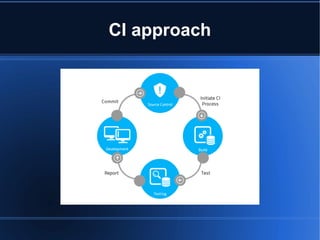
Continuous integration (CI) is a development practice where developers integrate code into a shared repository several times a day, with each check-in verified by an automated build to detect problems early. The key practices of CI are maintaining a single source repository, automating builds, making builds self-testing, building on every commit in an integration machine, keeping builds fast, testing in a production-like environment, making builds easily accessible, providing visibility into the process, and automating deployments. Benefits of CI include reducing time spent on integration issues, increasing communication, catching bugs early, spending less time debugging and more time adding features, and enabling more rapid software delivery.