The document discusses the Church-Turing thesis, which proposes that any function that is computable can be simulated by a Turing machine. It describes how Alan Turing invented Turing machines and Alonzo Church developed the λ-calculus to formally define computable functions. The Church-Turing thesis asserts that these are equivalent ways to define an algorithm or effective method. It also provides an example of a Turing machine that accepts strings with an even number of 1s.

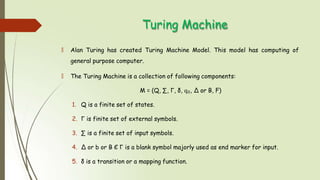


![Church Turing Thesis
🠶 A Turing machine is an abstract representation of a computing device.
🠶 It is more like a computer hardware than a computer software.
🠶 LCMs [Logical Computing Machines: Turing’s expression for Turing
machines] were first proposed by Alan Turing, in an attempt to give a
mathematically precise definition of "algorithm" or "mechanical
procedure".](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/churchturingthesis-160906170827-230111133702-21209c2b/85/churchturingthesis-160906170827-pptx-5-320.jpg)







