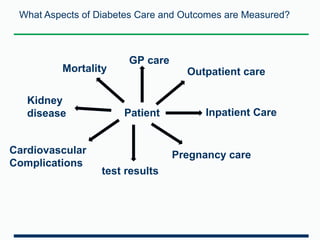
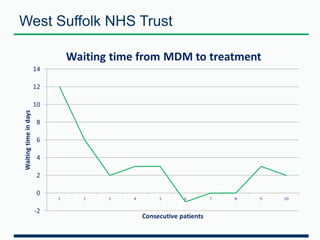
This document discusses clinical audit services and provides examples of clinical audits. It describes the process of developing, designing, and conducting clinical audits. Clinical audits measure care quality against standards, identify areas for improvement, and provide recommendations. They also track changes in care over time. The document uses the National Diabetes Audit as a case study. It measures various aspects of diabetes care and outcomes and involves many stakeholders. Reports provide benchmarked data to identify high-risk patients and drive quality improvements. An example is provided of how the audit found more patients were receiving a kidney test, leading to earlier detection and treatment of complications.