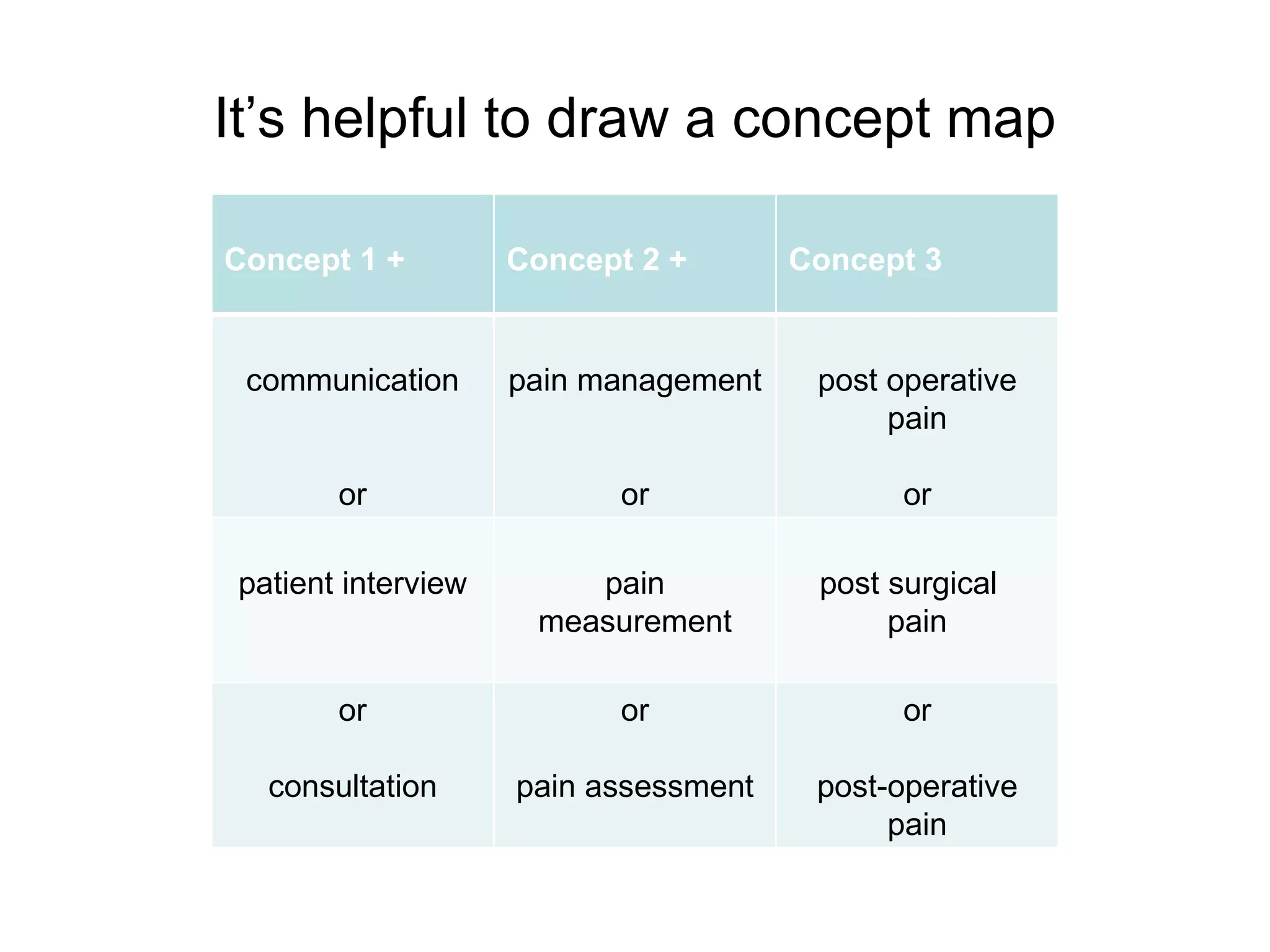
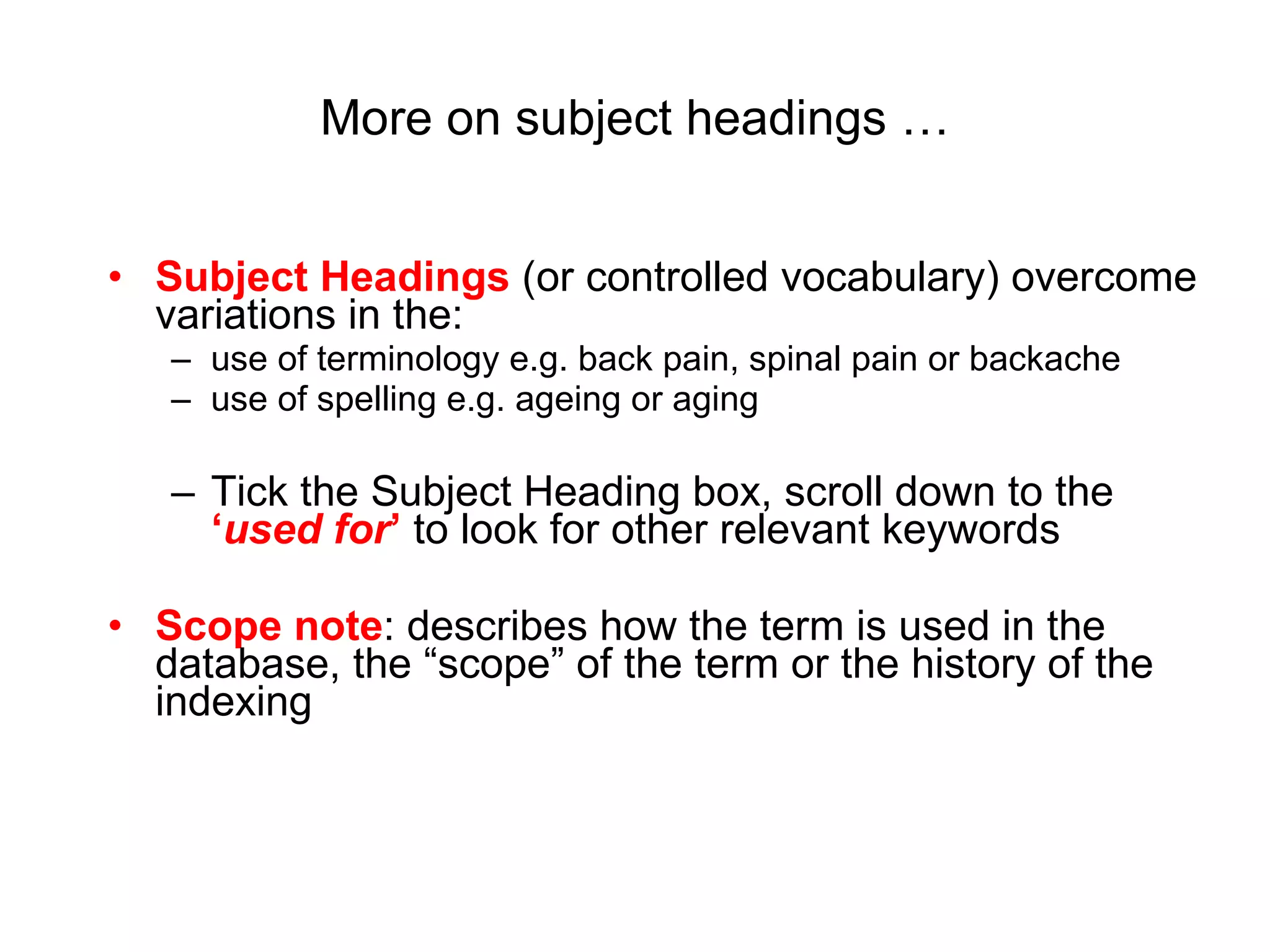
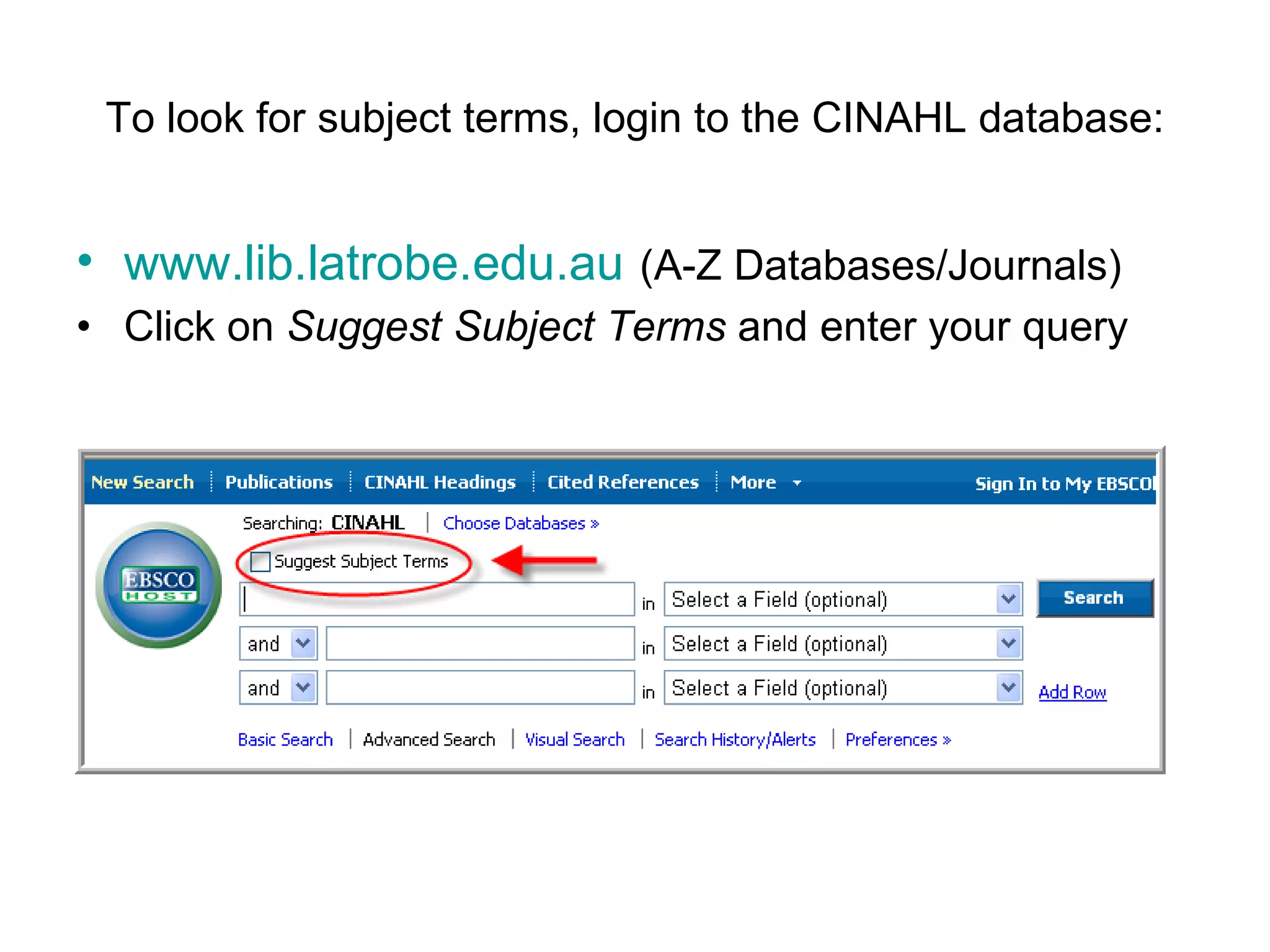
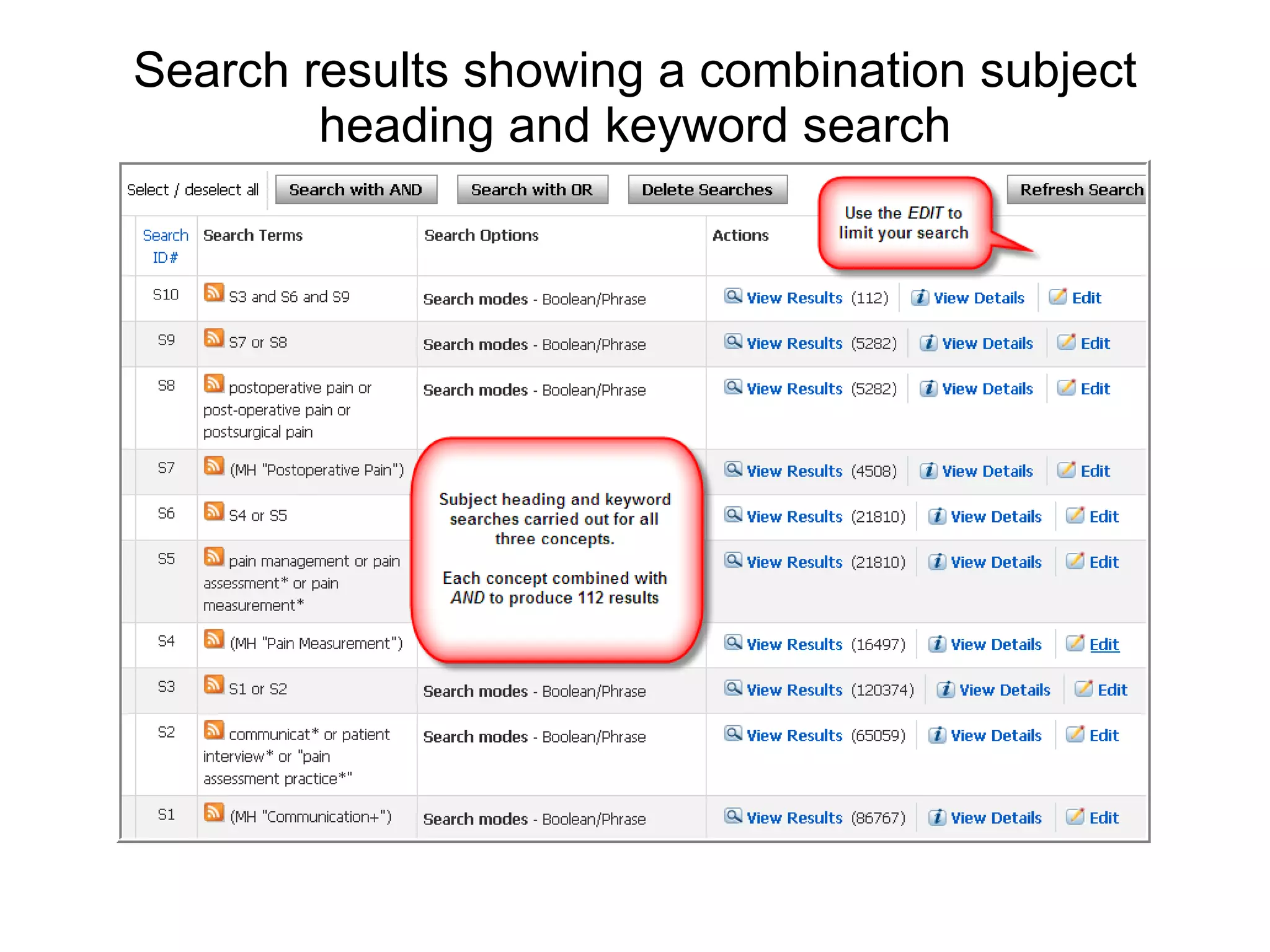
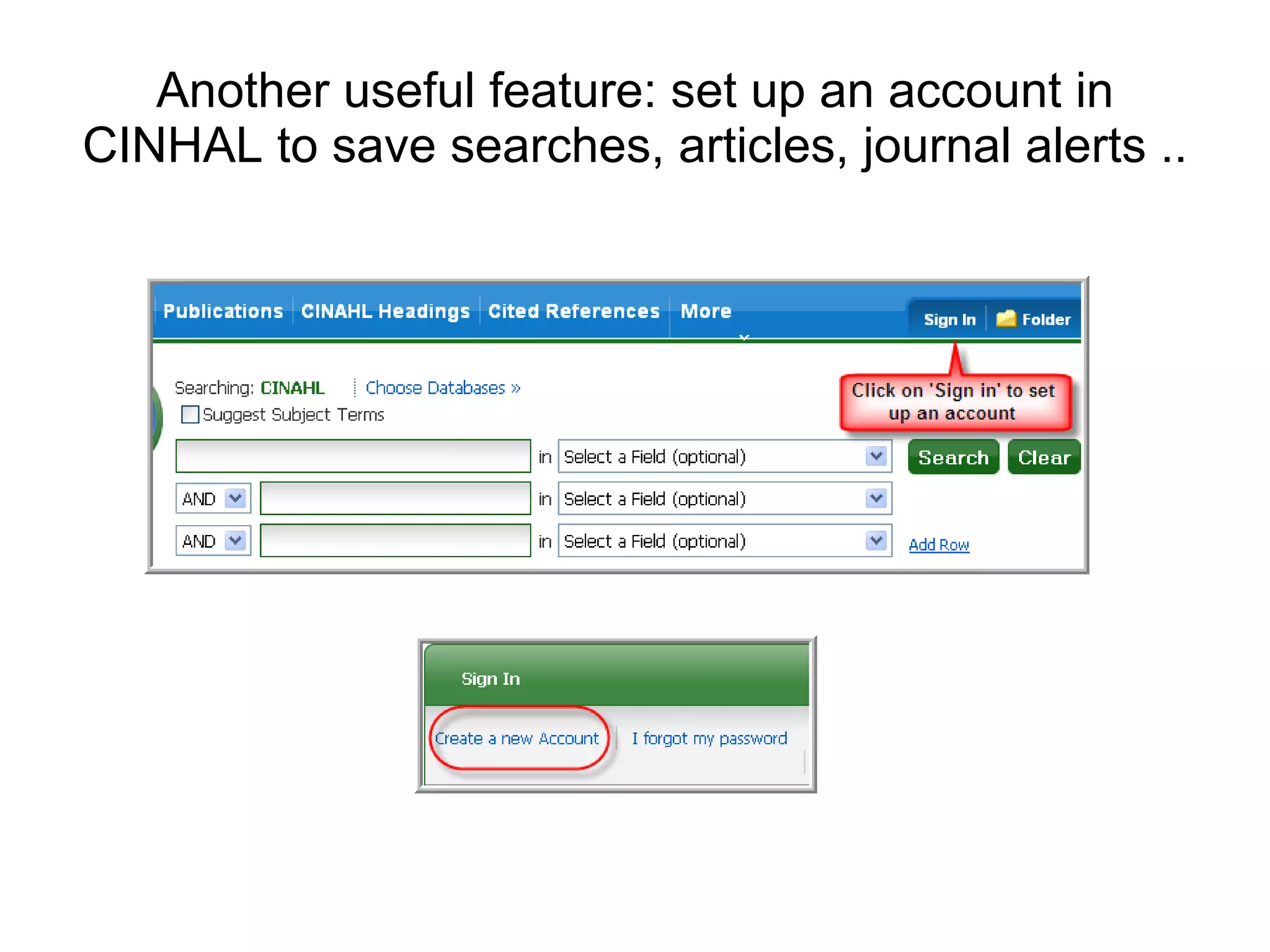
The document provides guidance on conducting an effective search of the CINAHL database to answer a question about factors that influence control of postoperative pain in older patients. It outlines a 3-stage process: developing a search strategy using relevant concepts and keywords; searching databases using subject headings and keywords; and finding the full text of articles. Sample searches are demonstrated combining subject headings like "pain measurement" with keywords like "pain management" or "pain assessment". Tips are provided on using Boolean operators, truncation, phrase searching and limiting searches. The document concludes by assigning homework to search for specific subject terms in CINAHL.
![Specialty Cancer/Palliative Care Nursing Searching the databases: CINAHL Sharon Karasmanis [email_address] Faculty Librarian, Health Sciences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cancernursing-110823180936-phpapp01/75/CINAHL-Advanced-Search-Techniques-1-2048.jpg)