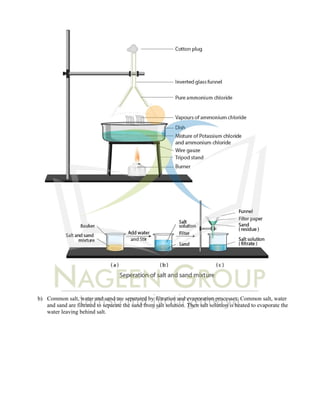
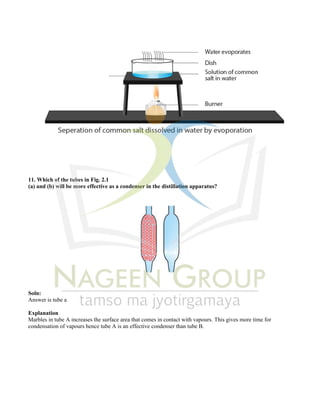
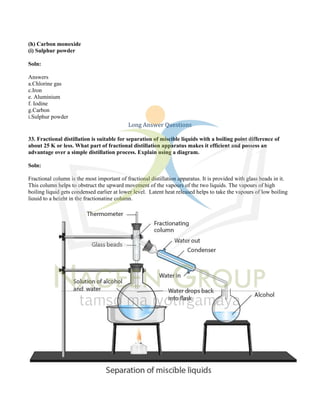
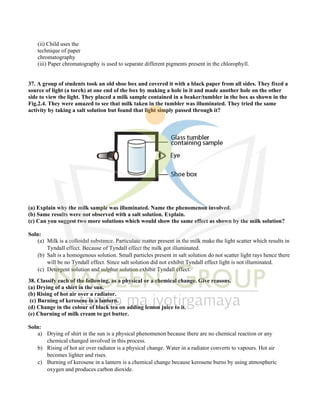
The document provides an extensive overview of concepts related to matter, including definitions and characteristics of pure substances, physical and chemical changes, and examples of mixtures and their separation techniques. It contains multiple-choice questions and explanations regarding topics such as rusting, solutions, and reactions, highlighting properties and behaviors of various substances. Additionally, it includes practical applications of scientific principles in real-life scenarios.