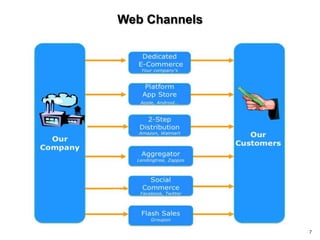
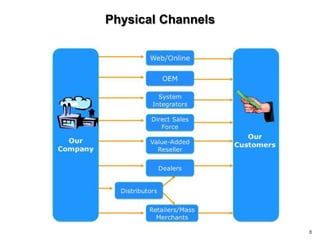
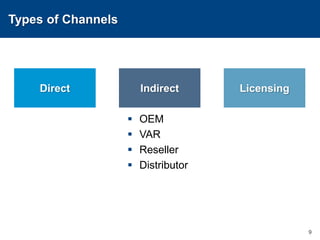
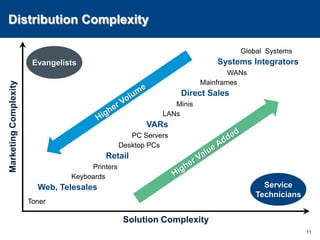
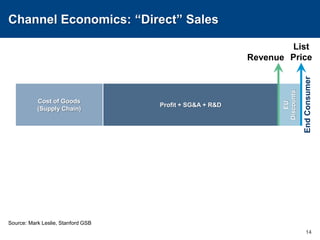
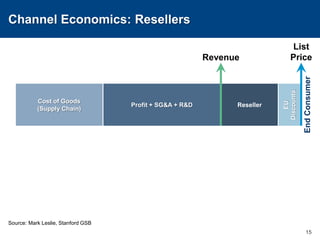
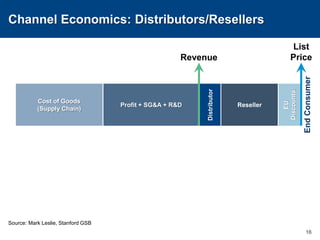
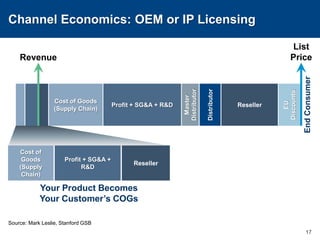
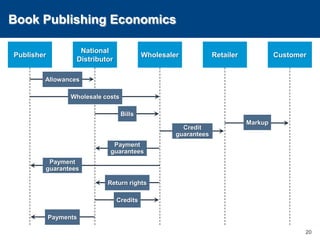
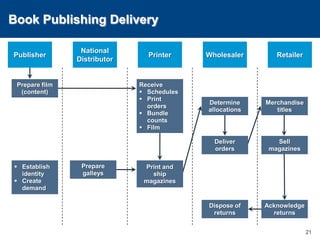
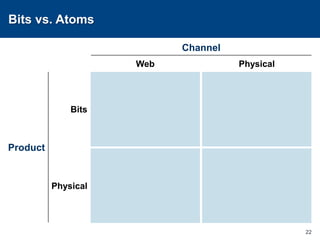
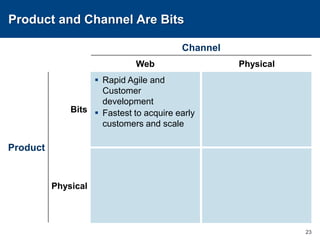
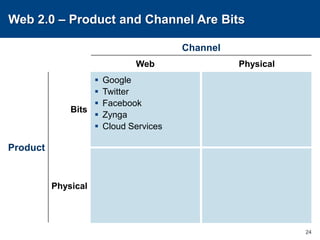
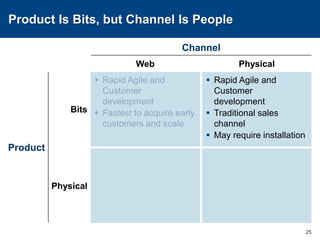
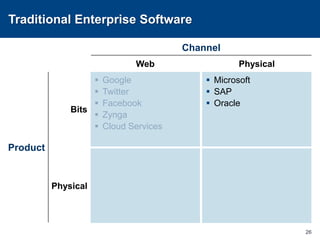
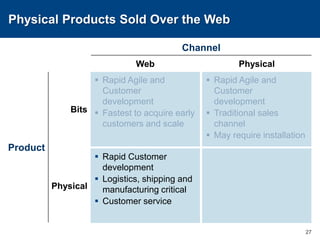
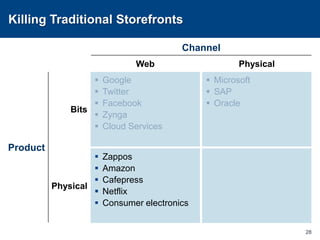
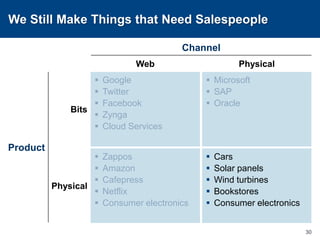
This document discusses channels and how products are delivered to customers. It addresses two key questions about channels: how you want to sell your product and how your customer wants to buy it. Different types of channels are examined, including direct sales, resellers, distributors, OEMs, and licensing. The economics of various channel models are analyzed using the example of book publishing. The impact of physical versus digital products on appropriate channels is also explored.