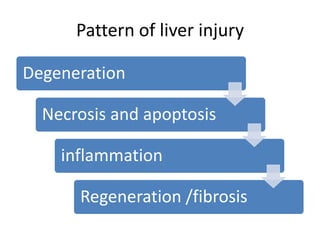
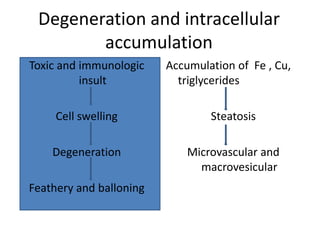
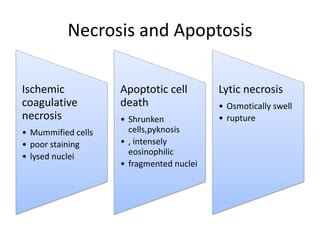
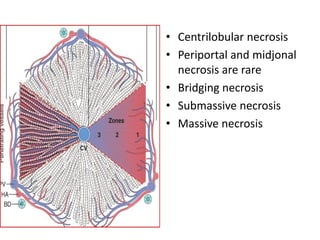
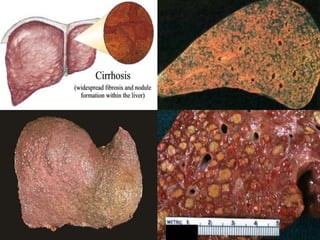
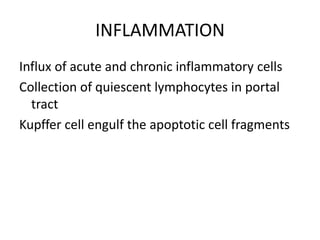
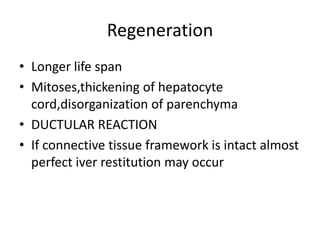
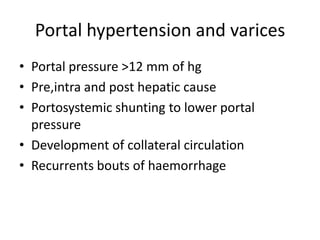
Chronic liver failure results from ongoing liver injury and inflammation that can lead to degeneration, necrosis, apoptosis, and regeneration or fibrosis over time. If damage is severe enough, this process can result in portal hypertension, varices, and complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal disease, and hepatopulmonary syndrome.