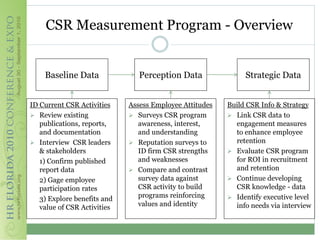
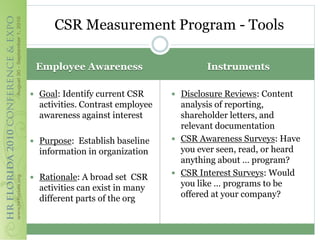
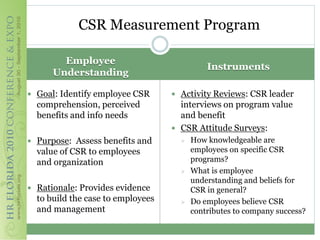
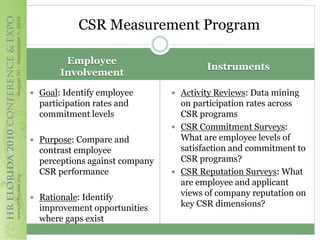
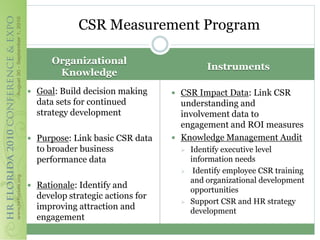
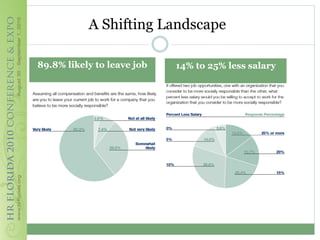
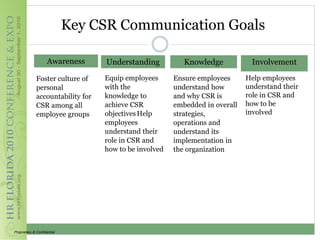
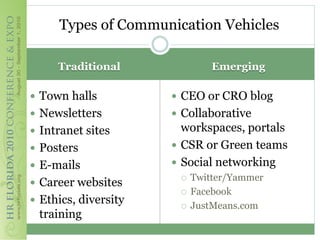
This document discusses how corporate social responsibility (CSR) programs can be used to recruit, engage, and retain employees. It recommends assessing current CSR programs, measuring employee awareness, interest, and knowledge of CSR through surveys, and using various communication methods to share how CSR is embedded in the organization's strategies and operations. The goal is to help employees understand their role in CSR and how to get involved, in order to build a highly engaged workforce and reap the benefits of CSR for attracting and retaining talent.