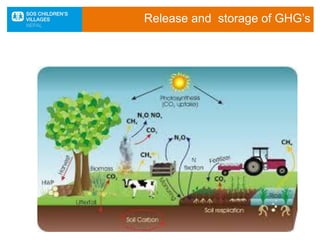
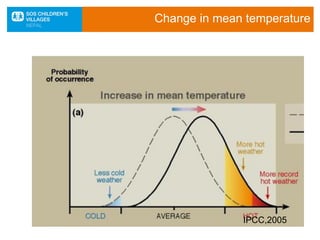
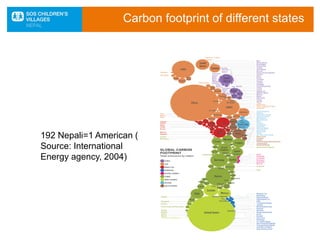
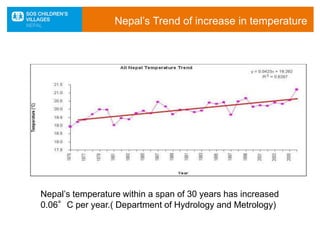
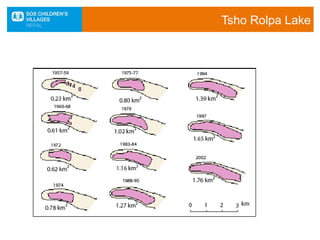
The document discusses the impact of climate change, particularly in Nepal, which is among the most vulnerable countries despite contributing only 0.025% to global greenhouse gas emissions. It highlights ongoing issues such as rising temperatures, changes in rainfall patterns, and the negative effects on ecosystems, food security, and human health. Mitigation and adaptation strategies are outlined, including afforestation, renewable energy usage, and community-based adaptation plans.
![Climate Change and
Disaster
(hnjfo' kl/jt{g tyf k|sf]k)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeanddisasters-240717160151-3dc78466/75/Climate-change-and-disasters-pdf-for-disaster-1-2048.jpg)