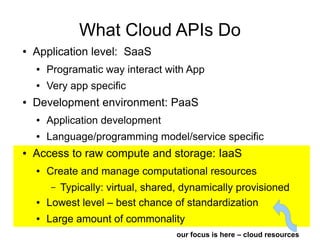
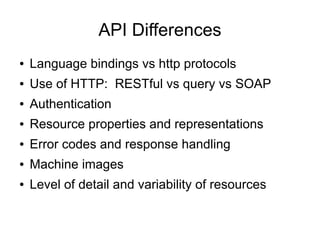
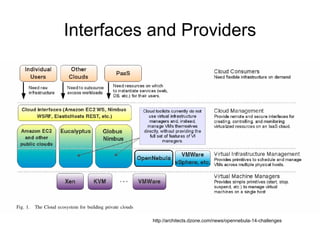
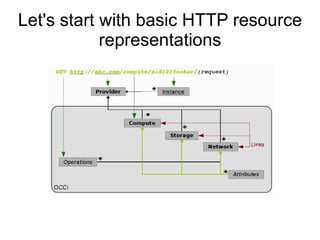
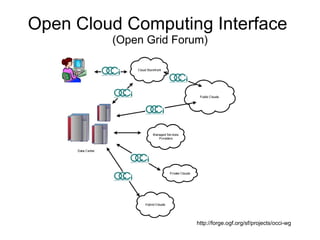
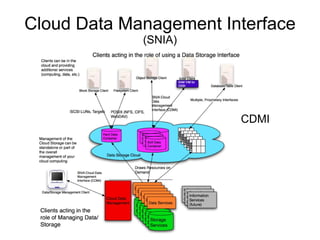
Cloud APIs provide programmatic access to cloud resources and services. They allow developers to interact with applications, development environments, and raw compute/storage resources through standardized interfaces. While each cloud provider currently has their own proprietary APIs, there is a push for open standards to accelerate development of higher-level services and commoditization of basic resources. Key areas for a common cloud API include resource representations, security requirements, and orchestration of ensembles of resources across providers.