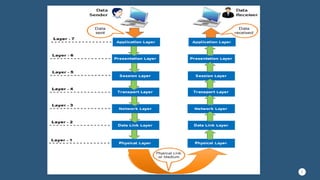
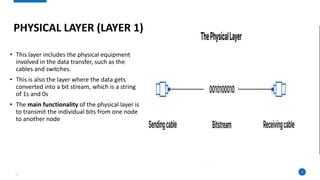
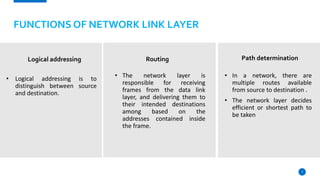
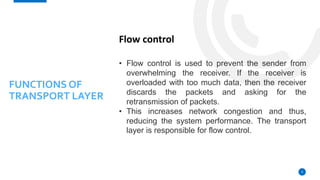
This document provides an overview of the 7-layer OSI model. It describes each layer from the physical layer to the application layer, including their key functions. The physical layer deals with physical equipment for data transmission like cables and switches. The data link layer forms frames from packets and performs error detection. The network layer delivers packets through logical addressing and routing. The transport layer provides reliable data delivery through segmentation, error control, and flow control. Higher layers include the session layer for managing communication sessions, the presentation layer for data translation and encryption, and the application layer for end-user software interaction.