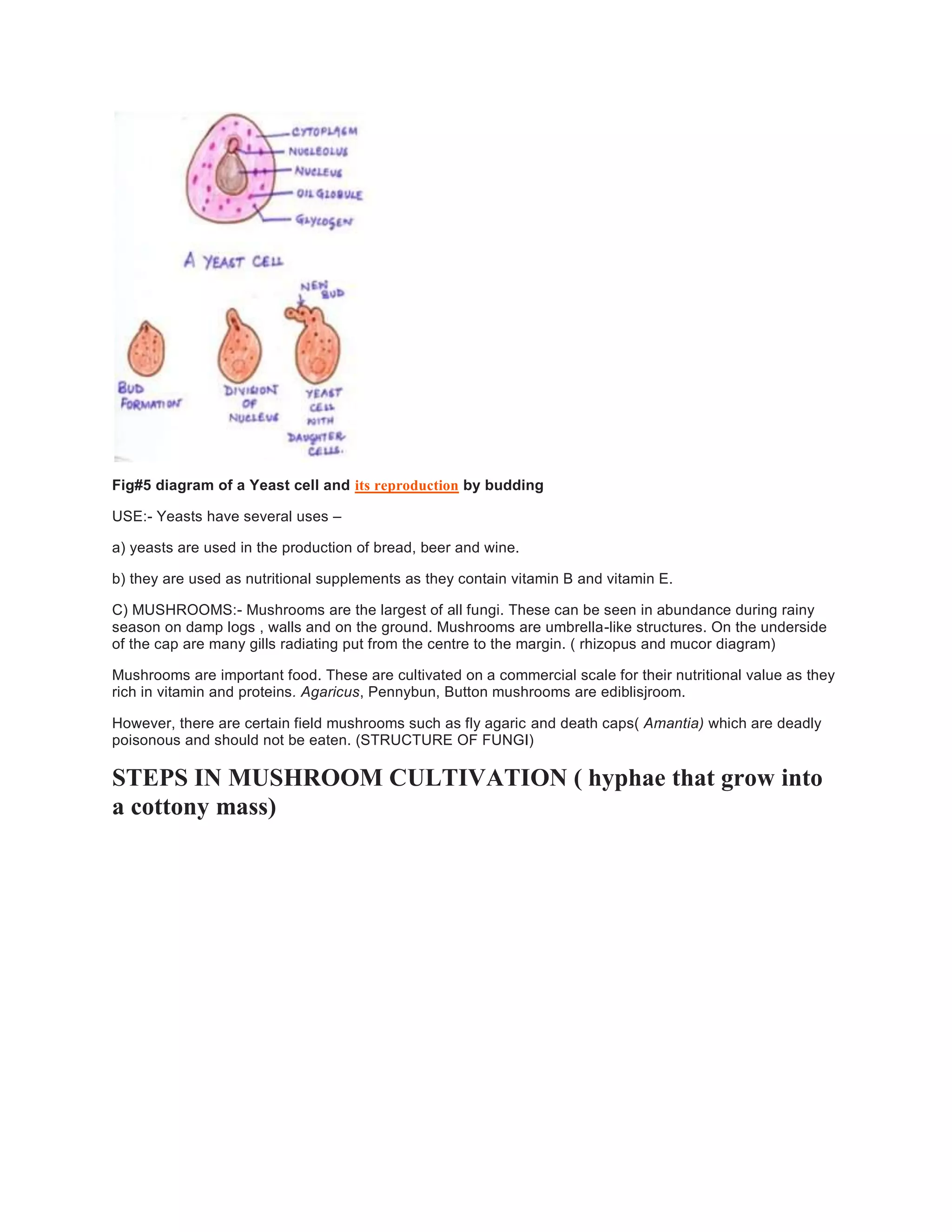
The document provides a comprehensive overview of fungi, highlighting their classification, structure, and roles in ecosystems. It discusses types of fungi such as moulds, yeasts, and mushrooms, detailing their characteristics, modes of reproduction, and nutritional methods. Additionally, it covers mushroom cultivation techniques and methods for food preservation, contrasting fungi with bacteria in important biological aspects.