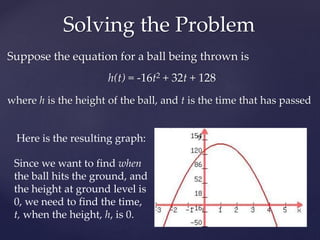
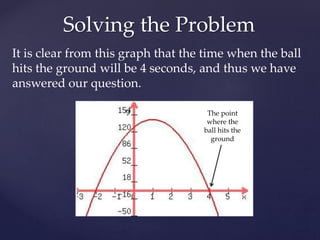
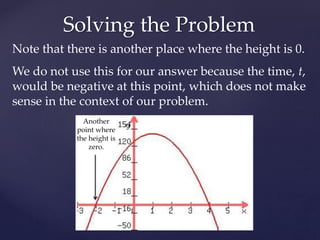
Quadratic equations describe parabolic shapes and can be used to model projectile motion. They take the form ax^2 + bx + c, where a cannot be 0. This document discusses using a quadratic equation, h(t) = -16t^2 + 32t + 128, to find the time when a ball thrown in the air hits the ground. By graphing the equation and finding where the quadratic intersects the x-axis at height h=0, the time is determined to be 4 seconds.