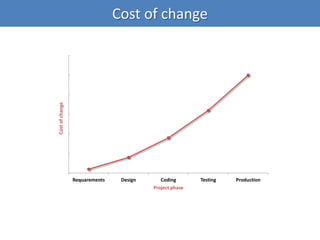
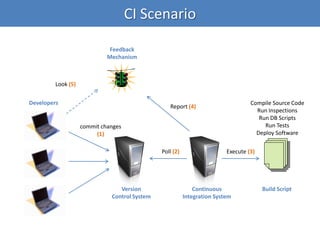
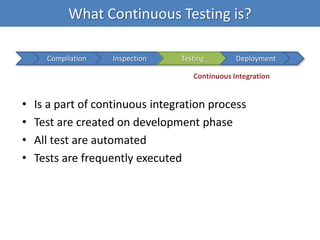
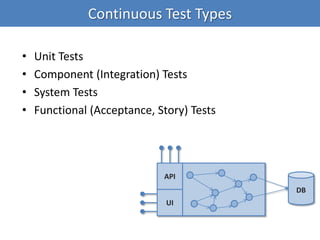
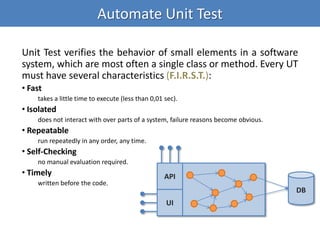
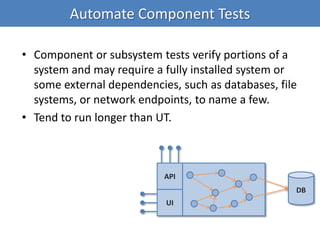
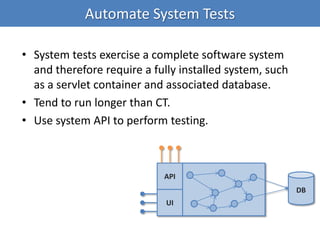
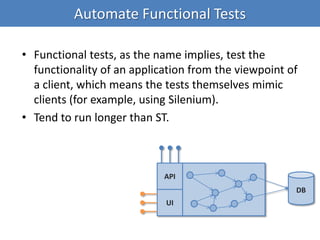
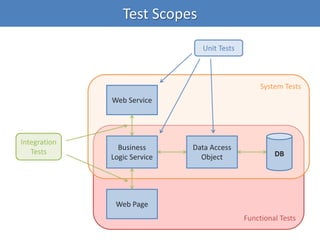
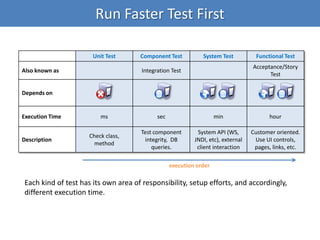
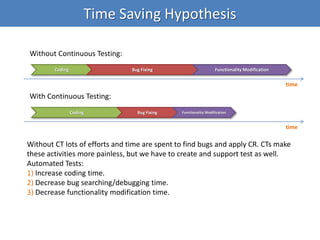
Continuous integration (CI) implements continuous processes of applying quality control through small, frequent pieces of effort. CI aims to improve software quality and reduce delivery time by replacing traditional quality control after development. CI involves: writing automated developer tests; running private builds where all tests and inspections must pass; committing code frequently; and avoiding getting broken code. It provides feedback through mechanisms like email, IM, and SMS to keep the right people informed at the right time. CI helps reduce code complexity, maintain standards, and assess test coverage through continuous inspection along with compilation, testing and deployment.

![Business Goal
Profit increasing
Total Profit = Project Profit [1] + … + Project Profit [N]
Project Profit = Project Revenue – Project Costs
Increase project
count
Increase project
price
Decrease project
costs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/continuousintegration-130614141608-phpapp02/85/Continuous-Integration-2-320.jpg)