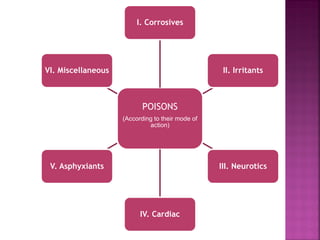
This document discusses different types of poisons categorized by their mode of action. It covers corrosives, irritants, neurotics, cardiac poisons, asphyxiants, and miscellaneous poisons. Specific examples are provided for each category, including strong acids, alkalis, inorganic and organic acids, metallic and non-metallic poisons, and gases that cause asphyxiation. Agrochemical poisons like pesticides and fumigants are also discussed. Neurotic poisons are separated into somniferous, inebriants, and deliriants with plant-based examples. Cardiac poisons include digitalis, oleander, and aconite. Food poisoning can be caused by