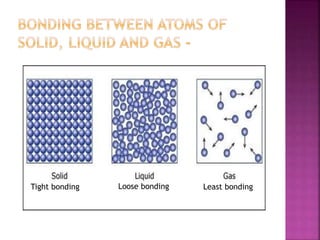
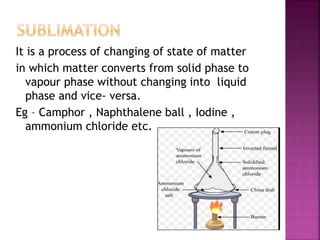
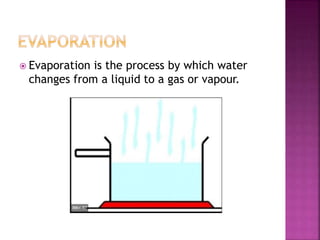
This document discusses the classification of matter and its different states. It was prepared by Yashovardhan Phadtare, a class 9 student at Wilson's Coaching Academy in Pune. The ancient Greeks classified matter into 5 states - air, earth, fire, sky and water. Modern science classifies the states of matter as solid, liquid, gas, plasma, and Bose-Einstein condensate. The document explores the properties and characteristics of each state of matter.