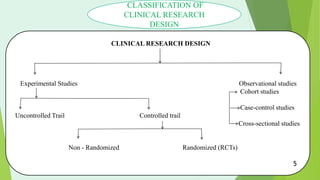
This document outlines the design of clinical trial protocols, detailing their purpose, structure, and the roles of team members involved. It covers the phases of clinical drug development, various research designs, and essential protocol elements to ensure safety and efficacy in drug testing. Conclusions emphasize the importance of adhering to a well-structured protocol for effective research outcomes.