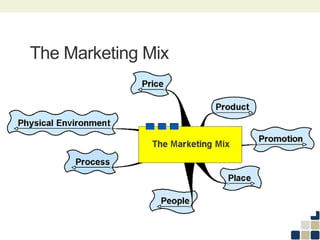
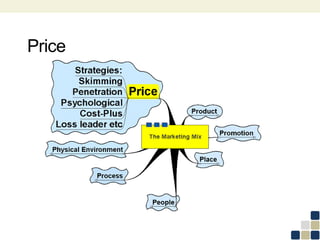
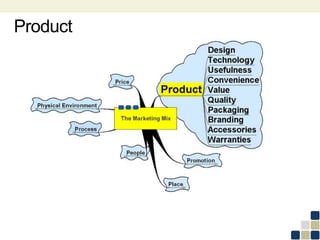
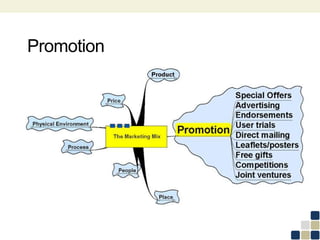
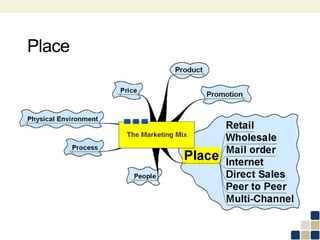
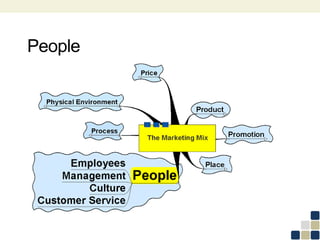
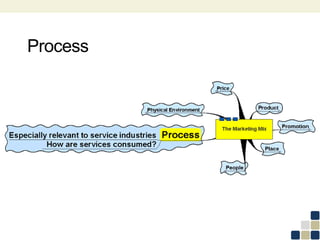
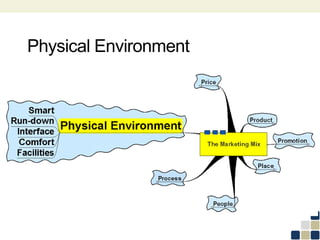
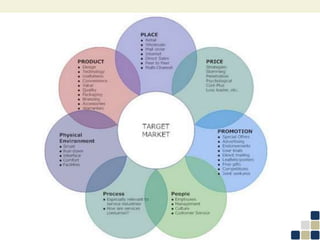
This document provides an overview of the marketing mix, also known as the 7Ps. It discusses each element of the marketing mix - product, price, place, promotion, people, process, and physical environment. For each P, key questions are provided to help analyze and optimize that element of the mix. The marketing mix is presented as a framework for developing a comprehensive marketing strategy to meet objectives and satisfy customers.