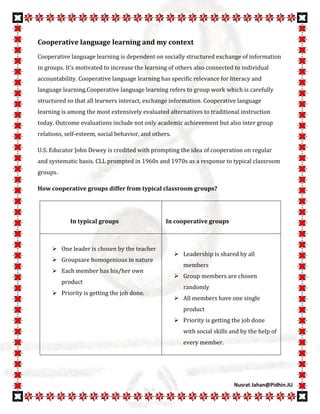
Cooperative language learning involves structuring group work so students interact and exchange information. It increases learning for all students through individual accountability and social exchange. John Dewey first promoted the idea of cooperation in education. Cooperative language learning differs from typical groups in that leadership is shared, members are chosen randomly, and the priority is completing tasks through social skills and group help rather than individual products. Benefits include improved achievement for all, positive relationships, social and cognitive development, and cooperation over competition. Cooperative language learning can be effective for language learning by encouraging meaningful communication through tasks and allowing use of first and target languages.