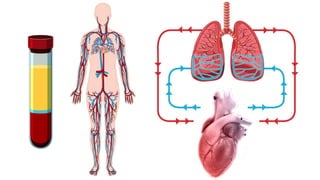
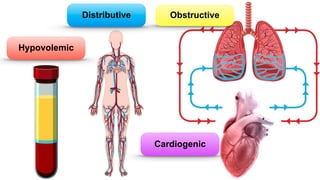
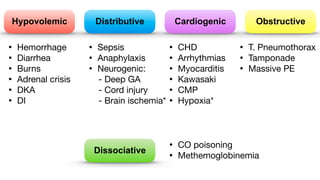
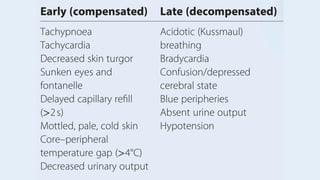
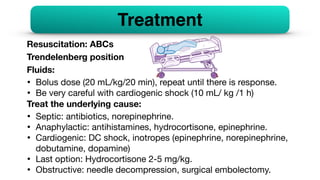
Shock is the inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues, causing organ damage. There are four main types of shock: distributive, hypovolemic, cardiogenic, and obstructive. Distributive shock includes septic shock and anaphylactic shock. Hypovolemic shock can be caused by hemorrhage, diarrhea, or burns. Cardiogenic shock results from heart issues like arrhythmias or myocarditis. Obstructive shock involves issues blocking blood flow like tension pneumothorax. Treatment for shock involves ABCs, fluids, treating the underlying cause, and sometimes hydrocortisone. Complications can include acute renal failure, respiratory failure, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.