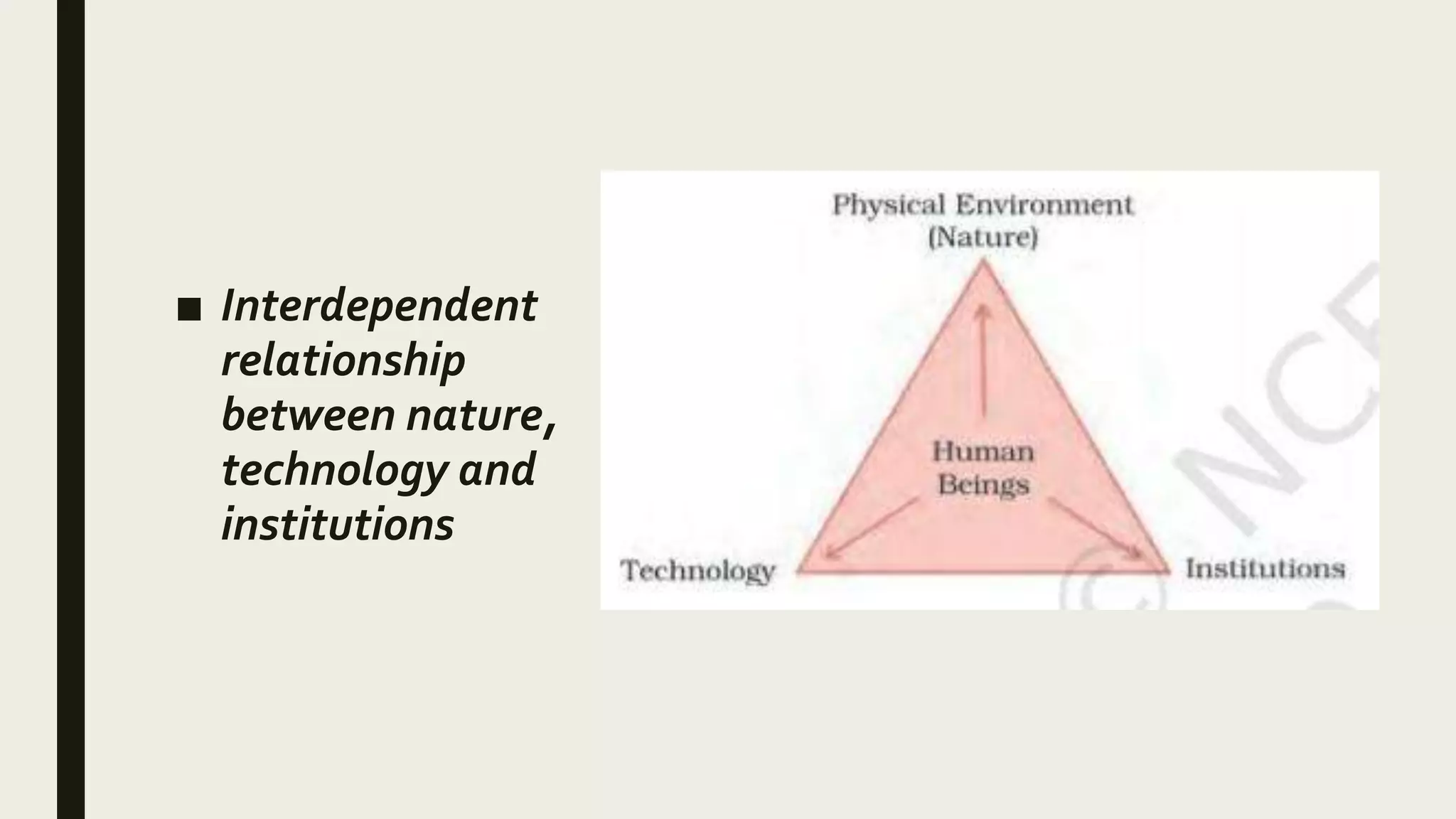
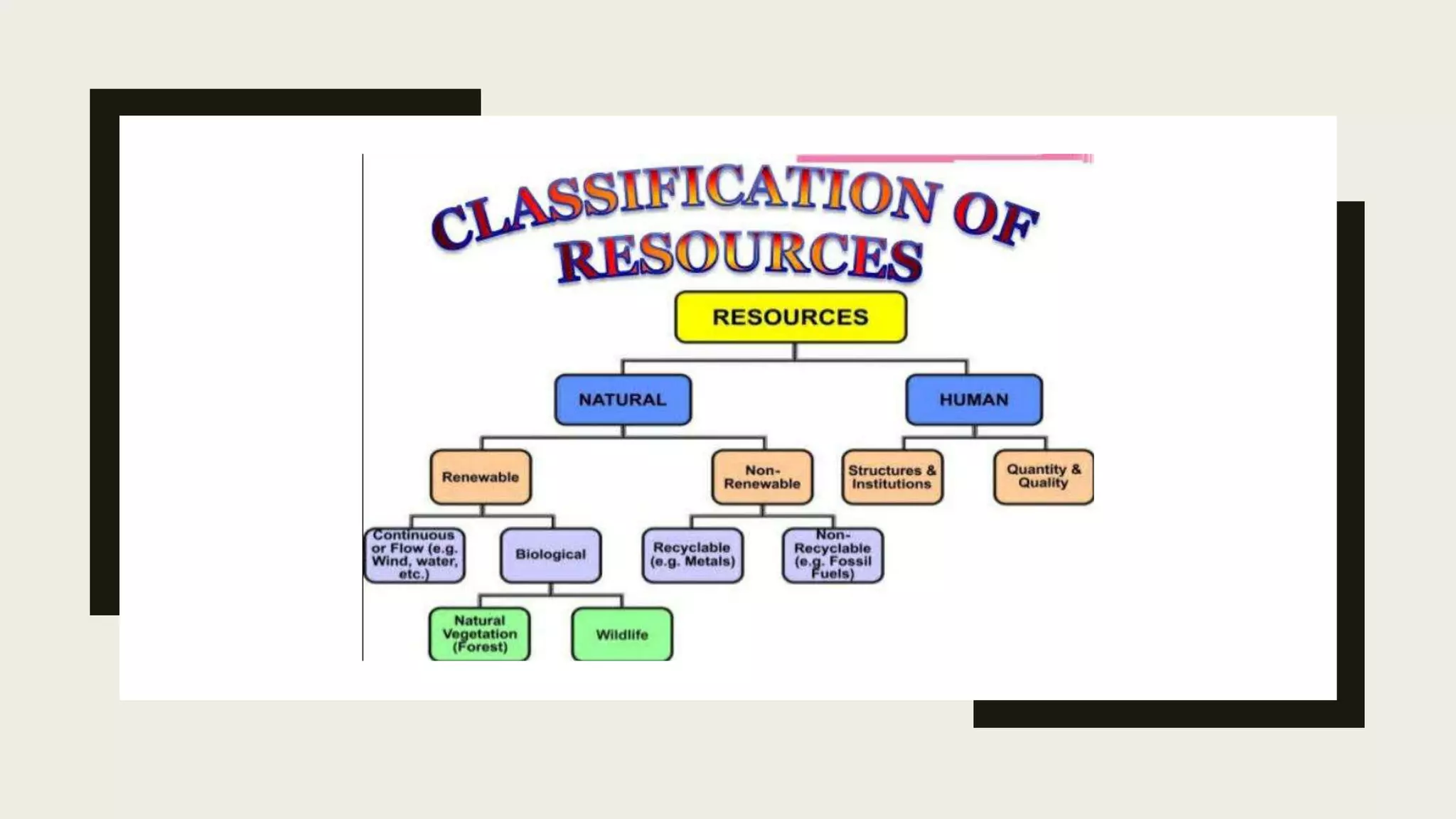
This document defines and classifies resources based on several criteria:
- Origin: Biotic resources come from the biosphere and include living things like plants and animals. Abiotic resources are non-living things like rocks and minerals.
- Exhaustibility: Renewable resources can replenish, like water, forests, and solar energy. Non-renewable resources form over long periods and cannot renew, like fossil fuels.
- Ownership: Resources can be individually, community, nationally, or internationally owned depending on who can access and utilize them.
- Status and development: Resources exist in potential, stock, or reserve forms depending on available technology and future needs.