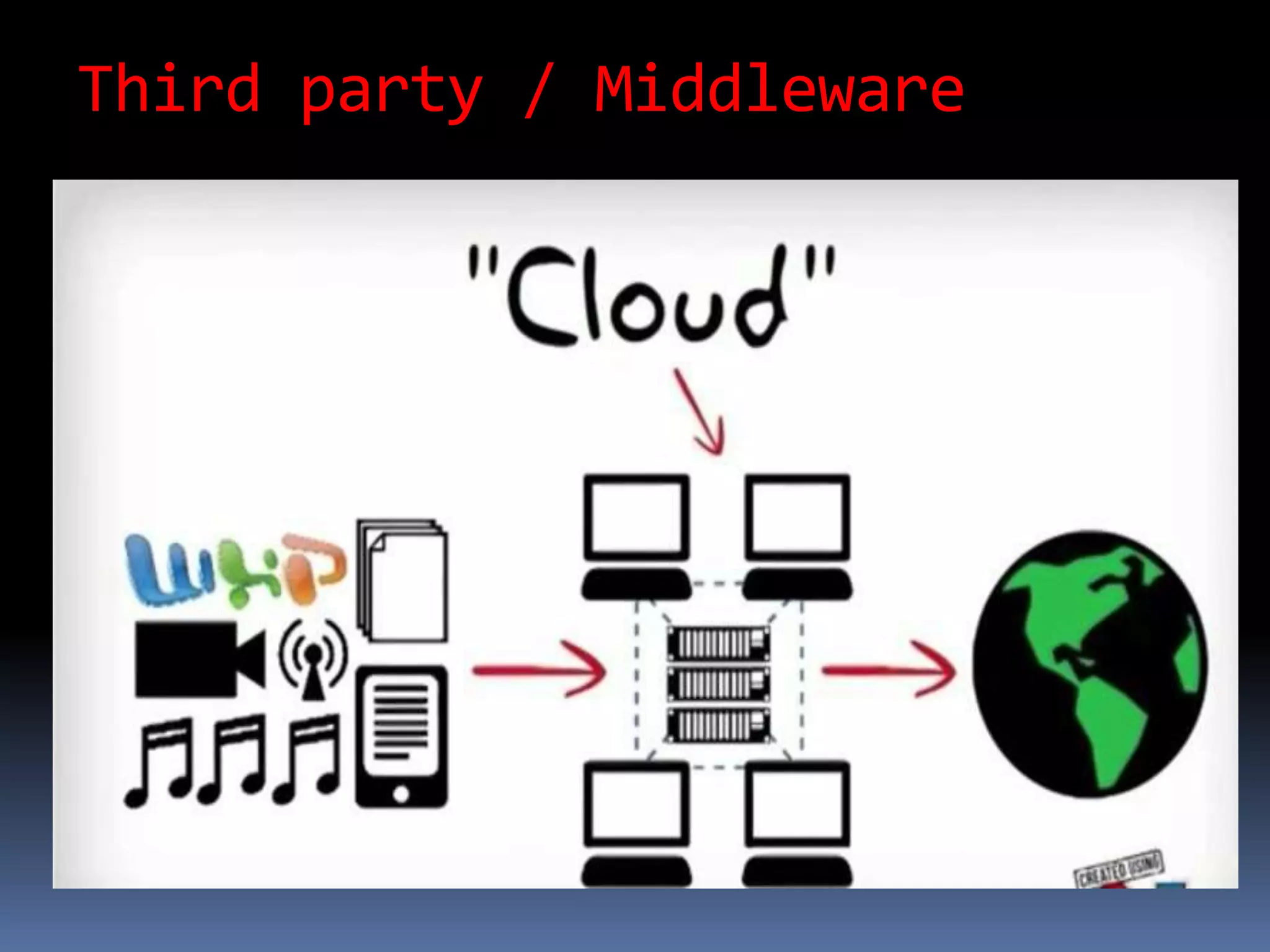
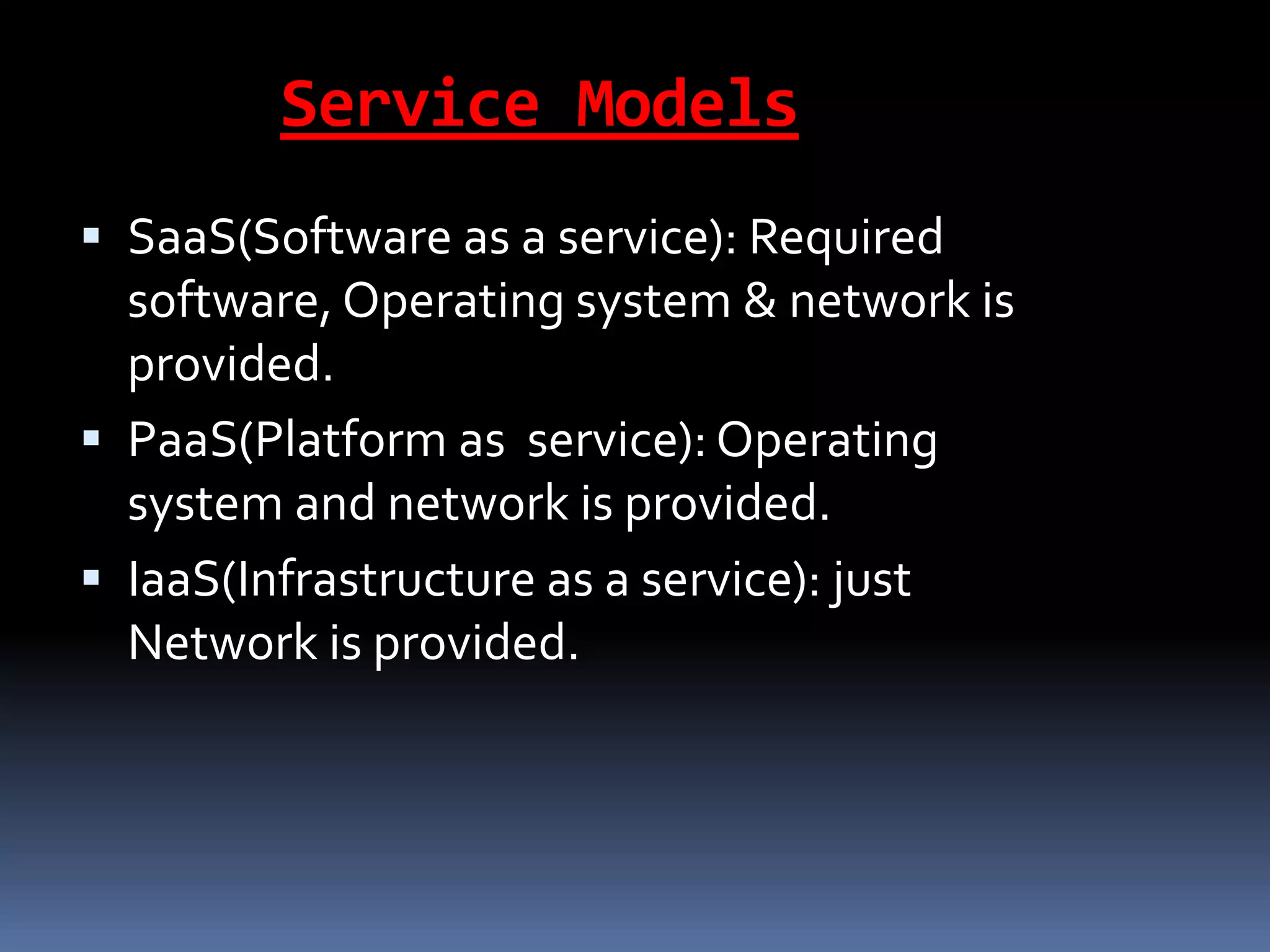
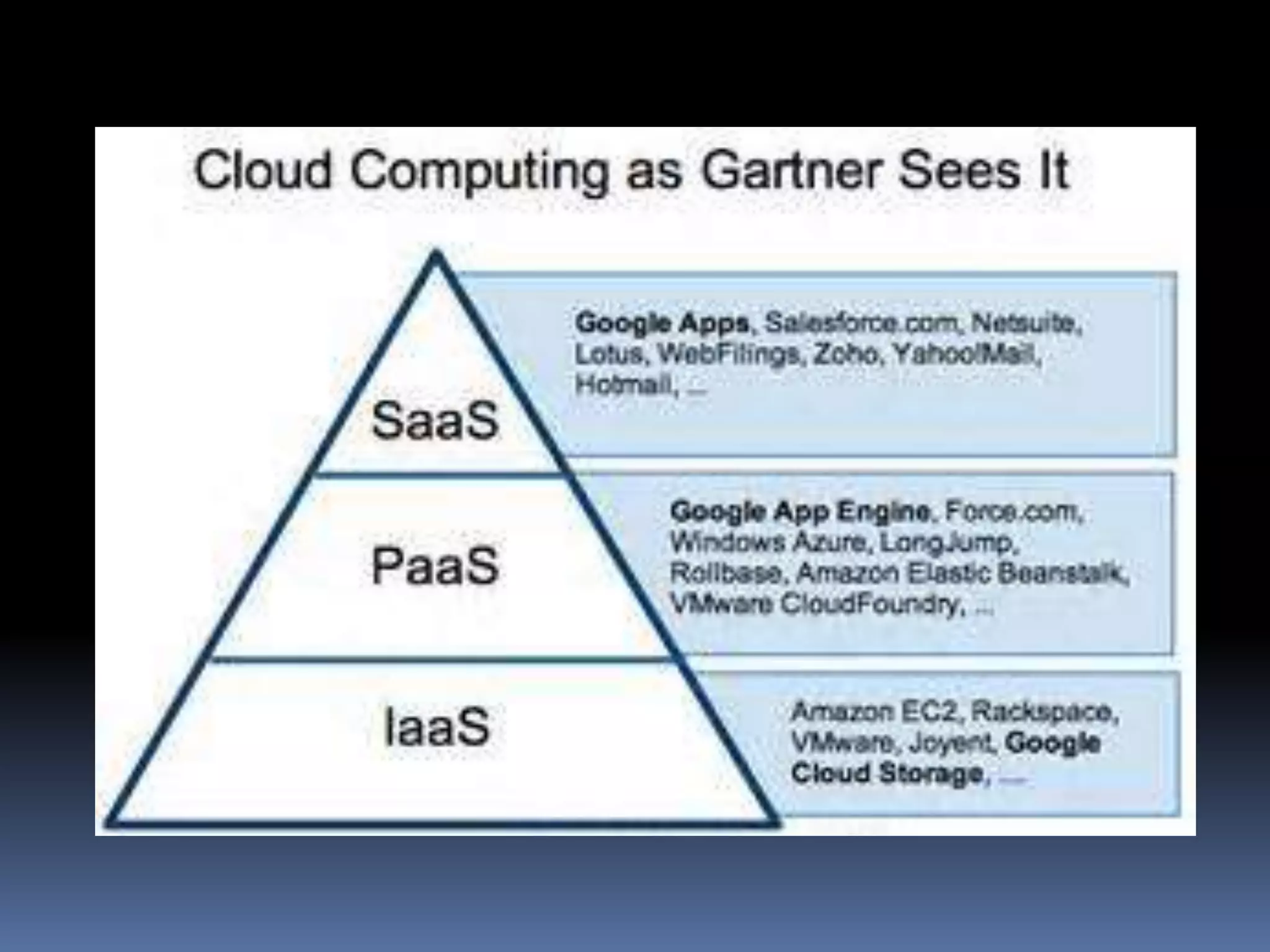
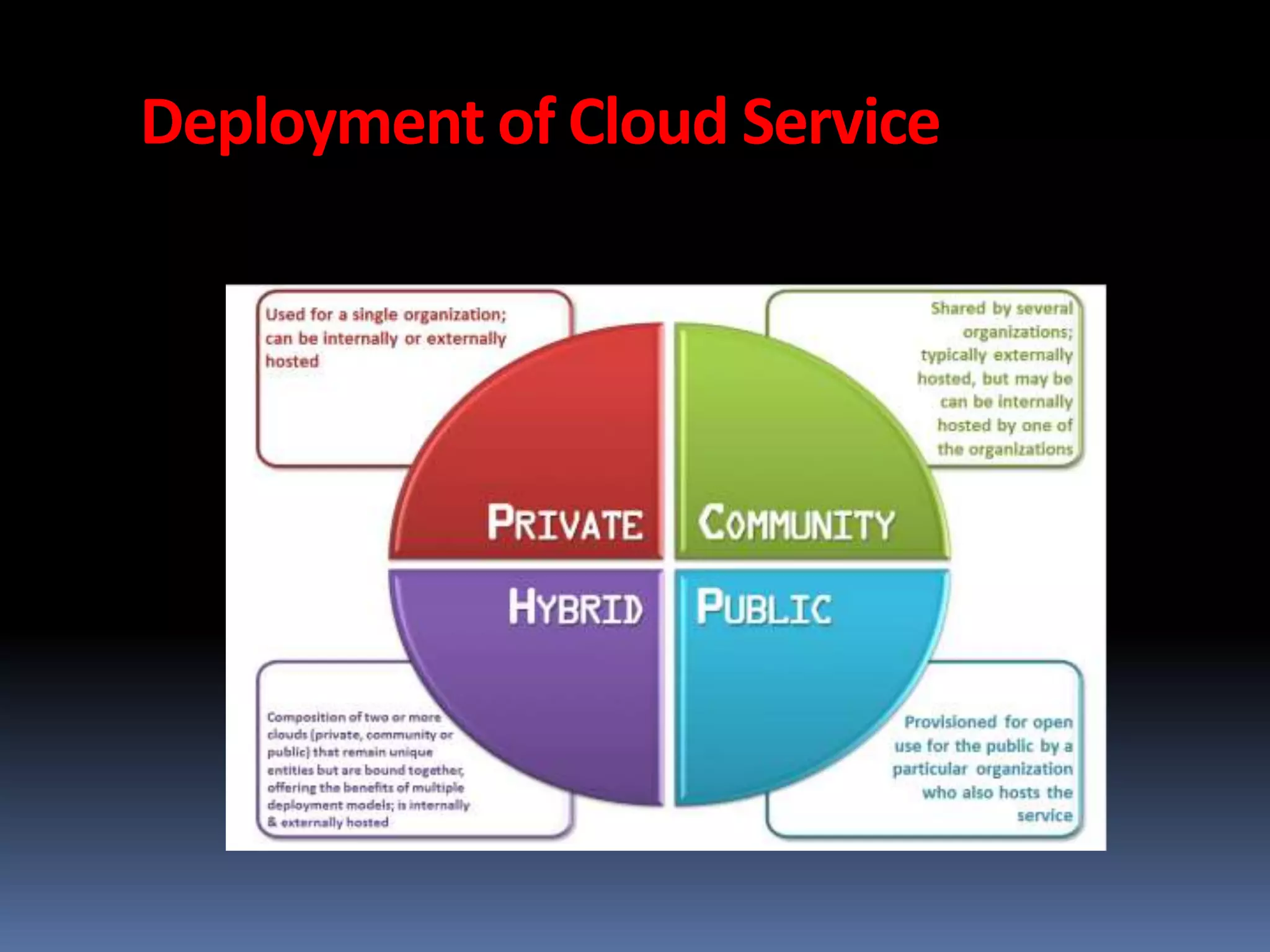
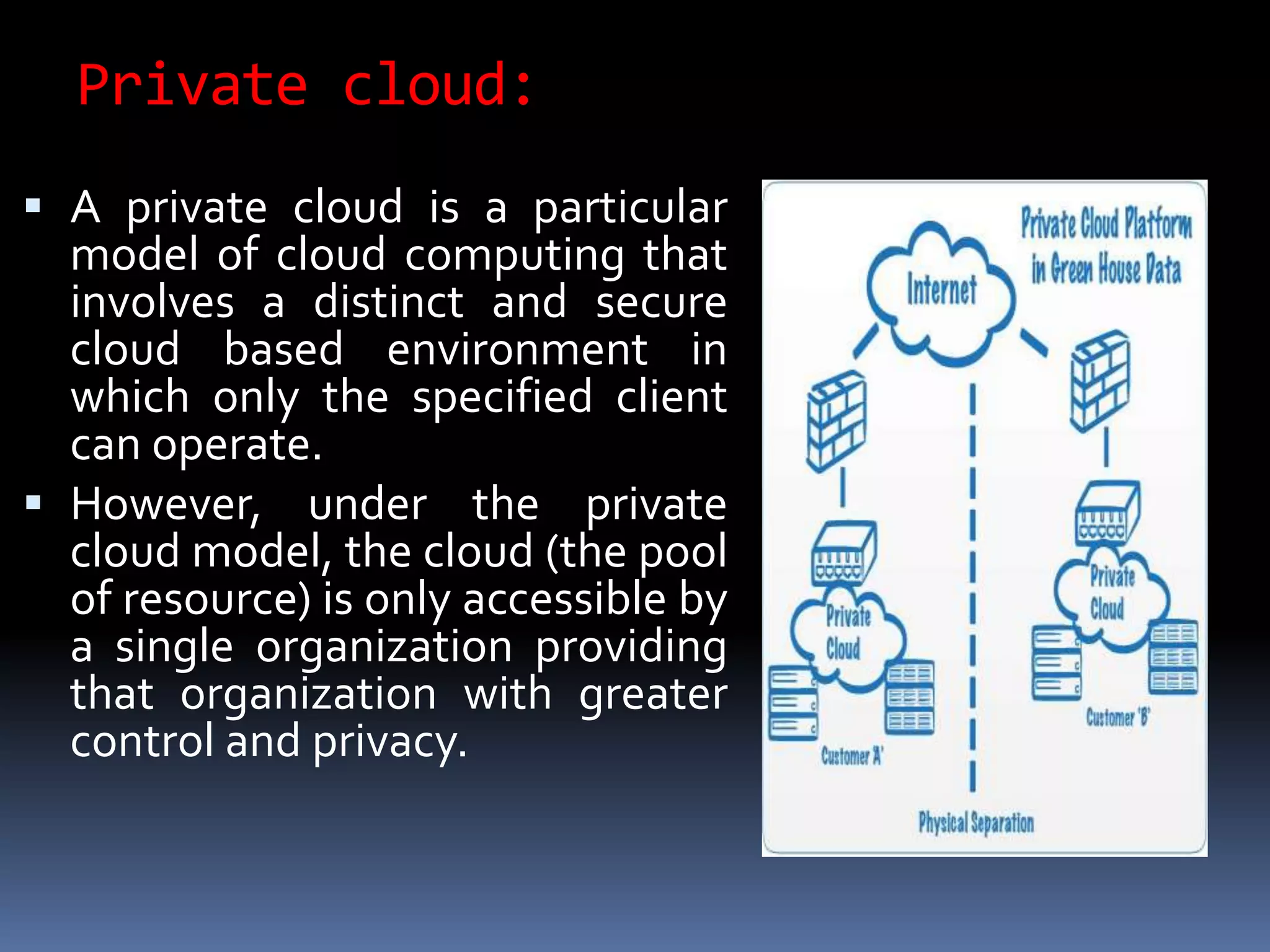
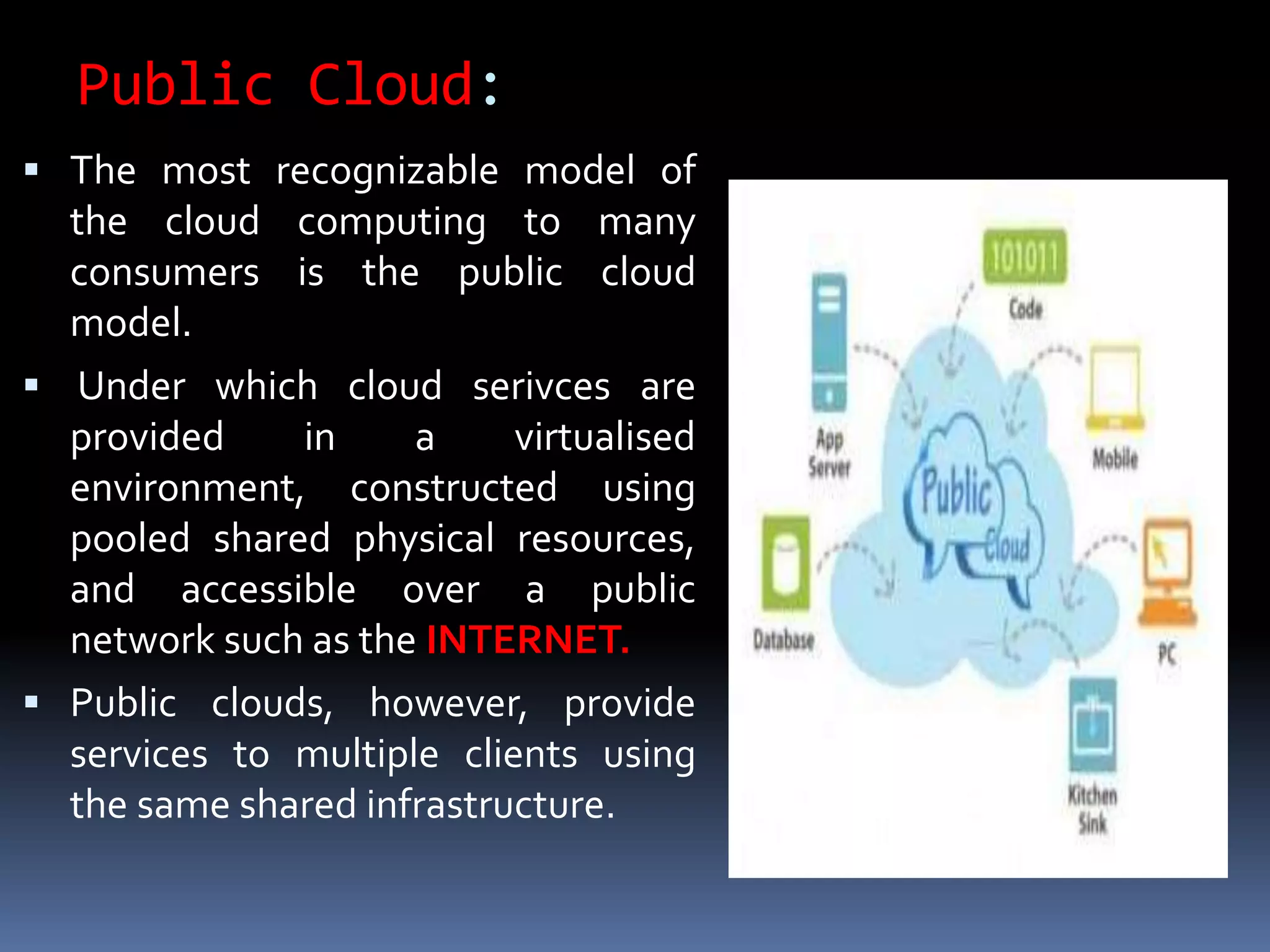
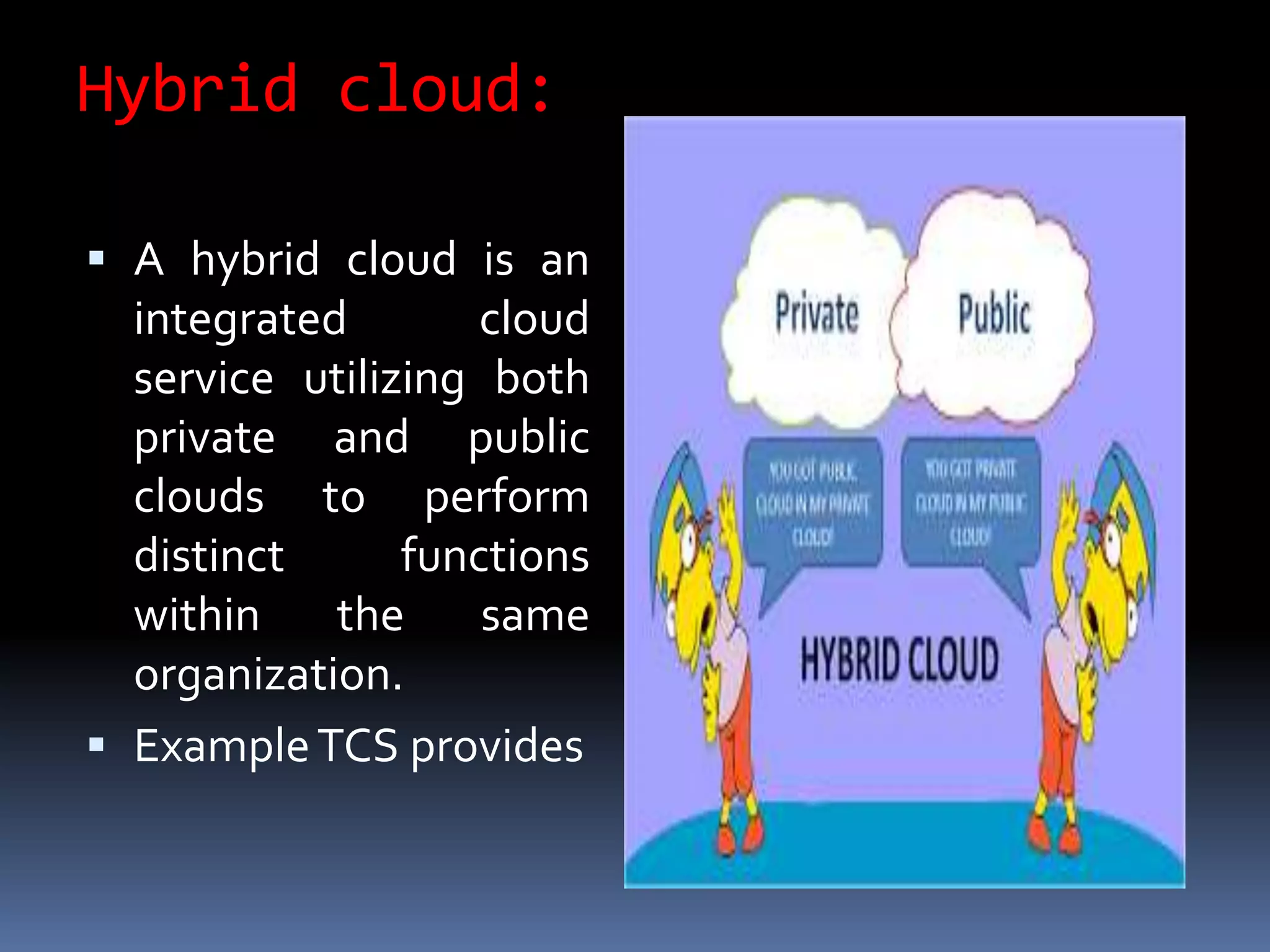
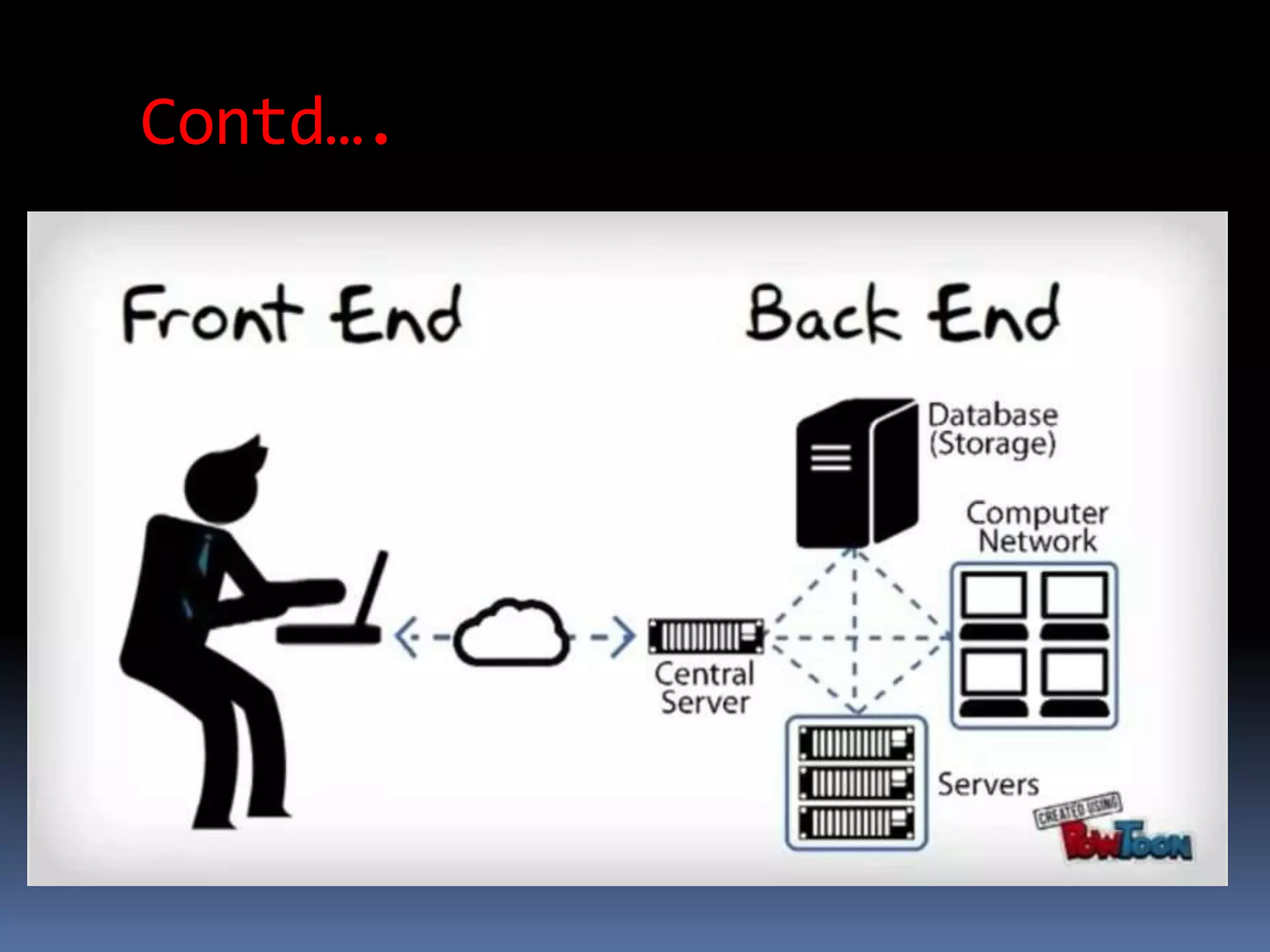
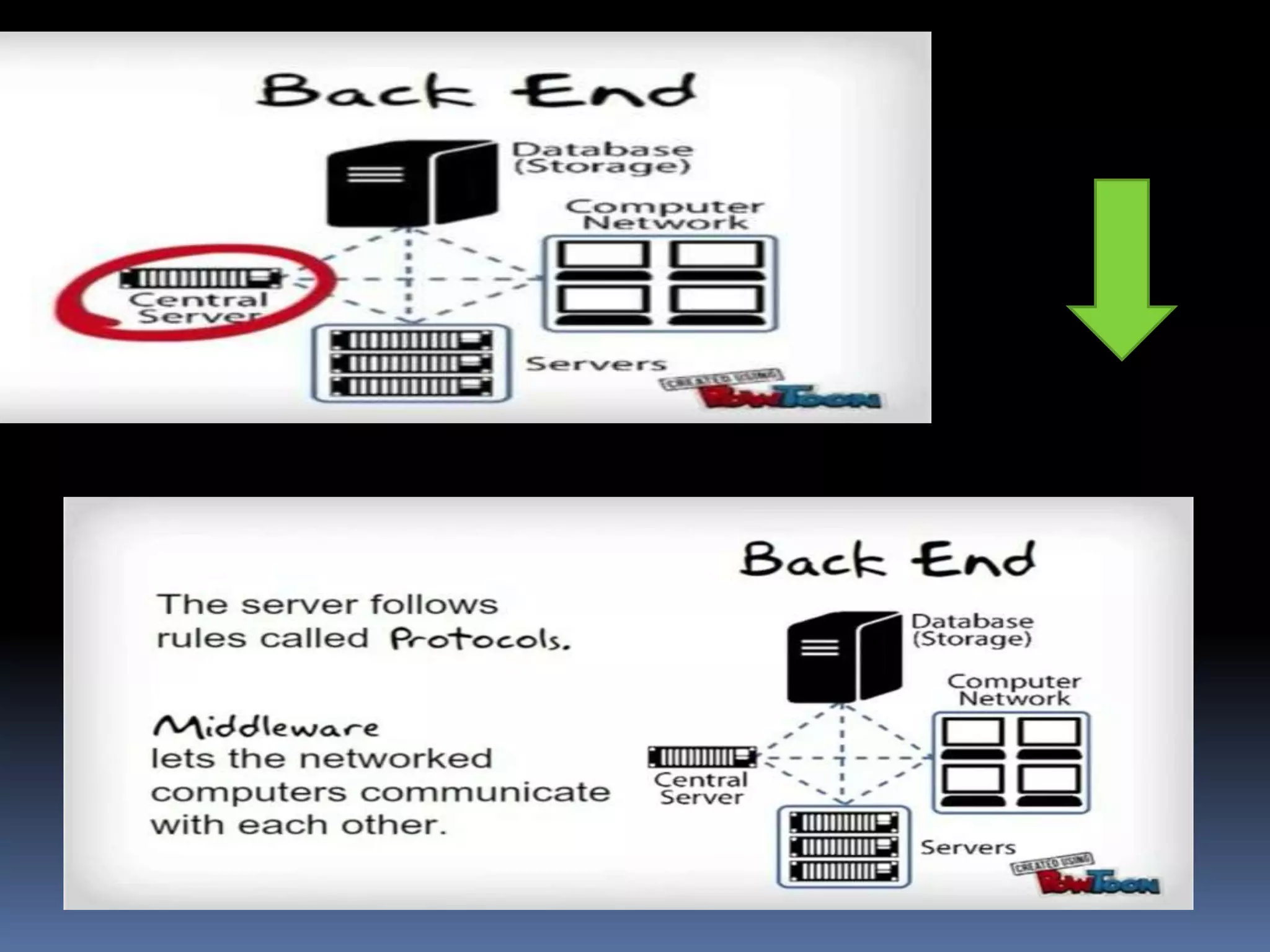
Cloud computing allows users to access applications, files, and data storage over the Internet rather than storing them locally. It provides access to shared computing resources like servers, databases, networks and software on demand. There are different service and deployment models for cloud computing including SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, private cloud, public cloud and hybrid cloud. While cloud computing provides benefits like flexibility, scalability and cost savings, it also poses security, privacy and reliability risks since data and applications are stored remotely on servers.