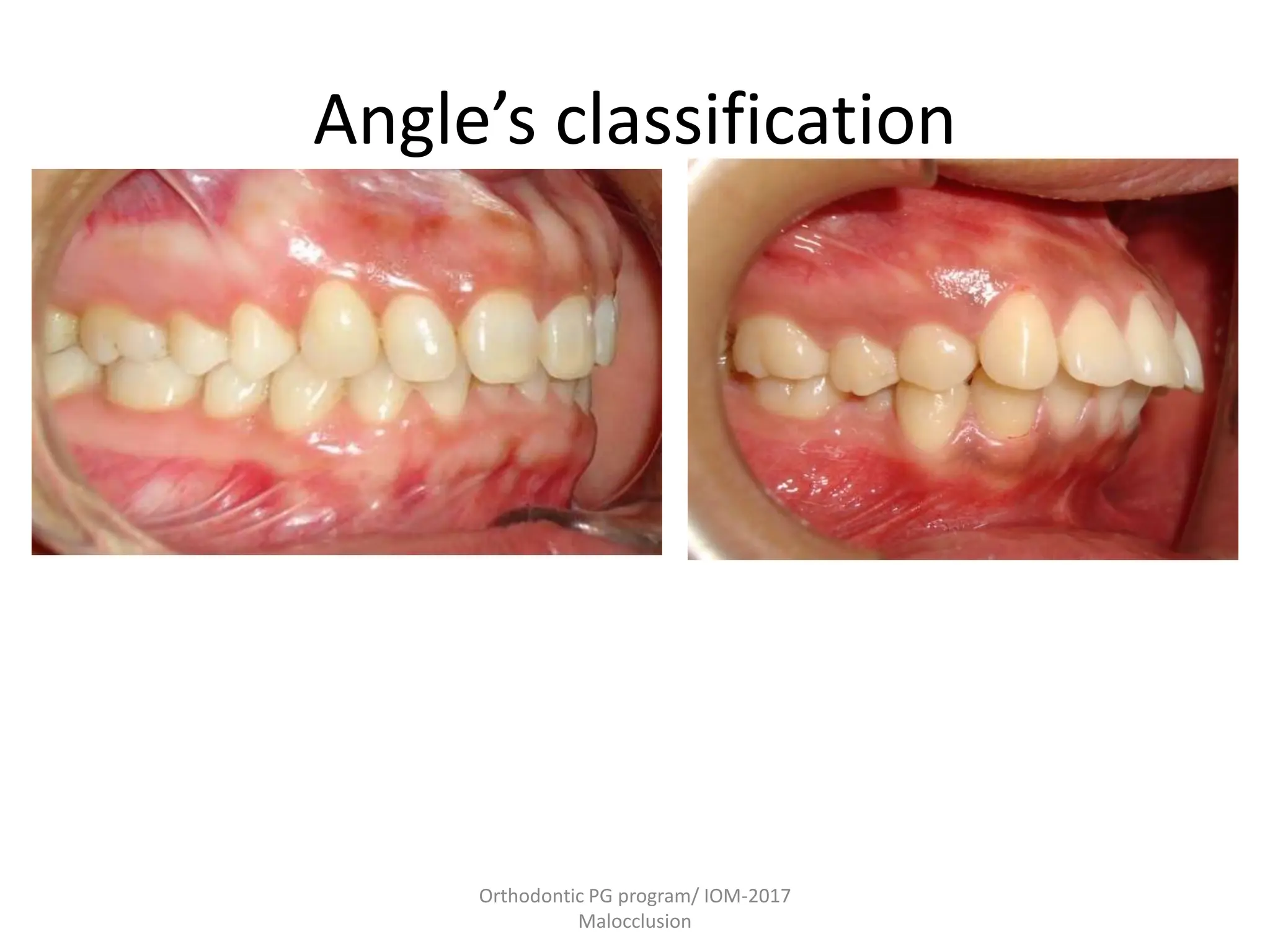
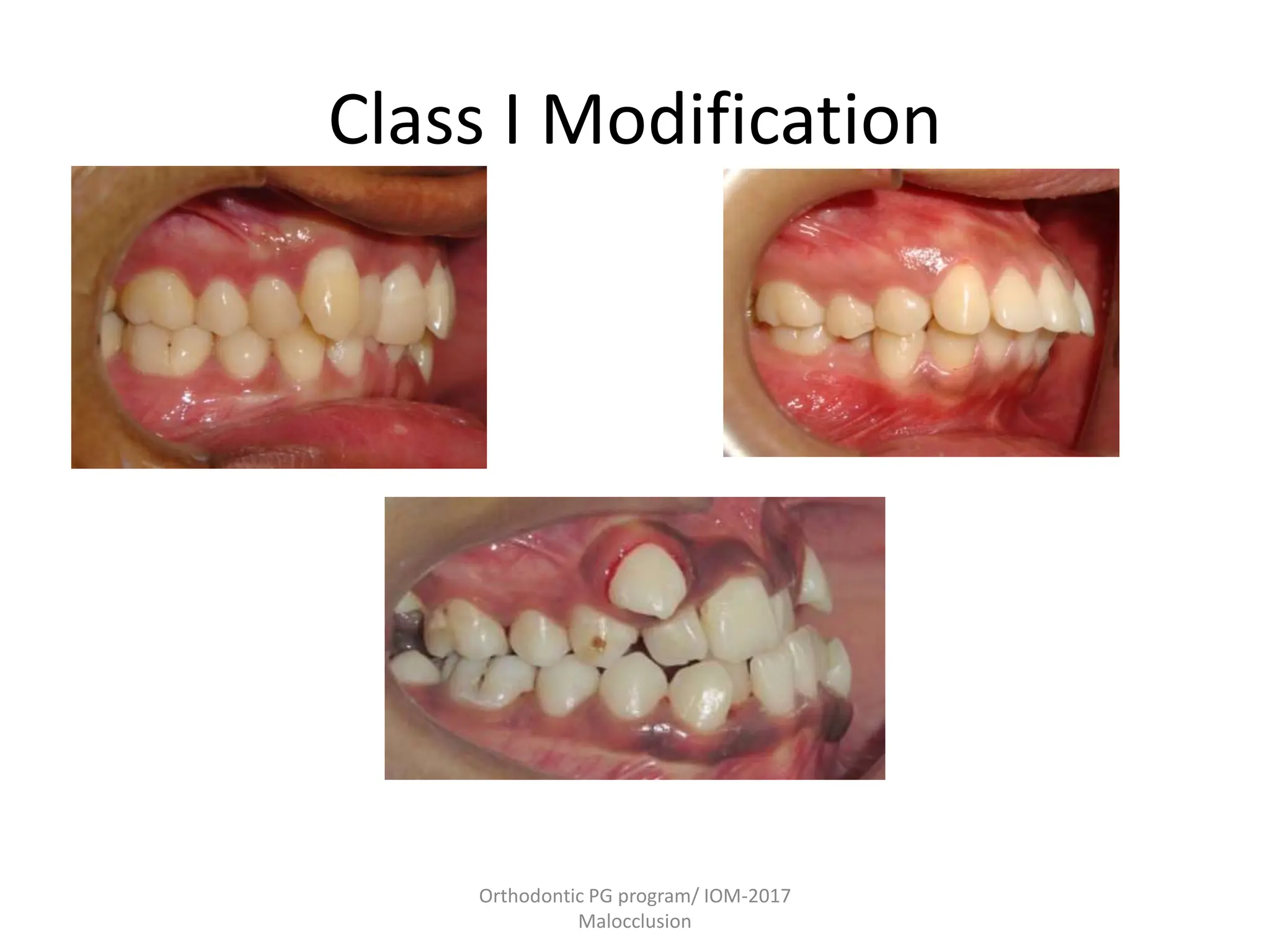
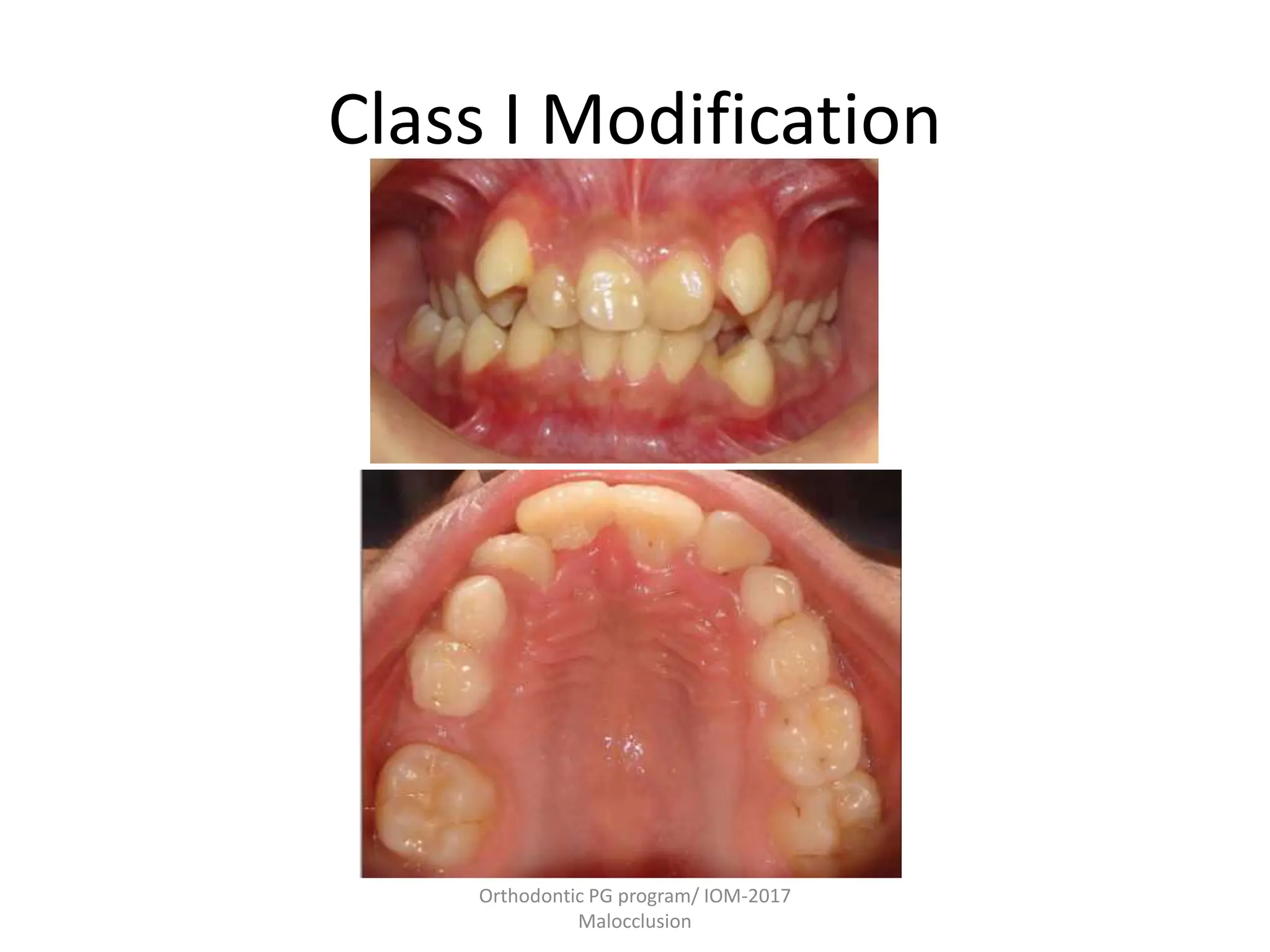
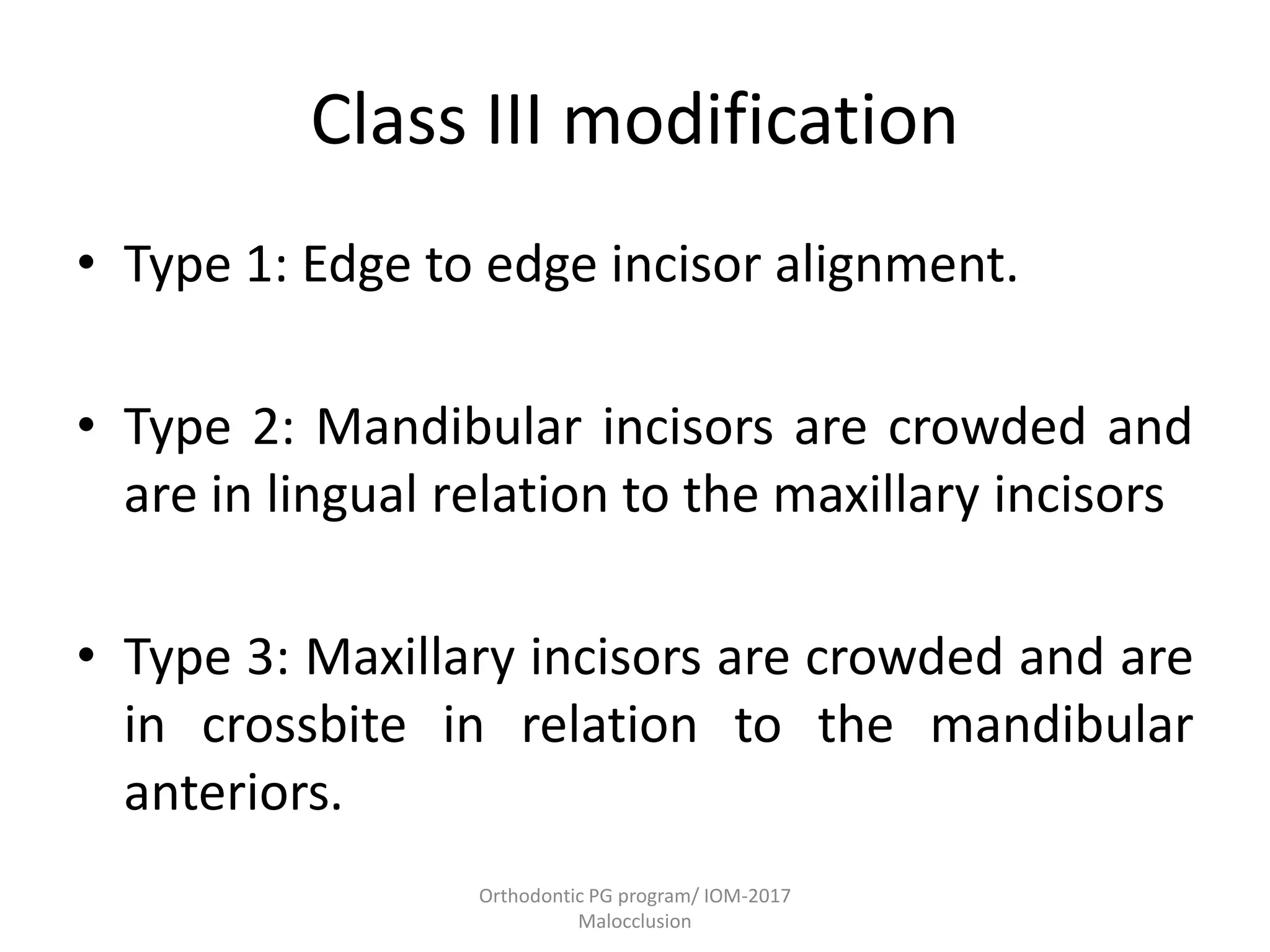
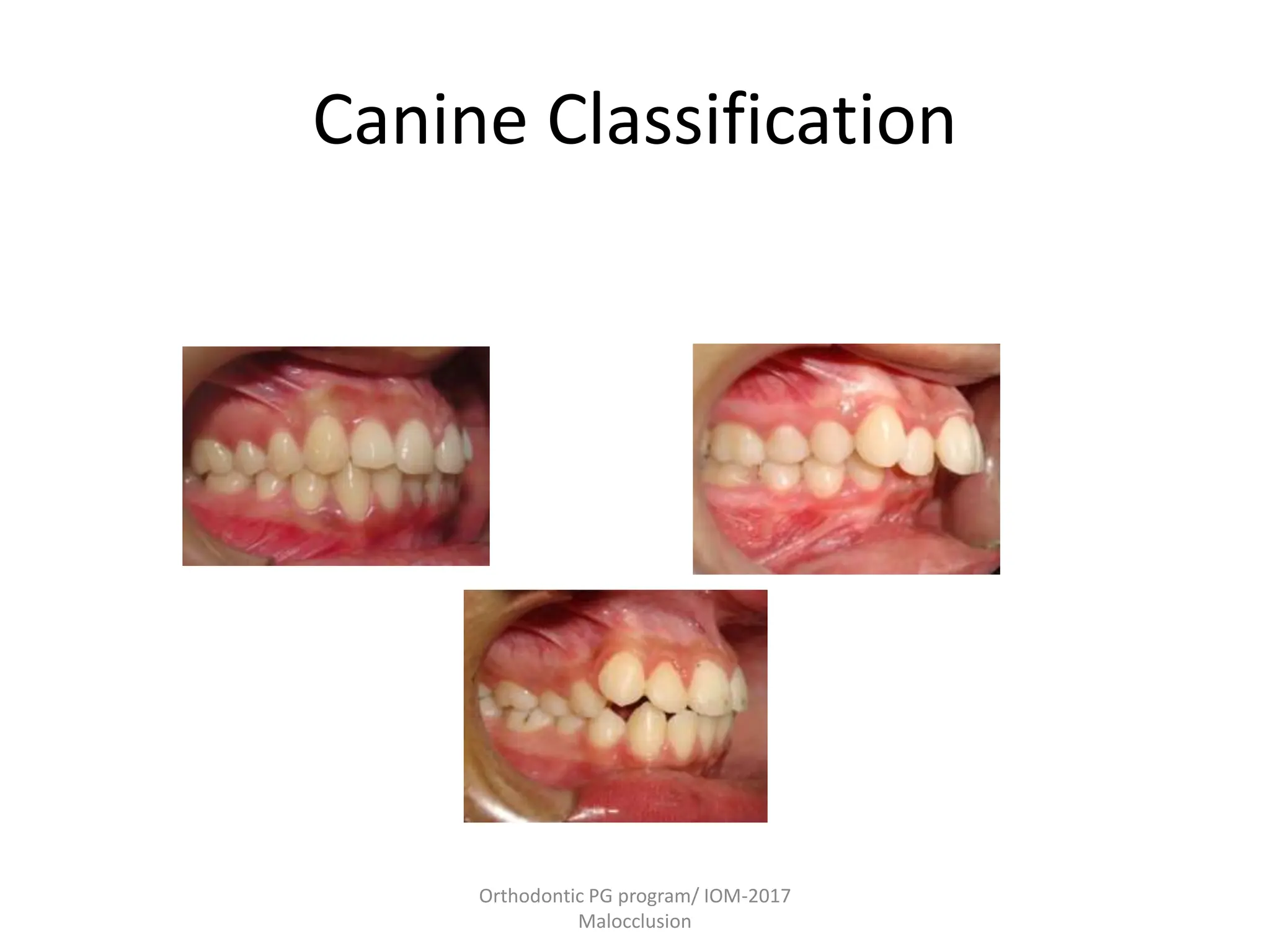
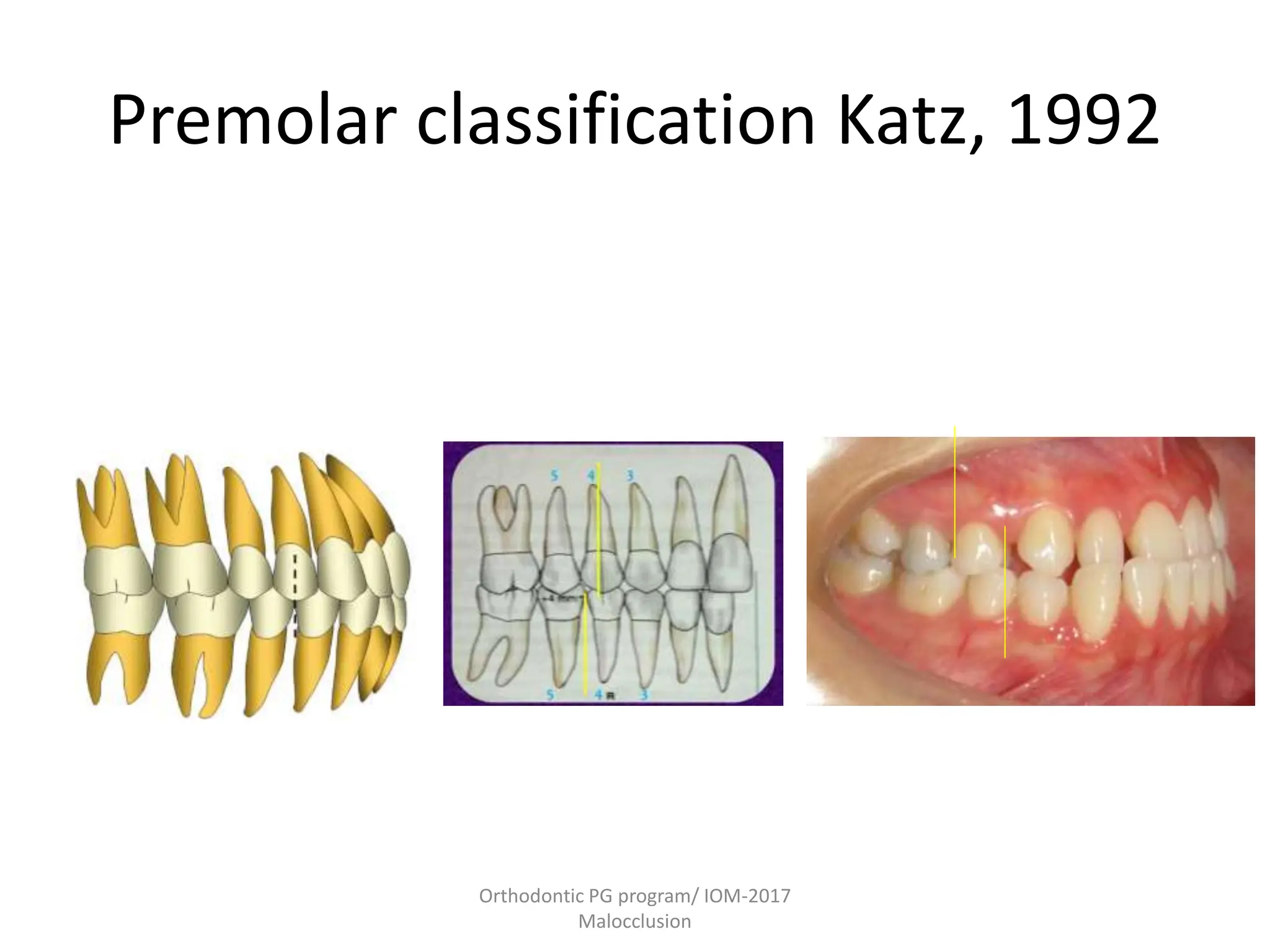
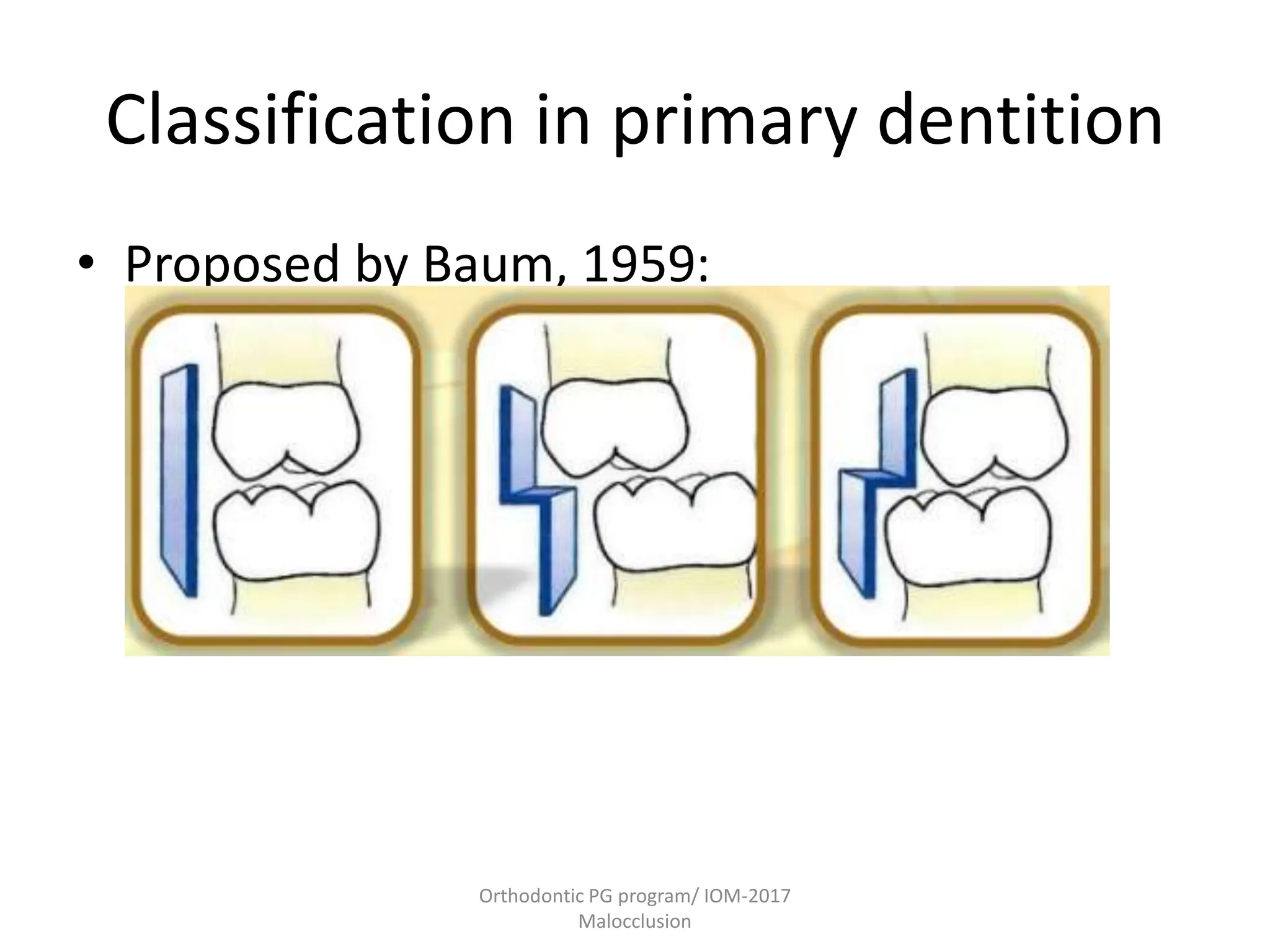
This document discusses the classification of malocclusion in orthodontics. It provides an overview of various classification systems used to group orthodontic problems by location and diagnose treatment plans. These include classifications by Angle, Dewey, Lischer, Simon, Bennett, Ackerman and Proffit, the WHO/FDI system, and classifications in primary and permanent dentition. Accurately classifying malocclusion allows for comparison between different malocclusion types, communication between orthodontists, documentation of problems, and assessment of treatment effects.