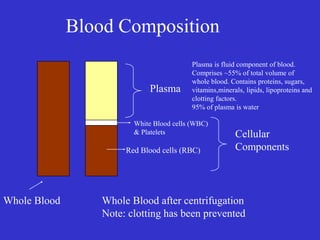
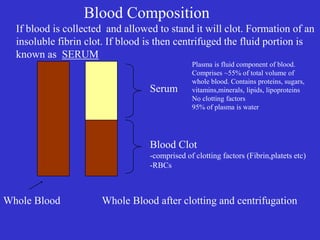
The document provides an overview of clinical biochemistry, including:
1) Testing procedures that will be used for exams, which will be based on lecture materials.
2) The roles and functions of a clinical chemistry laboratory, including providing diagnostic tests, consultation, education, and research support.
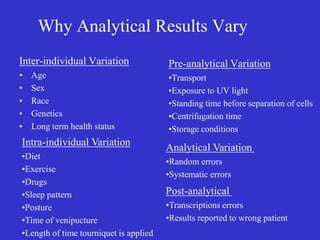
3) Sources of variation that can affect laboratory test results, such as pre-analytical factors related to specimen collection, transport, and processing, and analytical and post-analytical errors.